Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
120 followers
240 following
13 posts
Neuroscience PhD student at NYU in the Movshon and Chung Labs.
https://www.cns.nyu.edu/~saraf/
[email protected]
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29
Sonica Saraf
@sonicasaraf.bsky.social
· Jun 29

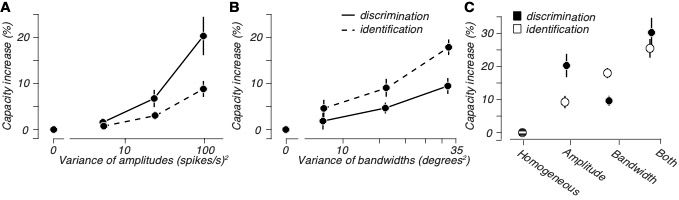
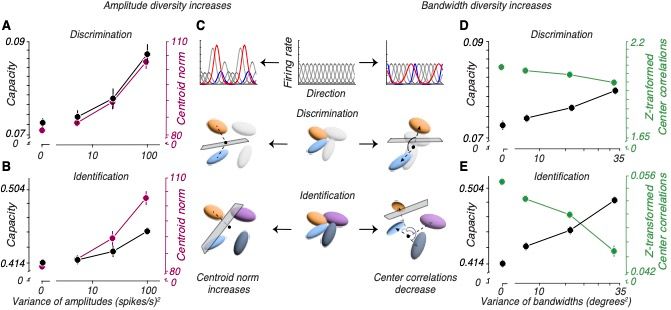
Variations in neuronal selectivity create efficient representational geometries for perception
Our visual capabilities depend on neural response properties in visual areas of our brains. Neurons exhibit a wide variety of selective response properties, but the reasons for this diversity are unkn...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Sonica Saraf
Reposted by Sonica Saraf
Jenelle Feather
@jfeather.bsky.social
· Apr 2