Marijn Schipper
@mjschipper.bsky.social
40 followers
56 following
7 posts
Geneticist, Programmer and Science Enthousiast
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Marijn Schipper
@mjschipper.bsky.social
· Feb 11
Marijn Schipper
@mjschipper.bsky.social
· Feb 11
Marijn Schipper
@mjschipper.bsky.social
· Feb 11
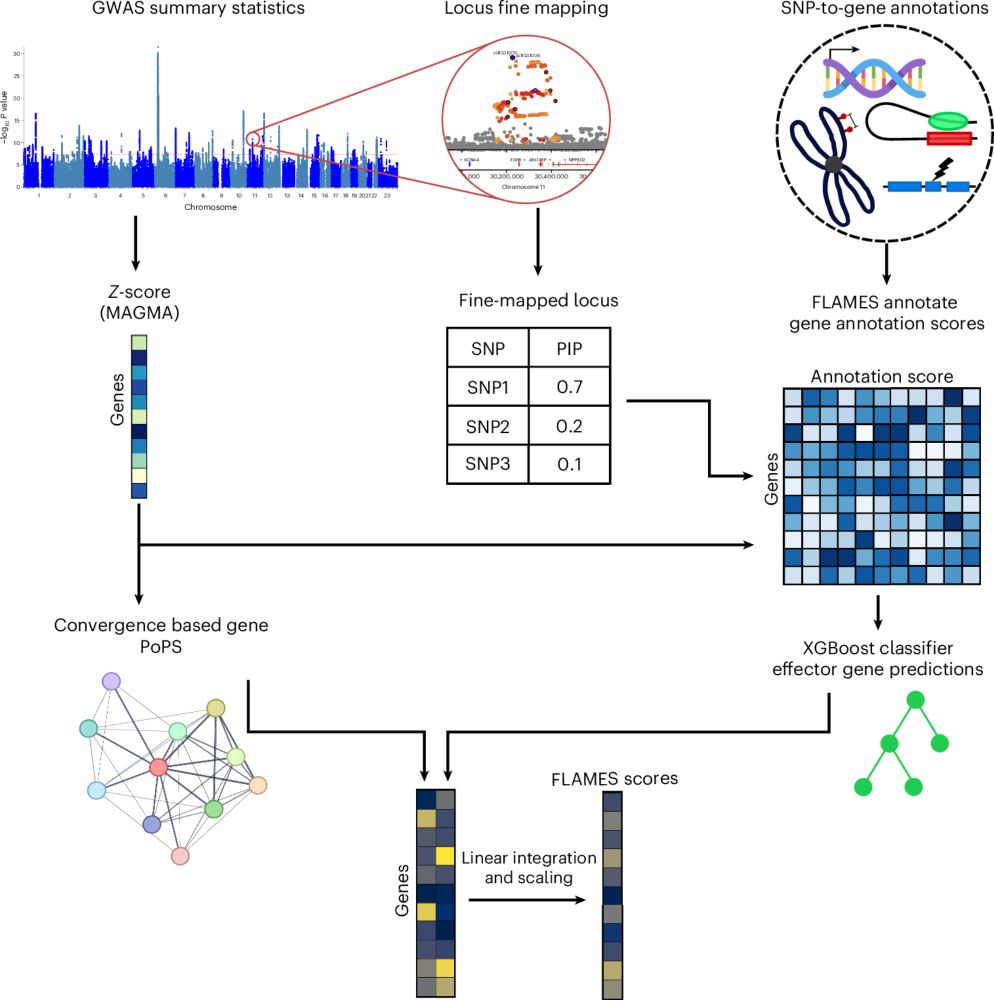
Prioritizing effector genes at trait-associated loci using multimodal evidence
Nature Genetics - FLAMES is a machine learning approach combining variant fine-mapping, SNP-to-gene annotations and convergence-based gene prioritization scores to identify candidate effector genes...
rdcu.be



