Joel MJ Tan
@joelmjtan.bsky.social
53 followers
23 following
2 posts
PhD Candidate in the Kranzusch Lab at Harvard Medical School
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Joel MJ Tan
Joel MJ Tan
@joelmjtan.bsky.social
· Aug 8
Reposted by Joel MJ Tan
Sorek Lab
@soreklab.bsky.social
· Jul 30
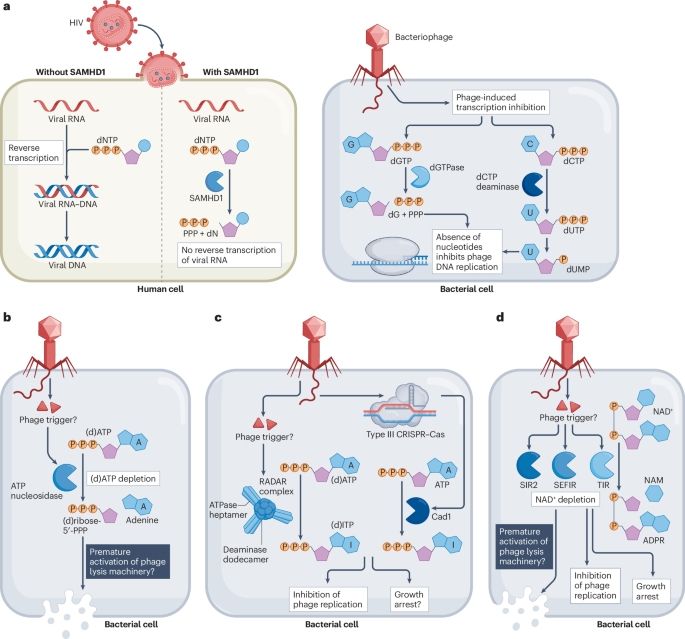
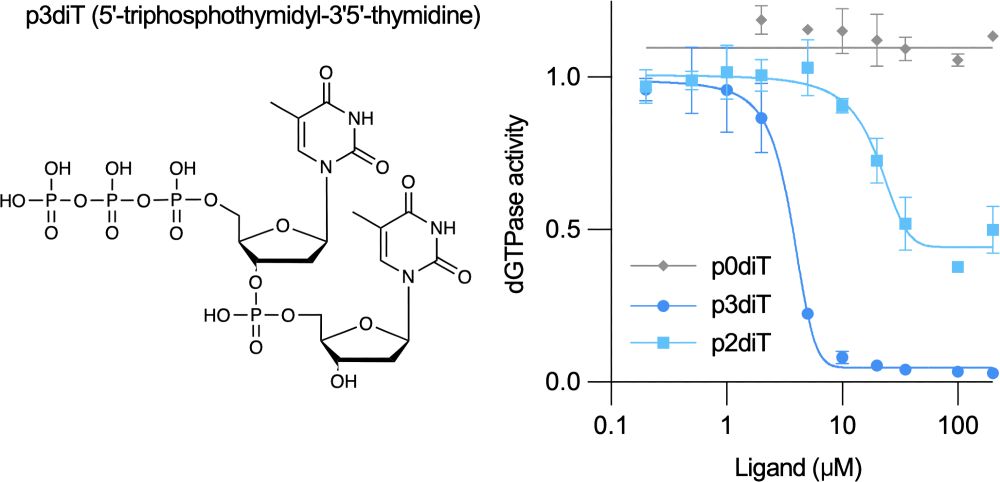
Manipulation of the nucleotide pool in human, bacterial and plant immunity - Nature Reviews Immunology
Modification of the nucleotide pool is emerging as key to innate immunity in animals, plants and bacteria. This Review explains how immune pathways conserved from bacteria to humans manipulate the nuc...
www.nature.com
Reposted by Joel MJ Tan
Reposted by Joel MJ Tan
Kranzusch Lab
@kranzuschlab.bsky.social
· Jul 15

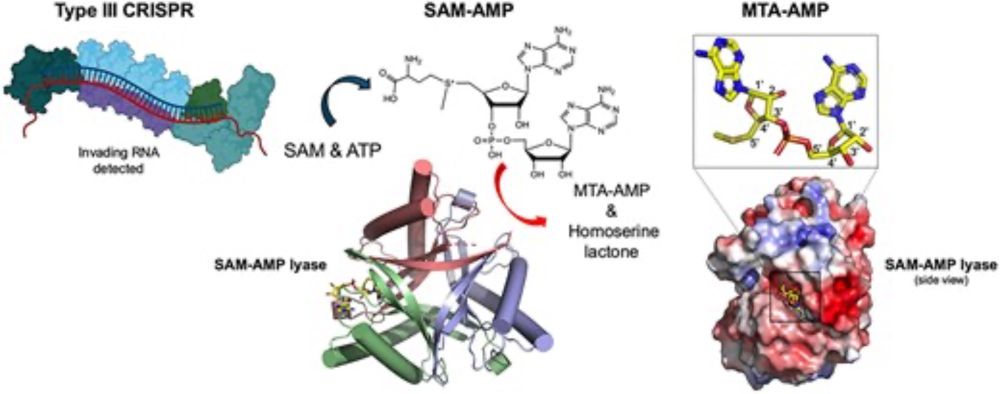
Nuclease-NTPase systems use shared molecular features to control bacterial anti-phage defense
Bacteria encode an enormous diversity of defense systems including restriction-modification and CRISPR-Cas that cleave nucleic acid to protect against phage infection. Bioinformatic analyses demonstra...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Joel MJ Tan
Nature
@nature.com
· May 1
A DNA-gated molecular guard controls bacterial Hailong anti-phage defence - Nature
Animal and bacterial cells use nucleotidyltransferase (NTase) enzymes to respond to viral infection and control major forms of immune signaling including cGAS-STING innate immunity and CBASS anti-phage defence1-4. Here we discover a family of bacterial defence systems, which we name Hailong, that use NTase enzymes to constitutively synthesize DNA signals and guard against phage infection. Hailong protein B (HalB) is an NTase that converts deoxy-ATP into single-stranded DNA oligomers. A series of X-ray crystal structures define a stepwise mechanism of HalB DNA synthesis initiated by a C-terminal tyrosine residue that enables de novo enzymatic priming. We show that HalB DNA signals bind to and repress activation of a partnering Hailong protein A (HalA) effector complex. A 2.0 Å cryo-EM structure of the HalA–DNA complex reveals a membrane protein with a conserved ion channel domain and a unique crown domain that binds the DNA signal and gates activation. Analyzing Hailong defence in vivo, we demonstrate that viral DNA exonucleases required for phage replication trigger release of the primed HalA complex and induce protective host cell growth arrest. Our results explain how inhibitory nucleotide immune signals can serve as molecular guards against phage infection and expand the mechanisms NTase enzymes use to control antiviral immunity.
go.nature.com
Reposted by Joel MJ Tan