CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
36 followers
100 following
43 posts
Computational Biology Unit led by Prof. Paolo Provero
Neurosciences Dept. at University of Turin.
https://proverolab.gitlab.io/
Tweets are from lab members.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· 3d

Polygenic and developmental profiles of autism differ by age at diagnosis - Nature
A study of several longitudinal birth cohorts and cross-sectional cohorts finds only moderate overlap in genetic variants between autism that is diagnosed earlier and that diagnosed later, so they may represent aetiologically different conditions.
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· 28d

Multiancestry brain pQTL fine-mapping and integration with genome-wide association studies of 21 neurologic and psychiatric conditions - Nature Genetics
Multiancestry fine-mapping of brain protein quantitative trait loci coupled with Mendelian randomization analyses identifies protein–trait pairs consistent with causal effects across neurological and ...
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Sep 11

Machine Learning Models Based on Histological Images from Healthy Donors Identify ImageQTLs and Predict Chronological Age
Histological images offer a wealth of data. Mining these data holds significant potential for enhancing disease diagnosis and prognosis, though challenges remain, especially in non-cancer contexts. In...
www.biorxiv.org
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Sep 9

Multiple overlapping binding sites determine transcription factor occupancy - Nature
A new method enables comprehensive screening and identification of low-affinity DNA binding sites for transcription factors, and reveals that nucleotides flanking high-affinity binding sites create ov...
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Sep 7

Genetic regulation of cell type–specific chromatin accessibility shapes immune function and disease risk
Understanding how genetic variation influences gene regulation at the single-cell level is crucial for elucidating the mechanisms underlying complex diseases. However, limited large-scale single-cell ...
www.medrxiv.org
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Sep 4

Single-cell genetics identifies cell type-specific causal mechanisms in complex traits and diseases
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have been instrumental in uncovering the genetic basis of complex traits. When integrated with expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) mapping, they can elucid...
www.medrxiv.org
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Sep 3

Endogenous fine-mapping and prioritization of functional regulatory elements in complex genetic loci
Most genetic loci linked to polygenic traits are in non-coding regions, with complex regulation and linkage disequilibrium (LD), complicating causal v…
www.sciencedirect.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Aug 22

Whole-genome sequencing of 490,640 UK Biobank participants - Nature
A study reports whole-genome sequences for 490,640 participants from the UK Biobank and combines these data with phenotypic data to provide new insights into the relationship between human variation a...
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Aug 21

Regulatory network topology and the genetic architecture of gene expression
In human populations, most of the genetic variance in gene expression can be attributed to trans -acting expression quantitative trait loci (eQTLs) spread across the genome. However, in practice it is...
www.biorxiv.org
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Aug 17

Single-cell eQTL mapping of human endogenous retroviruses reveals cell type-specific genetic regulation in autoimmune diseases - Nature Communications
Human endogenous retroviruses are abundant in the genome but poorly characterised. Here, the authors map their expression and genetic regulation in immune cells and identify disease-linked loci with p...
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Aug 11

Towards improved fine-mapping of candidate causal variants - Nature Reviews Genetics
Fine-mapping aims to distinguish between the causal and non-causal genetic variants identified in genome-wide association studies of complex traits. In this Review, Li and Zhou cover the recent method...
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· May 25
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· May 15
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Apr 11
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Apr 11

Exploring the molecular basis of the genetic correlation between body mass index and brain morphological traits
Author summary Obesity is linked to many chronic diseases and its prevalence worldwide is increasing. Susceptibility to obesity is known to be due, to some degree, to genetic factors, and such genetic...
journals.plos.org
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Apr 11

Genetically regulated eRNA expression predicts chromatin contact frequency and reveals genetic mechanisms at GWAS loci - Nature Communications
Here, the authors present trained models of genetically regulated enhancer RNA expression, finding that genetically regulated expression predicts chromatin contact frequency and that enhancer RNAs pla...
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Apr 1

An atlas of single-cell eQTLs dissects autoimmune disease genes and identifies novel drug classes for treatment
Most variants identified from genome-wide association studies (GWASs) are non-coding and regulate gene expression. However, many risk loci fail to col…
www.sciencedirect.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Feb 24
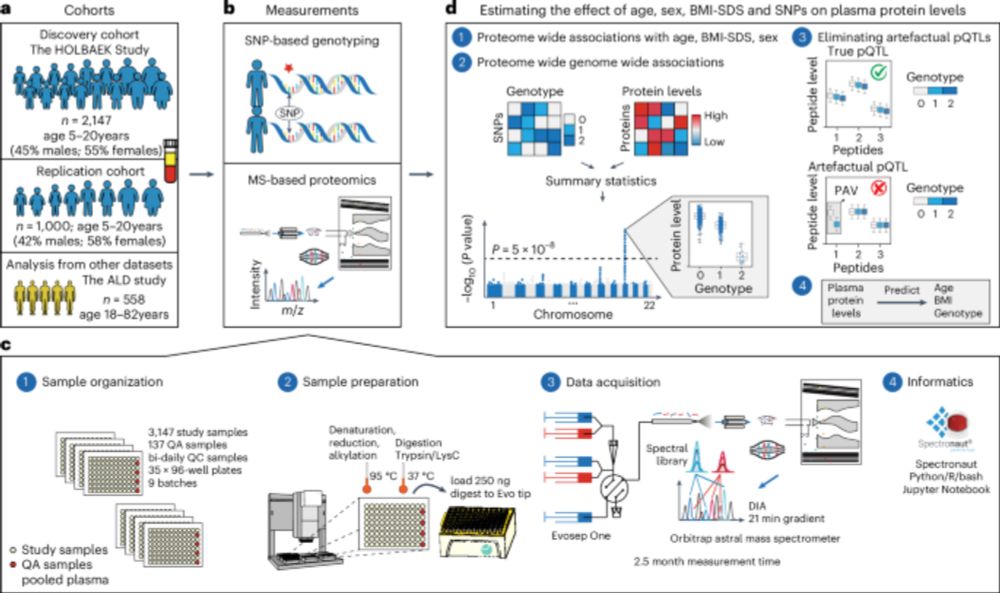
Plasma proteome variation and its genetic determinants in children and adolescents - Nature Genetics
This mass spectrometry-based proteomic study profiles the plasma proteome in 2,147 children and adolescents and reveals its association with age, sex, puberty, body mass index and genetics.
www.nature.com
CBU
@cbuunito.bsky.social
· Feb 22

Mapping the regulatory effects of common and rare non-coding variants across cellular and developmental contexts in the brain and heart
Whole genome sequencing has identified over a billion non-coding variants in humans, while GWAS has revealed the non-coding genome as a significant contributor to disease. However, prioritizing causal...
www.biorxiv.org











