Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
230 followers
290 following
14 posts
Welcome to the Sieber group BlueSky page. Here we keep you up to date on our research (and other interesting things) at the TUM.⚗️🧪🧫🧬🔬👩💻
Our homepage: https://www.bio.nat.tum.de/oc2/home/
Our LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/company/sieber-lab
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Apr 16

AI-guided Antibiotic Discovery Pipeline from Target Selection to Compound Identification
Antibiotic resistance presents a growing global health crisis, demanding new therapeutic strategies that target novel bacterial mechanisms. Recent advances in protein structure prediction and machine ...
arxiv.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Feb 19

Chemical proteomics reveal human off‐targets of fluoroquinolone induced mitochondrial toxicity
Fluoroquinolones (FQs) are an important class of potent broad-spectrum antibiotics. However, their general use is more and more limited by adverse side effects. While general mechanisms for the fluor....
doi.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Feb 6
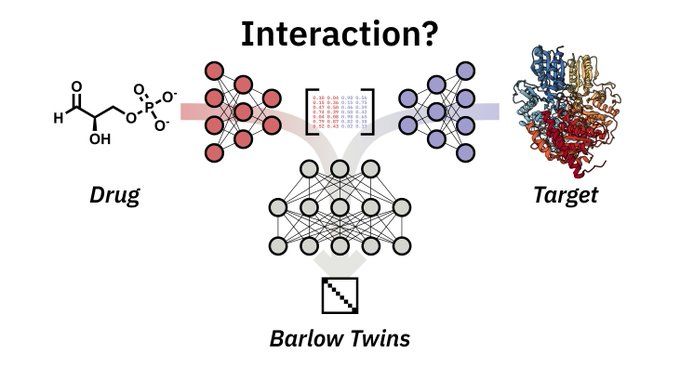
Barlow Twins deep neural network for advanced 1D drug–target interaction prediction - Journal of Cheminformatics
Abstract Accurate prediction of drug–target interactions is critical for advancing drug discovery. By reducing time and cost, machine learning and deep learning can accelerate this laborious discovery...
doi.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Feb 5
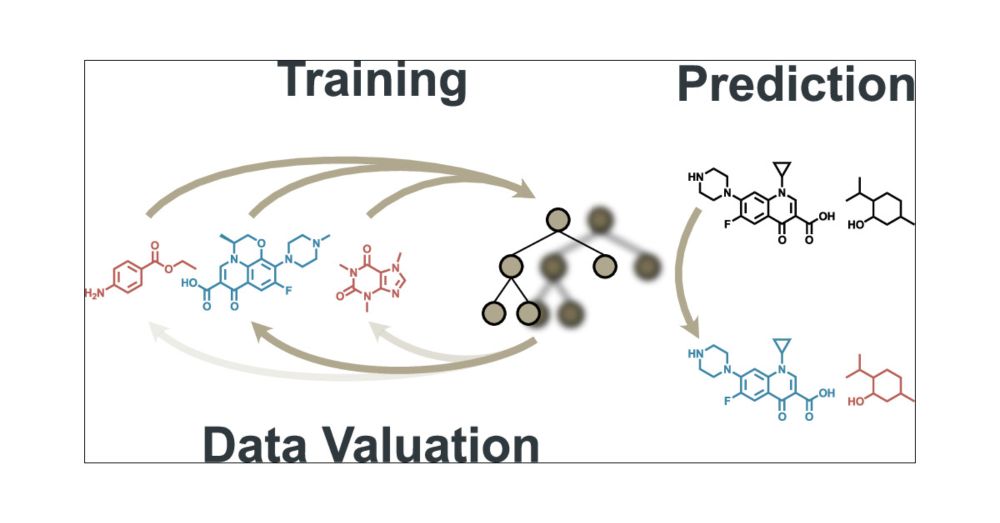
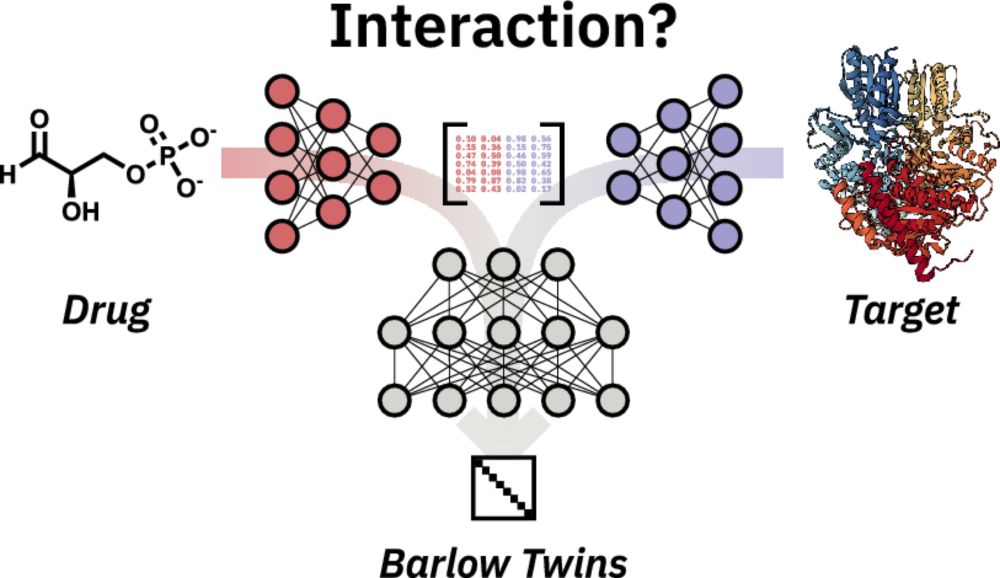
Machine Learning-Driven Data Valuation for Optimizing High-Throughput Screening Pipelines
In the rapidly evolving field of drug discovery, high-throughput screening (HTS) is essential for identifying bioactive compounds. This study introduces a novel application of data valuation, a concept for evaluating the importance of data points based on their impact, to enhance drug discovery pipelines. Our approach improves active learning for compound library screening, robustly identifies true and false positives in HTS data, and identifies important inactive samples in an imbalanced HTS training, all while accounting for computational efficiency. We demonstrate that importance-based methods enable more effective batch screening, reducing the need for extensive HTS. Machine learning models accurately differentiate true biological activity from assay artifacts, streamlining the drug discovery process. Additionally, importance undersampling aids in HTS data set balancing, improving machine learning performance without omitting crucial inactive samples. These advancements could significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of drug development.
pubs.acs.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
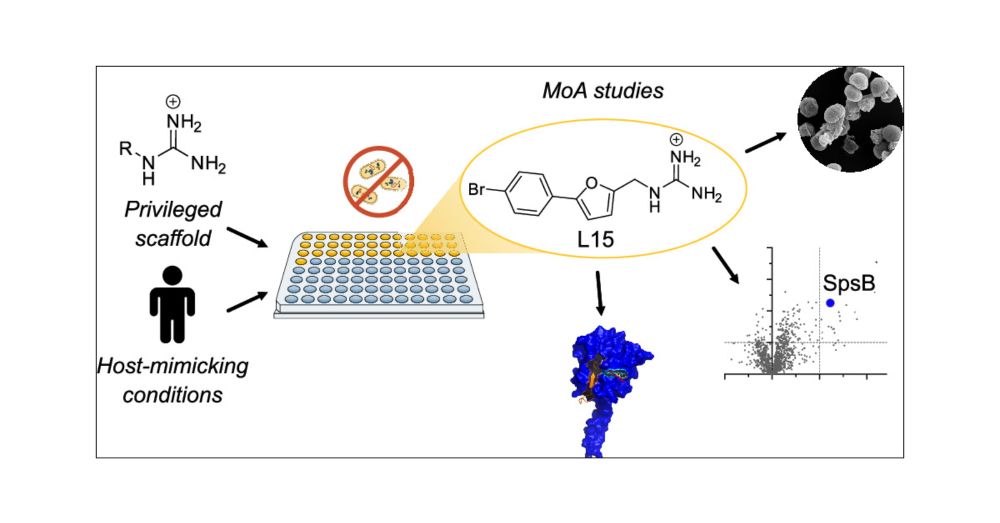
Screening Privileged Alkyl Guanidinium Motifs under Host-Mimicking Conditions Reveals a Novel Antibiotic with an Unconventional Mode of Action
Screening large molecule libraries against pathogenic bacteria is often challenged by a low hit rate due to limited uptake, underrepresentation of antibiotic structural motifs, and assays that do not resemble the infection conditions. To address these limitations, we present a screen of a focused library of alkyl guanidinium compounds, a structural motif associated with antibiotic activity and enhanced uptake, under host-mimicking infection conditions against a panel of disease-associated bacteria. Several hit molecules were identified with activities against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, highlighting the fidelity of the general concept. We selected one compound (L15) for in-depth mode of action studies that exhibited bactericidal activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus USA300 with a minimum inhibitory concentration of 1.5 μM. Structure-activity relationship studies confirmed the necessity of the guanidinium motif for antibiotic activity. The mode of action was investigated using affinity-based protein profiling with an L15 probe and identified the signal peptidase IB (SpsB) as the most promising hit. Validation by activity assays, binding site identification, docking, and molecular dynamics simulations demonstrated SpsB activation by L15, a recently described mechanism leading to the dysregulation of protein secretion and cell death. Overall, this study highlights the need for unconventional screening strategies to identify novel antibiotics.
pubs.acs.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
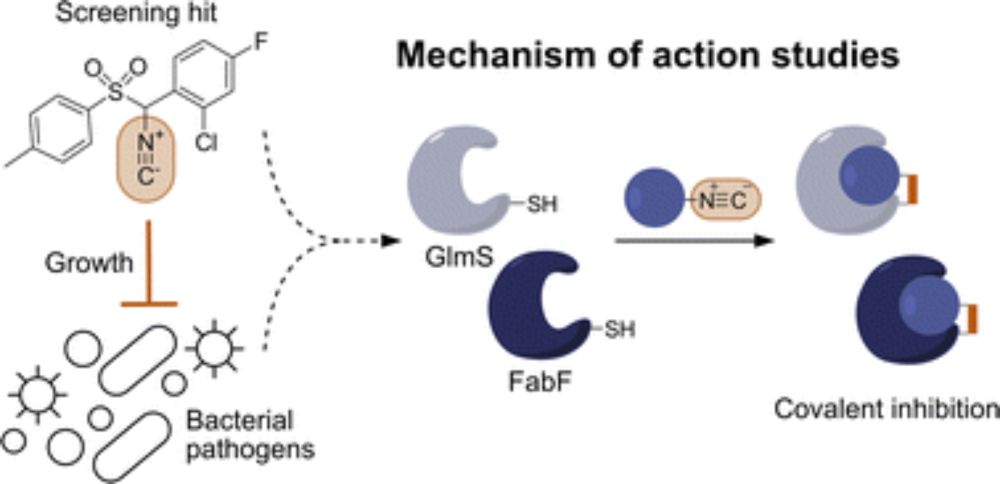
Isocyanides inhibit bacterial pathogens by covalent targeting of essential metabolic enzymes
Isonitrile natural products, also known as isocyanides, demonstrate potent antimicrobial activities, yet our understanding of their molecular targets remains limited. Here, we focus on the so far negl...
pubs.rsc.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
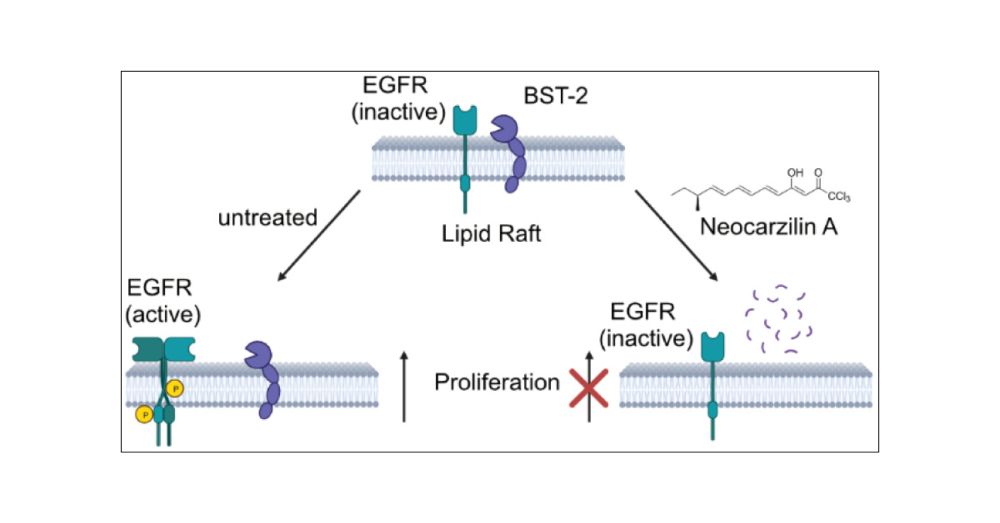
Neocarzilin Inhibits Cancer Cell Proliferation via BST-2 Degradation, Resulting in Lipid Raft-Trapped EGFR
Neocarzilin (NCA) is a natural product exhibiting potent antimigratory as well as antiproliferative effects. While vesicle amine transport protein 1 (VAT-1) was previously shown to inhibit migration upon NCA binding, the molecular mechanisms responsible for impaired proliferation remained elusive. We here introduce a chemical probe closely resembling the structural and stereochemical features of NCA and unravel bone marrow stromal antigen 2 (BST-2) as one of the targets responsible for the antiproliferative effect of NCA in cancer cells. The antiproliferative mechanism of NCA was confirmed in corresponding BST-2 knockout (KO) HeLa cells, which were less sensitive to compound treatment. Vice versa, reconstitution of BST-2 in the KO cells again reduced proliferation upon NCA addition, comparable to that of wild-type (wt) HeLa cells. Whole proteome mass spectrometric (MS) analysis of NCA-treated wt and KO cancer cells revealed regulated pathways and showed reduced levels of BST-2 upon NCA treatment. In-depth analysis of BST-2 levels in response to proteasome and lysosome inhibitors unraveled a lysosomal degradation path upon NCA treatment. As BST-2 mediates the release of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) from lipid rafts to turn on proliferation signaling pathways, reduced BST-2 levels led to attenuated phosphorylation of STAT3. Furthermore, fluorescence microscopy confirmed increased colocalization of EGFR and lipid rafts in the presence of NCA. Overall, NCA represents a versatile anticancer natural product with a unique dual mode of action and unconventional inhibition of proliferation via BST-2 degradation.
pubs.acs.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
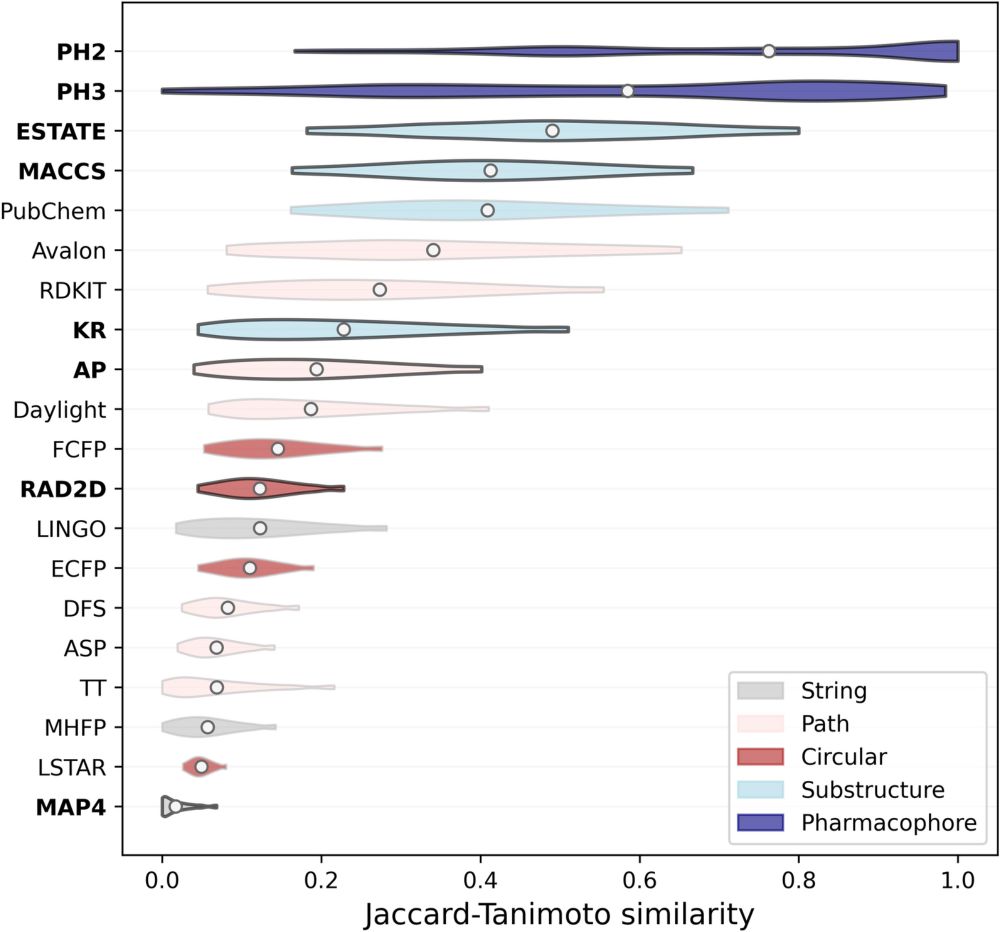
Effectiveness of molecular fingerprints for exploring the chemical space of natural products - Journal of Cheminformatics
Natural products are a diverse class of compounds with promising biological properties, such as high potency and excellent selectivity. However, they have different structural motifs than typical drug...
jcheminf.biomedcentral.com
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
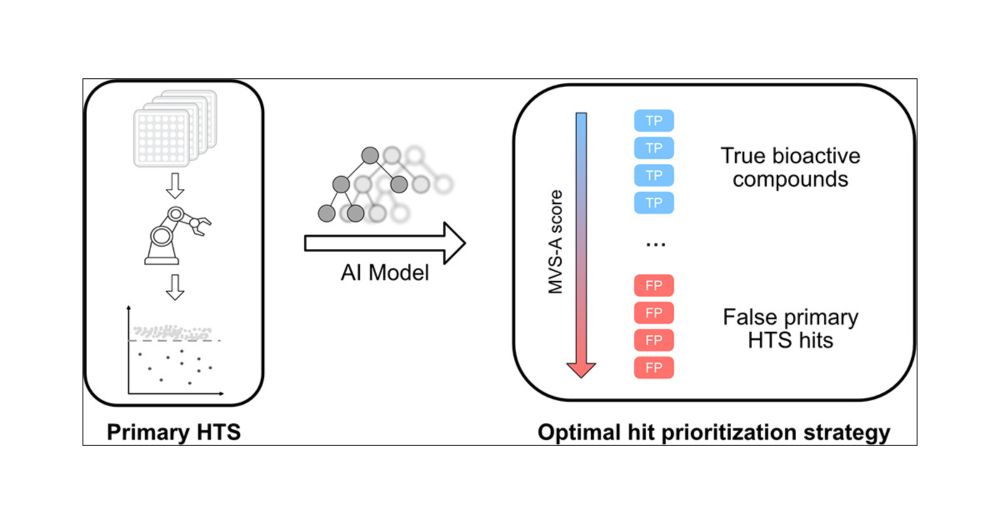
Machine Learning Assisted Hit Prioritization for High Throughput Screening in Drug Discovery
Efficient prioritization of bioactive compounds from high throughput screening campaigns is a fundamental challenge for accelerating drug development efforts. In this study, we present the first data-...
pubs.acs.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
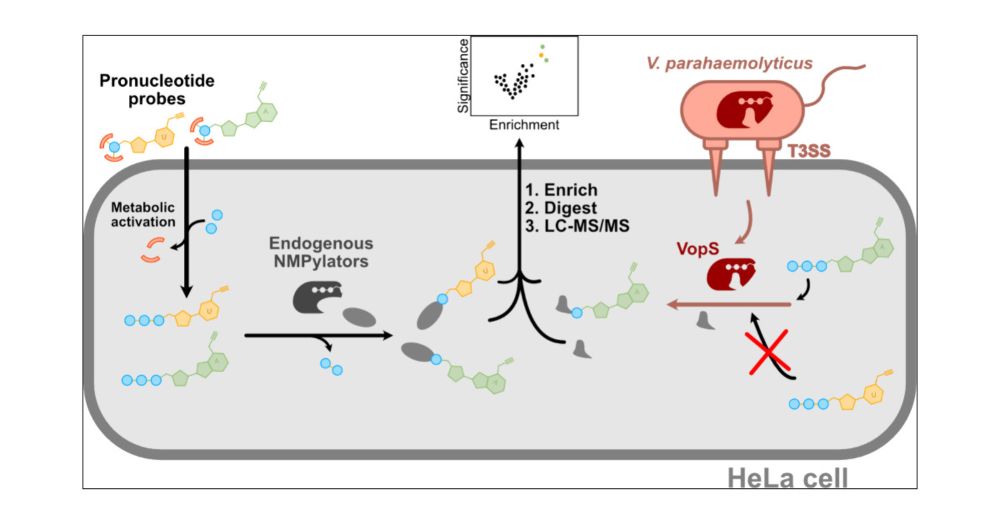
Pronucleotide Probes Reveal a Diverging Specificity for AMPylation vs UMPylation of Human and Bacterial Nucleotide Transferases
AMPylation is a post-translational modification utilized by human and bacterial cells to modulate the activity and function of specific proteins. Major AMPylators such as human FICD and bacterial VopS have been studied extensively for their substrate and target scope in vitro. Recently, an AMP pronucleotide probe also facilitated the in situ analysis of AMPylation in living cells. Based on this technology, we here introduce a novel UMP pronucleotide probe and utilize it to profile uninfected and Vibrio parahaemolyticus infected human cells. Mass spectrometric analysis of labeled protein targets reveals an unexpected promiscuity of human nucleotide transferases with an almost identical target set of AMP- and UMPylated proteins. Vice versa, studies in cells infected by V. parahaemolyticus and its effector VopS revealed solely AMPylation of host enzymes, highlighting a so far unknown specificity of this transferase for ATP. Taken together, pronucleotide probes provide an unprecedented insight into the in situ activity profile of crucial nucleotide transferases, which can largely differ from their in vitro activity.
pubs.acs.org
Sieber Lab
@sieberlab.bsky.social
· Jan 21
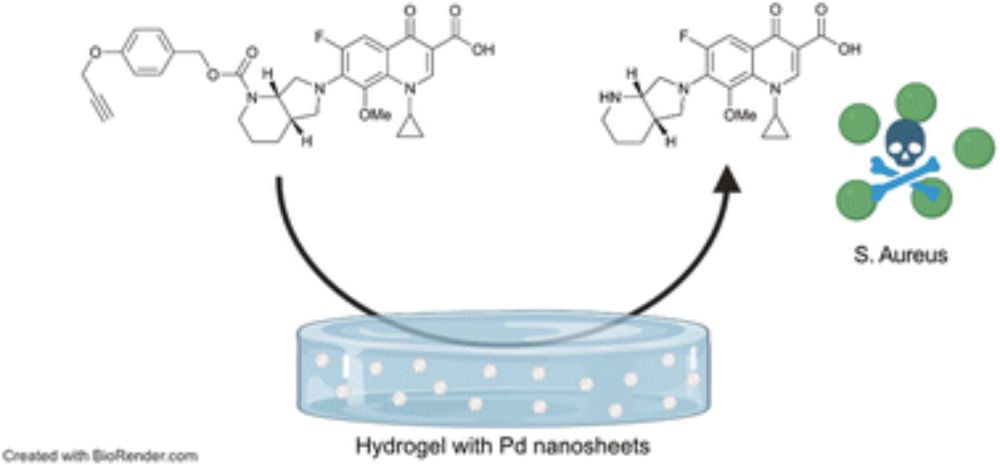
A Pd-labile fluoroquinolone prodrug efficiently prevents biofilm formation on coated surfaces
Surface-adhered bacteria on implants represent a major challenge for antibiotic treatment. We introduce hydrogel-coated surfaces loaded with tailored Pd-nanosheets which catalyze the release of antibi...
doi.org