Marcos Palmeira
@palmeiramarcoss.bsky.social
170 followers
240 following
10 posts
Postdoctoral on Medicinal Inorganic Chemistry at UFSCar 🇧🇷 / Previously at CPT-PSL with prof Gilles Gasser 🇨🇵 / PhD at UFF 🇧🇷 with training at UB with prof Patrick Gamez 🇪🇸
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
nanoBIC
@nanobic.bsky.social
· Jul 8

Exploring the toxicity of mononuclear piano-stool Ru(II) anticancer agents: A comprehensive literature review
Piano-stool Ru(II) complexes have emerged as a promising class of anticancer agents characterized by structural modularity and diverse cytotoxic activ…
tinyurl.com
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Patrick Cieslik
@pacieslik.bsky.social
· May 23

Light-Induced Synthesis and Radiotheranostic Treatment of Gastric Cancer with 161Tb-Labeled Monoclonal Antibodies
Radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) form a major branch of nuclear medicine and are used in the development of tracers for both diagnostic imaging and molecularly targeted radio(immuno)therapy (RIT). Since treatment options for many types of late-stage cancers are limited and these diseases become refractory to classic chemotherapy, new tools are required to improve patient outcomes. The high tumor uptake and specificity of mAbs, coupled with increased therapeutic range of energetic β–-emitting radionuclides, offers a potential solution to overcome traditional problems associated with poor tissue penetration of antibody-drug conjugates, chemotherapeutic resistance, and off-target accumulation, which can lead to adverse responses. The challenge is to develop efficient and reliable chemical methods that provide simultaneous selectivity and high stabilization of the radiometal via complexation chemistry, with rapid access to new bioconjugate bonds on protein that avoid the loss of bioactivity. Here, we designed a new octadentate bispidine-chelating system, functionalized with a light-responsive tetrazole unit, and demonstrated the chemoselective derivatization of sulfhydryl groups introduced on the protein surface. High radiolabeling and bioconjugation yields of 161Tb-onartuzumab─an engineered mAb fragment targeting the human hepatocyte growth-factor receptor (c-MET; a characteristic biomarker found in clinical samples of several diseases, including gastric adenocarcinomas)─were obtained under ambient conditions after 5 min of light-induced coupling. Comprehensive biochemical and animal experiments including cellular binding assays, noninvasive γ-ray imaging, biodistribution studies, and pharmacokinetic measurements established the viability of using 161Tb-onartuzumab to target c-MET expression in vivo. Subsequent RIT studies in MKN-45 xenograft models demonstrated that the 161Tb-onartuzumab radiotracer formed by photoradiosynthesis permitted low-dose therapy studies that led to efficient targeting and treatment of tumor models. Collectively, the new complexation and chemoselective photoconjugation chemistries overcome some of the limitations in traditional labeling approaches. Photoradiosynthesis represents an excellent platform for building future antibody-based radiotracers for applications in diagnostic and therapeutic medicine.
doi.org
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
ERIKA HILTON
@erikahilton.bsky.social
· Apr 30
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Reposted by Marcos Palmeira
Oliver Wenger
@wengeroliver.bsky.social
· Feb 28
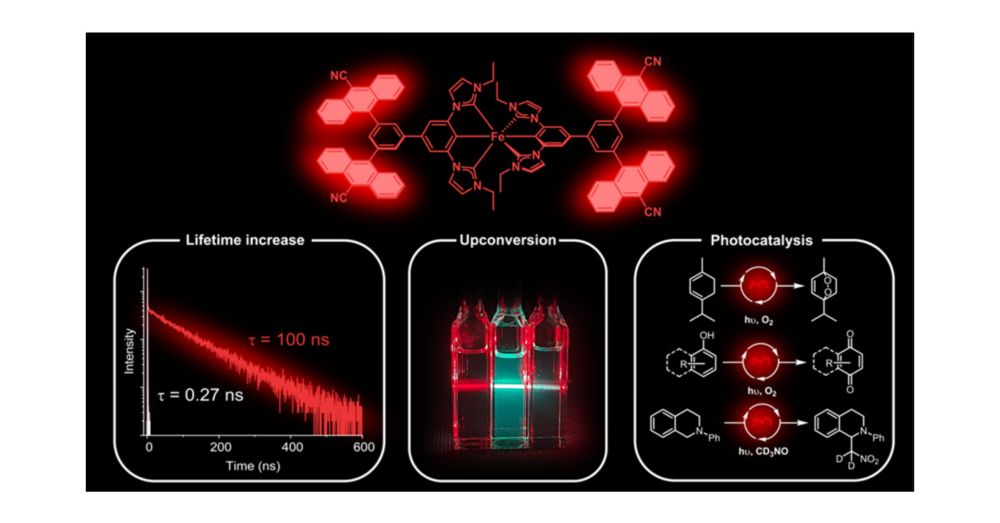
Iron(III) Complexes with Luminescence Lifetimes of up to 100 ns to Enhance Upconversion and Photocatalysis
Iron is the most abundant transition metal element and would be the ideal replacement for noble metals in many applications that rely on luminescent and long-lived electronically excited states. We sh...
pubs.acs.org