Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
53 followers
23 following
12 posts
PhD student @YalePsychology | @HarvardChanSPH‘19 | @OUC1924 ‘17 computational biology, neuroscience, affective dynamics, mechanisms of change
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
· Apr 17
Reposted by Xi-Han Zhang
Reposted by Xi-Han Zhang
Loïc Labache
@loiclabache.bsky.social
· Apr 12

The molecular and cellular underpinnings of human brain lateralization
Hemispheric specialization is a fundamental characteristic of human brain organization, where most individuals exhibit left-hemisphere dominance for language and right-hemisphere dominance for visuosp...
doi.org
Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
· Dec 4
Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
· Dec 3
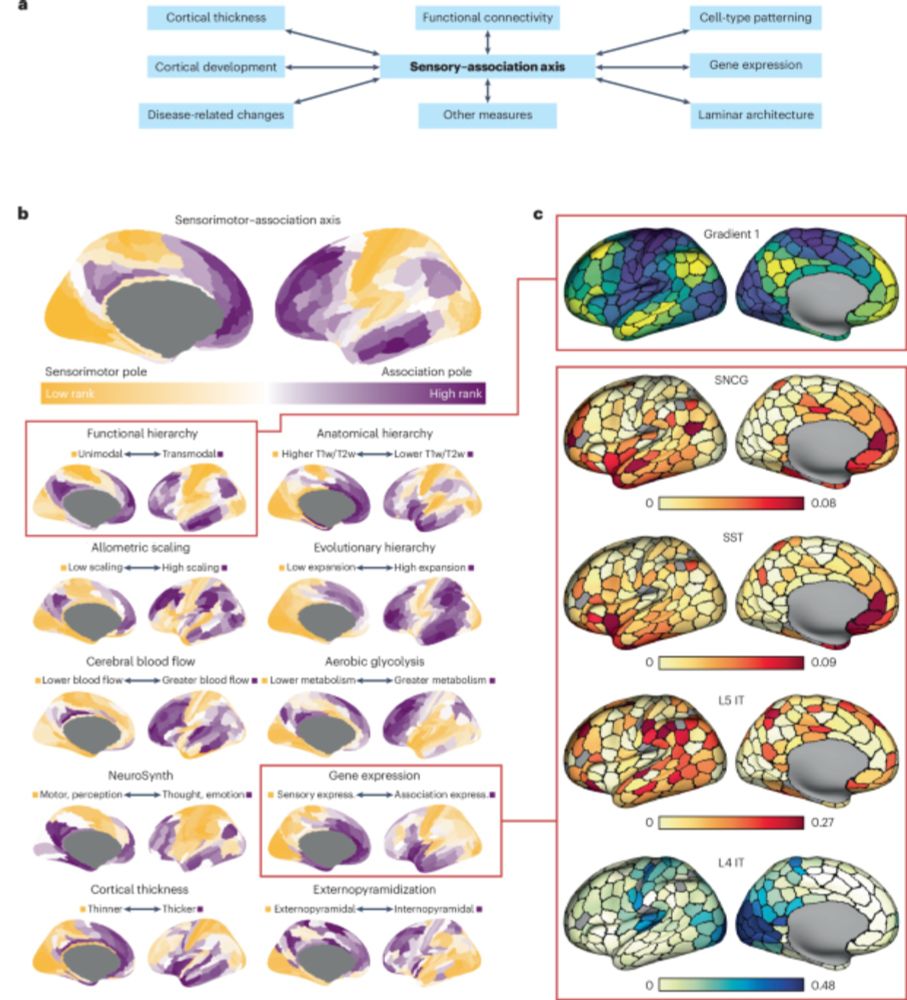
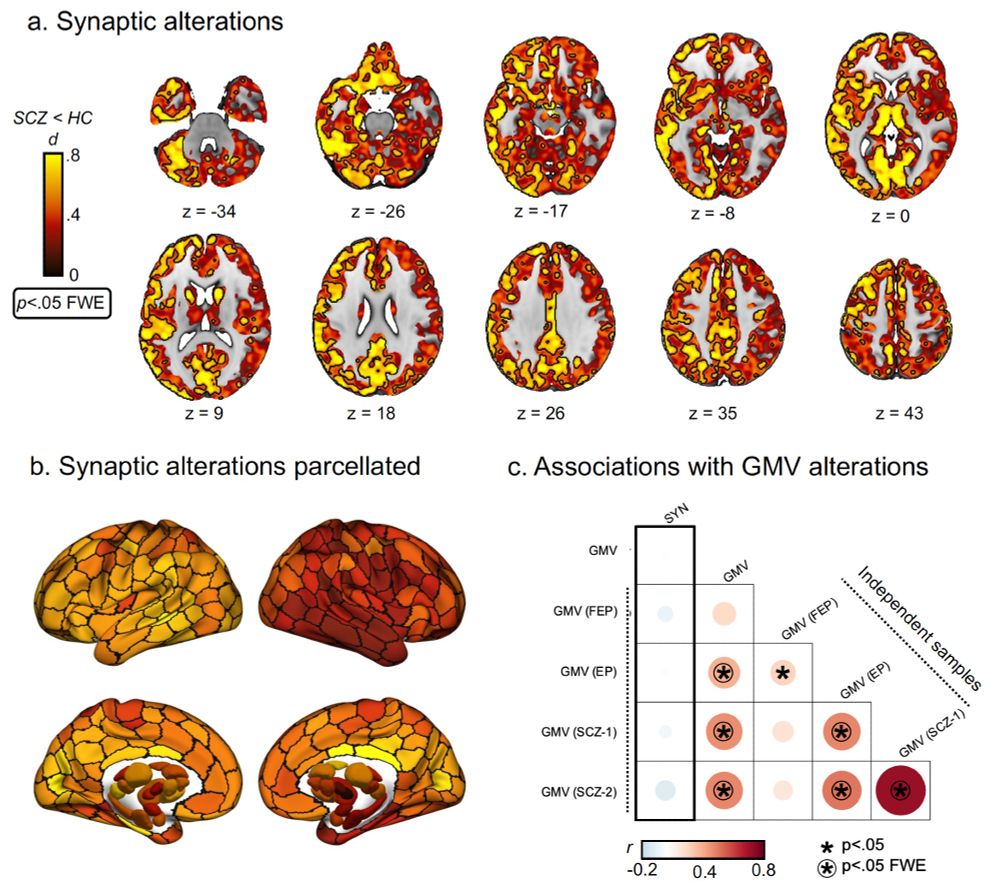
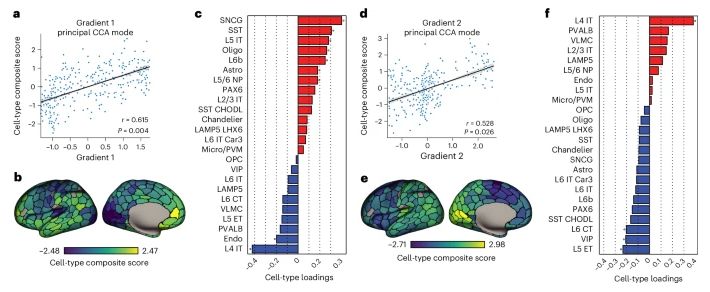
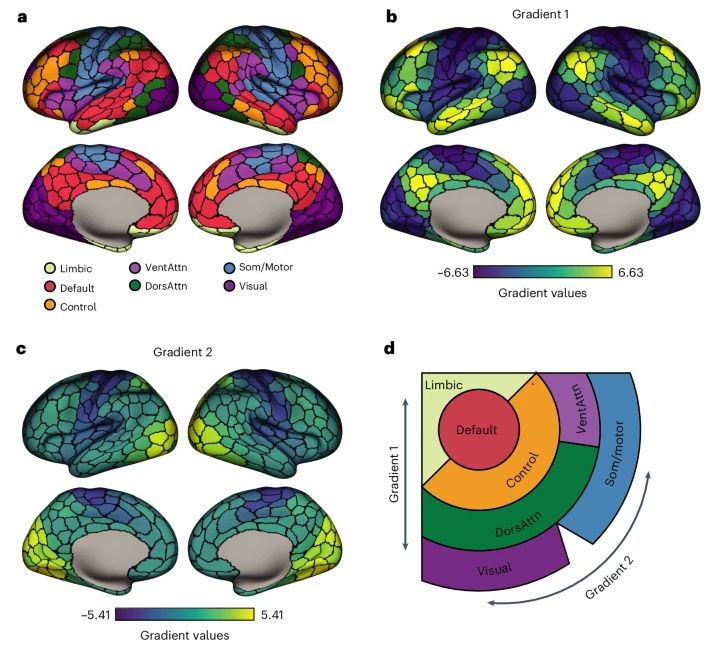
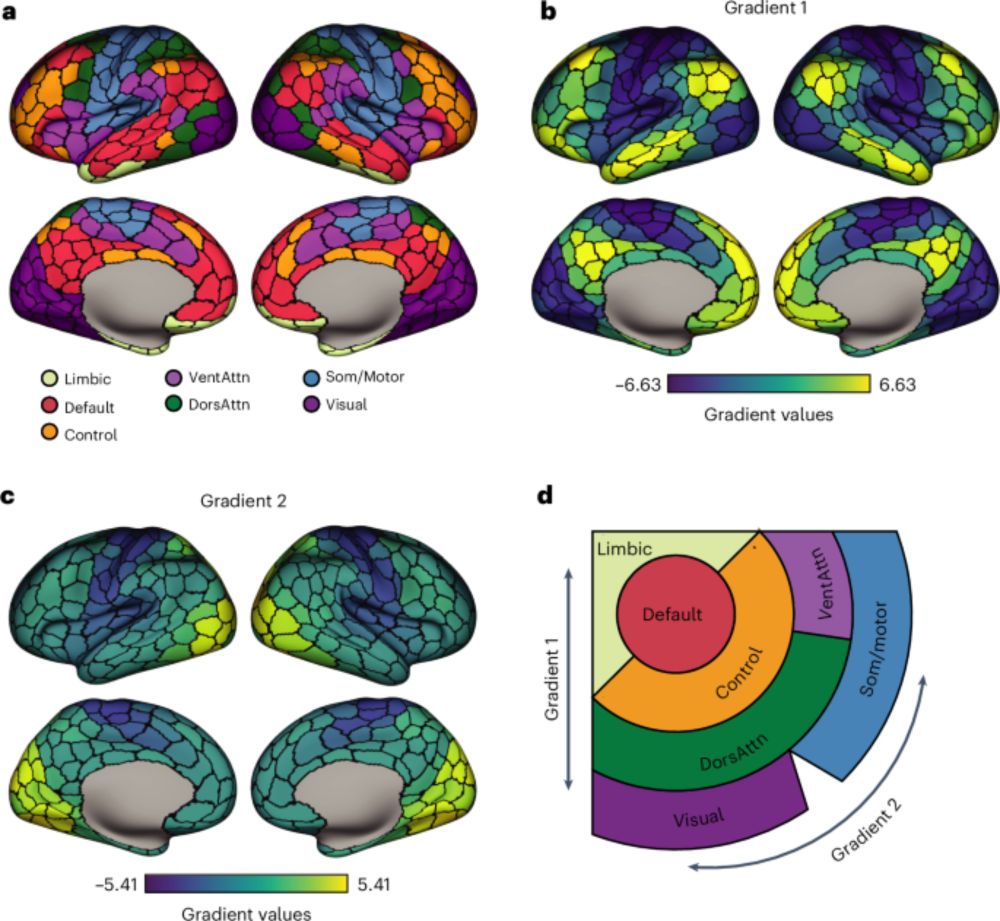
Converging cortical axes - Nature Neuroscience
The cerebral cortex shows complex organization across diverse biological scales, from regional chemical and cellular specializations to macroscale functional networks. Zhang et al. report that macrosc...
www.nature.com
Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
· Dec 3
Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
· Dec 3
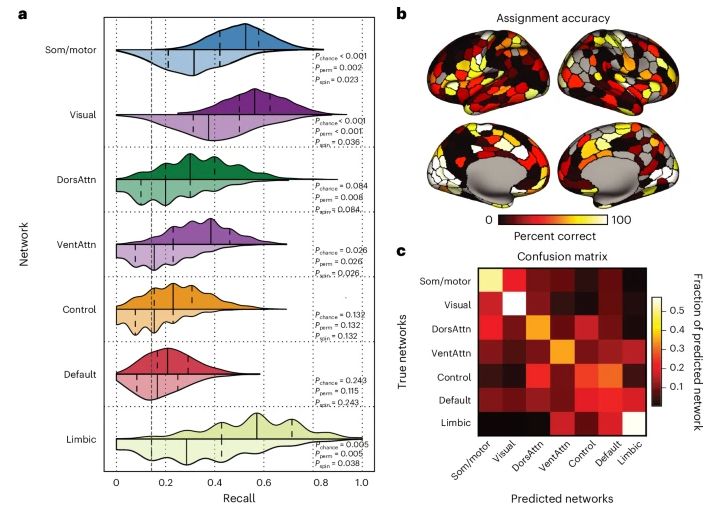
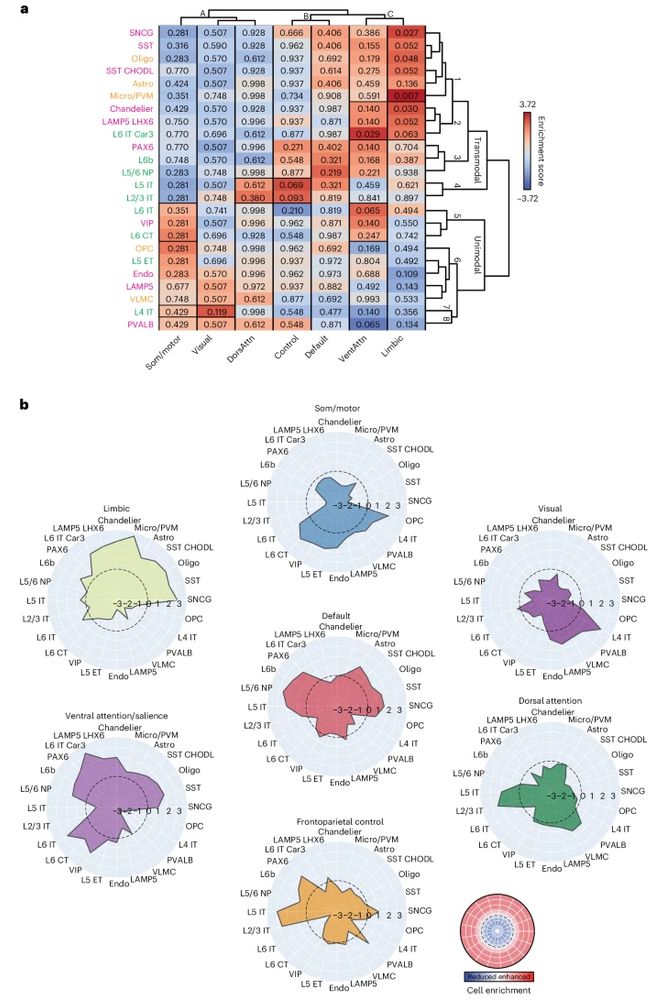
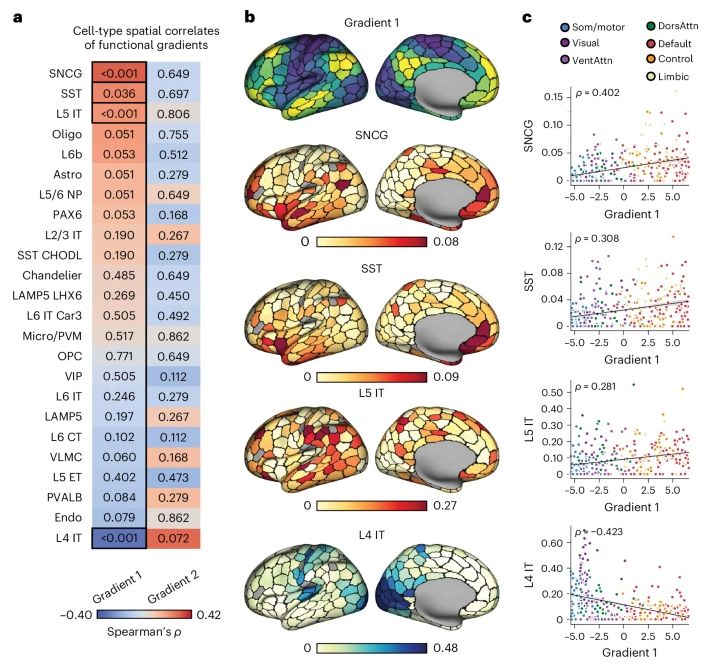
The cell-type underpinnings of the human functional cortical connectome - Nature Neuroscience
Here Zhang et al. establish multiscale relationships that link postmortem cell-type distributions with the in vivo functional organization of the human cerebral cortex, as assessed through functional ...
nature.com
Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
· Dec 3
Xi-Han Zhang
@xi-hanzhang.bsky.social
· Dec 3
Reposted by Xi-Han Zhang
Konrad Wagstyl
@konradwagstyl.bsky.social
· Nov 21
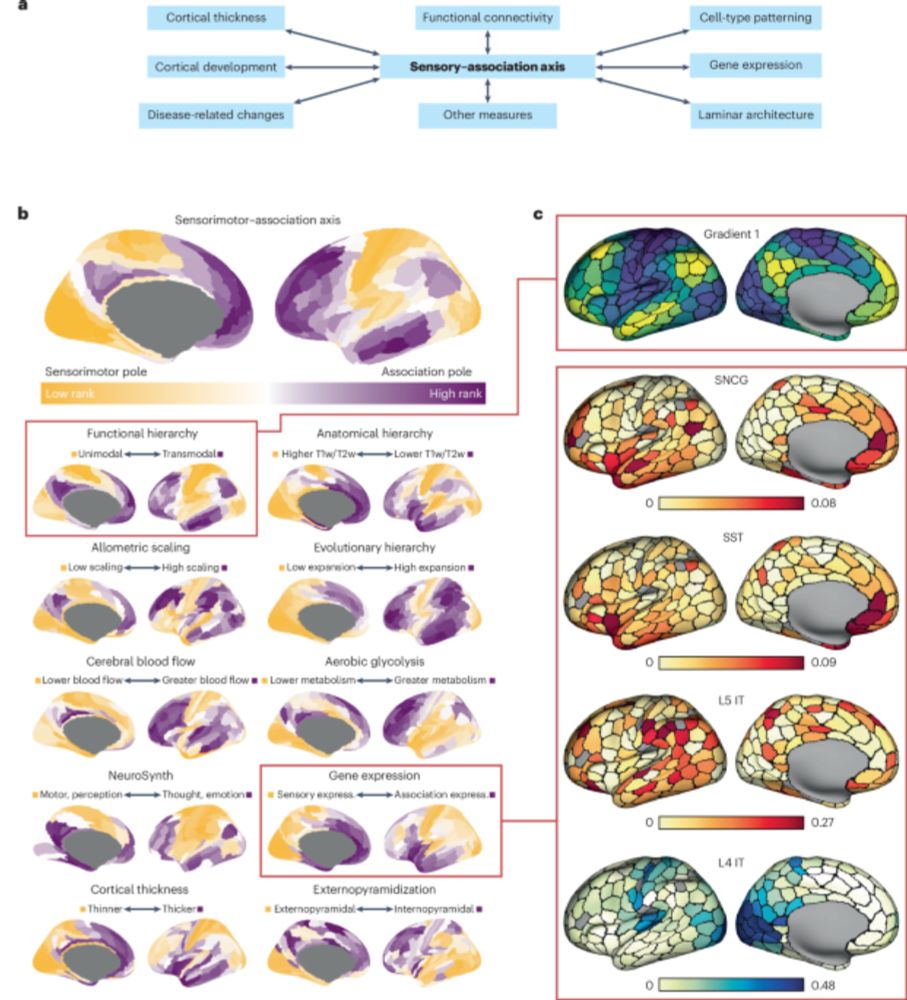
Converging cortical axes - Nature Neuroscience
The cerebral cortex shows complex organization across diverse biological scales, from regional chemical and cellular specializations to macroscale functional networks. Zhang et al. report that macrosc...
shorturl.at
Reposted by Xi-Han Zhang
Elvisha Dhamala
@elvisha.bsky.social
· Nov 21
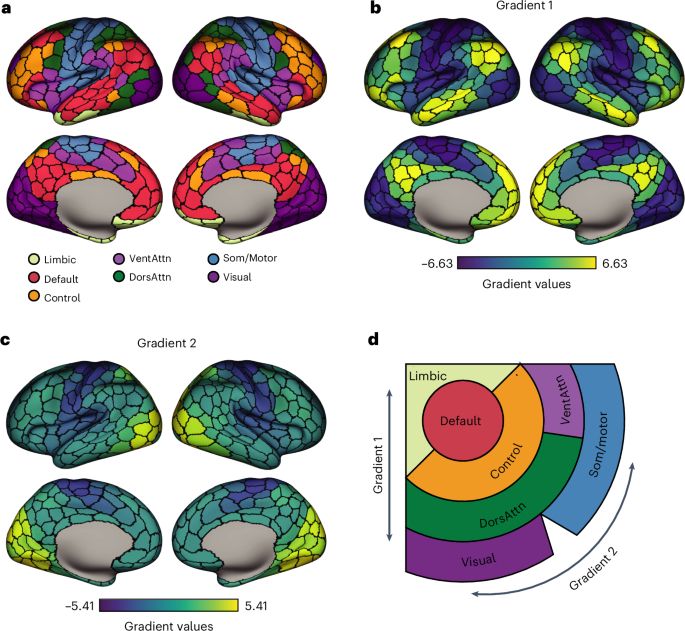
The cell-type underpinnings of the human functional cortical connectome - Nature Neuroscience
Here Zhang et al. establish multiscale relationships that link postmortem cell-type distributions with the in vivo functional organization of the human cerebral cortex, as assessed through functional ...
www.nature.com