But how does piRNA-guided target interaction translate into silencing?
PhD student Júlia Portell Montserrat has an intriguing answer
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...

But how does piRNA-guided target interaction translate into silencing?
PhD student Júlia Portell Montserrat has an intriguing answer
www.cell.com/molecular-ce...

Our paper looking at resistance genes from a century of NCTC historical isolates now out in mGen:
www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...

Our paper looking at resistance genes from a century of NCTC historical isolates now out in mGen:
www.microbiologyresearch.org/content/jour...
We designed synthetic proteins that can block bacterial immune systems, allowing phages + plasmids to overcome natural defenses.
This could transform phage therapy + genetic engineering.
Here’s what we found 🧵
Preprint🔗: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

We designed synthetic proteins that can block bacterial immune systems, allowing phages + plasmids to overcome natural defenses.
This could transform phage therapy + genetic engineering.
Here’s what we found 🧵
Preprint🔗: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
We found mutually exclusive evolutionary pathways to multidrug resistance in E. coli & P. aeruginosa - some resistance mechanisms actively prevent others from coexisting www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

We found mutually exclusive evolutionary pathways to multidrug resistance in E. coli & P. aeruginosa - some resistance mechanisms actively prevent others from coexisting www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

https://www.theverge.com/news/757461/microsoft-github-thomas-dohmke-resignation-coreai-team-transition
https://go.nature.com/40wPxkB

https://go.nature.com/40wPxkB
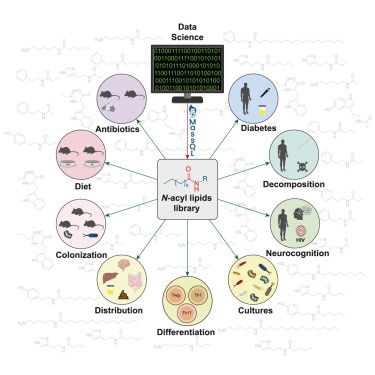
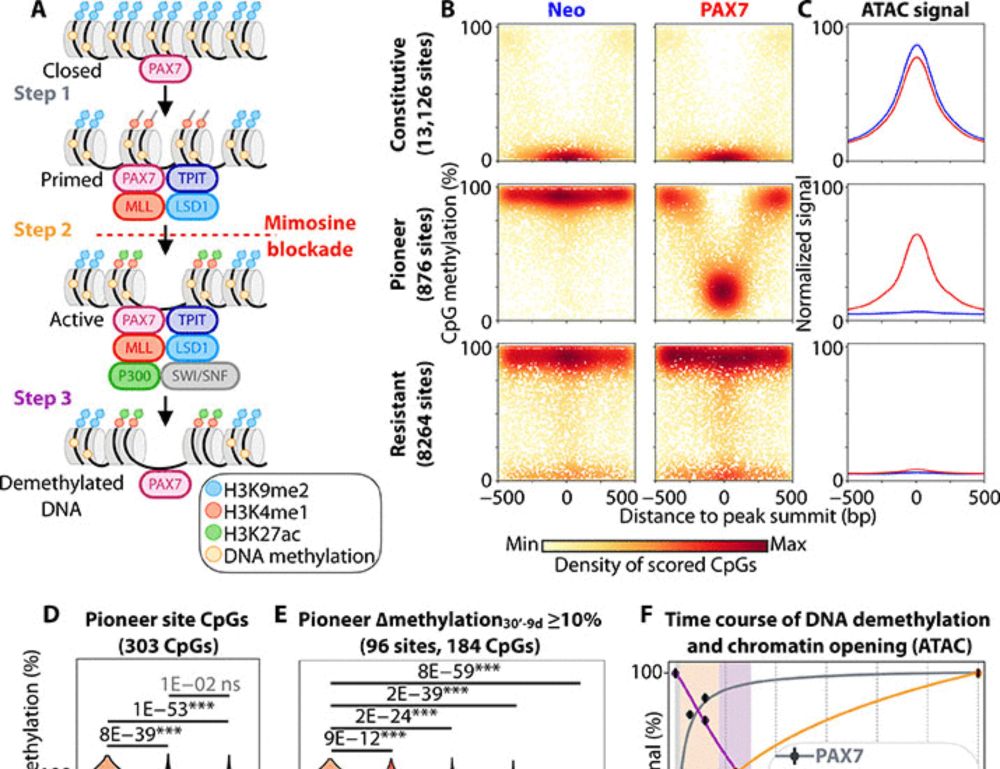

You don't catch lightning in a bottle like that every day.
You don't catch lightning in a bottle like that every day.
We hope this will be one more tool to help integrate genomics into undergraduate education by supporting evidence-based curriculum design with a set of standardized concepts.
journals.plos.org/plosone/arti...

We hope this will be one more tool to help integrate genomics into undergraduate education by supporting evidence-based curriculum design with a set of standardized concepts.
journals.plos.org/plosone/arti...
Earlier that day:

Earlier that day:
www.bbc.com/news/article...

www.bbc.com/news/article...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...

