The figure shows a comparison of pellet fragmentation under different loading orientations. Each colour represents distinct fragments formed after primary failure.
The figure shows a comparison of pellet fragmentation under different loading orientations. Each colour represents distinct fragments formed after primary failure.
#FDEM #MaterialModeling #FractureMechanics #Engineering #Geomechanics #Simulation #FEM #DEM #TanukiTechnologies
#FDEM #MaterialModeling #FractureMechanics #Engineering #Geomechanics #Simulation #FEM #DEM #TanukiTechnologies
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
Using high-speed video recording of mechanical crushing experiments, I was able to compare simulation results with real-world fracture behaviour—proving that FDEM is a powerful tool for modelling complex material failure.
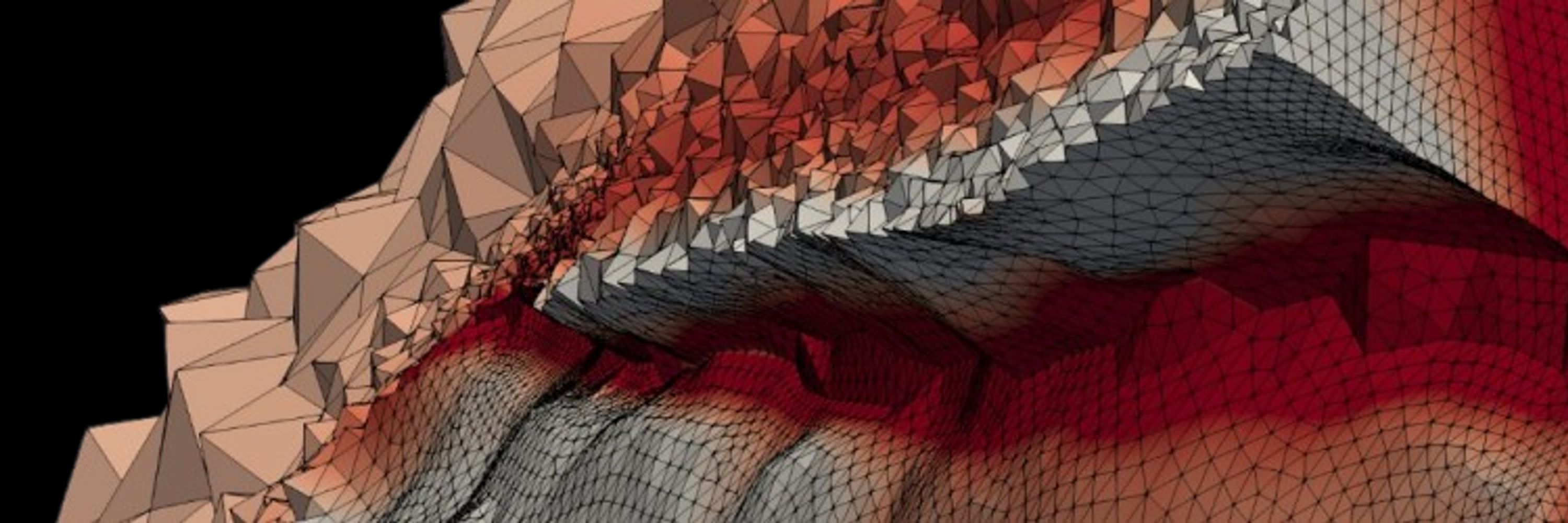
The figure below gives an overview of FDEM in action:
(a) Contact interactions and body motion
(b) Stress and deformation calculations
(c) Fracture and fragmentation processes
https://buff.ly/4b6tkhH
The figure below gives an overview of FDEM in action:
(a) Contact interactions and body motion
(b) Stress and deformation calculations
(c) Fracture and fragmentation processes
https://buff.ly/4b6tkhH
FDEM is a great tool for solving complex problems in engineering, geomechanics, and material science.
FDEM is a great tool for solving complex problems in engineering, geomechanics, and material science.
You can read the publication here: https://buff.ly/3WRAd0i
You can read the publication here: https://buff.ly/3WRAd0i
#FDEM #BrazilianDiscTest #FractureMechanics #MaterialModeling #Geomechanics #RockMechanics #NumericalModeling #EngineeringSimulation #ComputationalMechanics #FEM #DEM #TanukiTechnologies
Additionally, you can see two frames from a video recording of a uniaxial compressive test on a cylinder, further highlighting FDEM’s ability to capture fracture mechanics in brittle materials.
Additionally, you can see two frames from a video recording of a uniaxial compressive test on a cylinder, further highlighting FDEM’s ability to capture fracture mechanics in brittle materials.
🔹 (a) The tensile stress field before failure, reaching the tensile strength at the disc’s center.
🔹 (b) Crack propagation from the centre outward.
🔹 (c) The splitting of the disc.
🔹 (a) The tensile stress field before failure, reaching the tensile strength at the disc’s center.
🔹 (b) Crack propagation from the centre outward.
🔹 (c) The splitting of the disc.
#ShapeOptimization #ComputationalMechanics #NumericalSimulations #FEniCS #PhaseField #FEM

