
https://www.assafzaritsky.com/
doi.org/10.1016/j.ce...
We propose a self-supervised anomaly representation that encodes morphological inter-feature dependencies for high-content image-based cell phenotyping!
1/3

doi.org/10.1016/j.ce...
We propose a self-supervised anomaly representation that encodes morphological inter-feature dependencies for high-content image-based cell phenotyping!
1/3
meetings.cshl.edu/meetings.asp...
Bringing together experiments, computation and theory to explore dynamic, multi-scale cellular organization and function!
1/3

meetings.cshl.edu/meetings.asp...
Bringing together experiments, computation and theory to explore dynamic, multi-scale cellular organization and function!
1/3

Apply to lead a lab at Janelia & advance biology using theory, computational modeling & machine learning.
🔹5-year renewable appointment
🔹Pioneer new tools & approaches
🔹Collaborate across disciplines
Apply by Nov. 4👉 https://janelia.link/groupleader

Apply to lead a lab at Janelia & advance biology using theory, computational modeling & machine learning.
🔹5-year renewable appointment
🔹Pioneer new tools & approaches
🔹Collaborate across disciplines
Apply by Nov. 4👉 https://janelia.link/groupleader
Apply here:
embl.wd103.myworkdayjobs.com/EMBL/job/Hei...
Please re-post 🙏
Apply here:
embl.wd103.myworkdayjobs.com/EMBL/job/Hei...
Please re-post 🙏
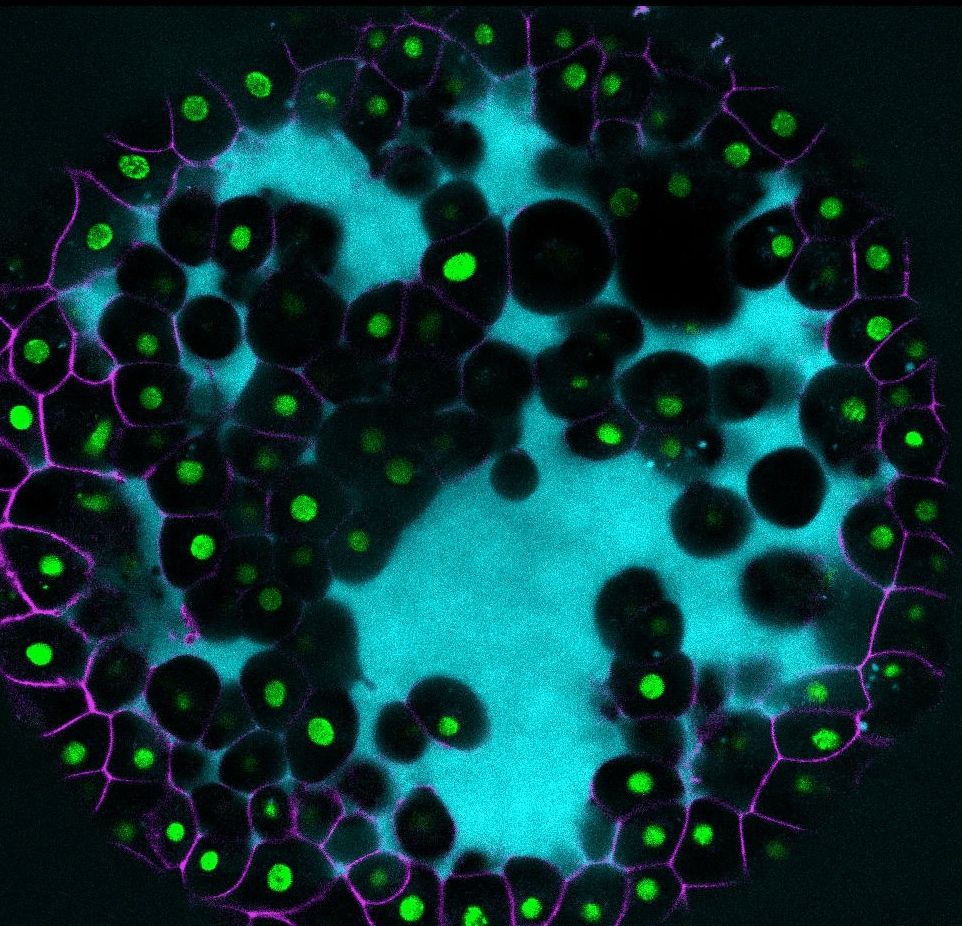
ADIs @cohenlaboratory.bsky.social, @assafzaritsky.bsky.social , and @mattersoflight.bsky.social are using ML and cell engineering to explore the #FrontierScience of stem cell differentiation.
alleninstitute.org/division/fro...
ADIs @cohenlaboratory.bsky.social, @assafzaritsky.bsky.social , and @mattersoflight.bsky.social are using ML and cell engineering to explore the #FrontierScience of stem cell differentiation.
alleninstitute.org/division/fro...
@royalmicrosoc.bsky.social @eurobioimaging.bsky.social @globias.bsky.social @bioimaginguk.bsky.social @globalbioimaging.bsky.social

@royalmicrosoc.bsky.social @eurobioimaging.bsky.social @globias.bsky.social @bioimaginguk.bsky.social @globalbioimaging.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
🧵
1/n

doi.org/10.1101/2025...
🧵
1/n
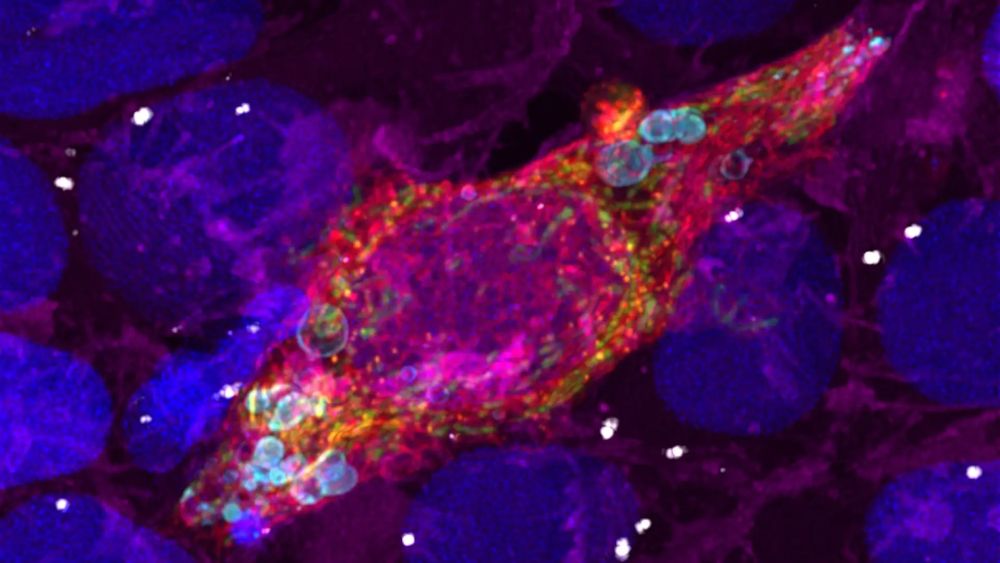
This timelapse illuminates the height of nuclei from 4μm (turquoise) to 11μm (fuchsia). 🔗👇
This timelapse illuminates the height of nuclei from 4μm (turquoise) to 11μm (fuchsia). 🔗👇
www.ascb.org/society-news...
Submit your application by May 22, 2025!

www.ascb.org/society-news...
Submit your application by May 22, 2025!
cytodata25.eu-openscreen.eu

cytodata25.eu-openscreen.eu
Find the slides here: zenodo.org/records/1441...

Find the slides here: zenodo.org/records/1441...
We proposed a new coupled variational auto-encoder architecture to solve the problem of data integration for small and unpaired datasets (diagonal integration)
arxiv.org/abs/2503.18856


We proposed a new coupled variational auto-encoder architecture to solve the problem of data integration for small and unpaired datasets (diagonal integration)
arxiv.org/abs/2503.18856

