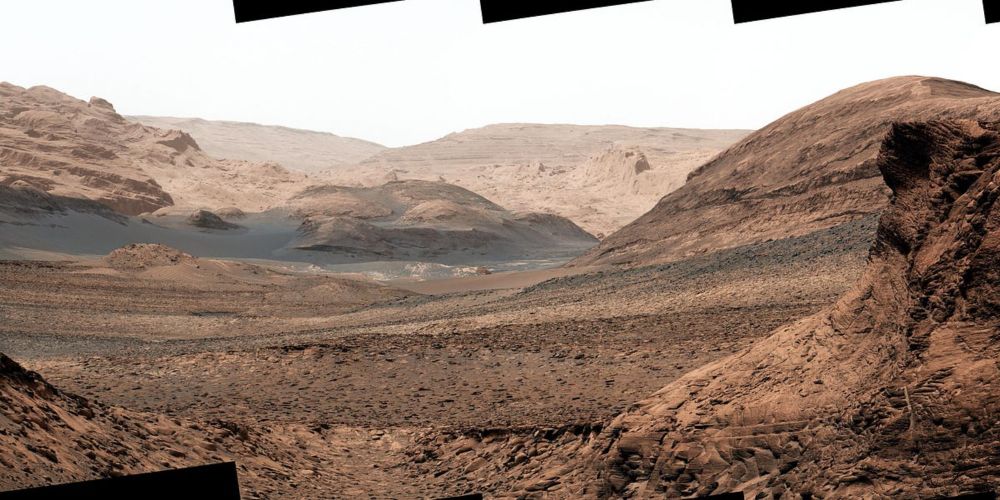
marsterraforming.substack.com/p/a-million-...

marsterraforming.substack.com/p/a-million-...
marsterraforming.substack.com/p/a-million-...

marsterraforming.substack.com/p/a-million-...
Madison Turner et al., "Early thinning, late persistence, diachronous boundaries, and a regional dichotomy in Mars' young sedimentary rocks", Communications Earth and Environment: (open access link) www.nature.com/articles/s43...
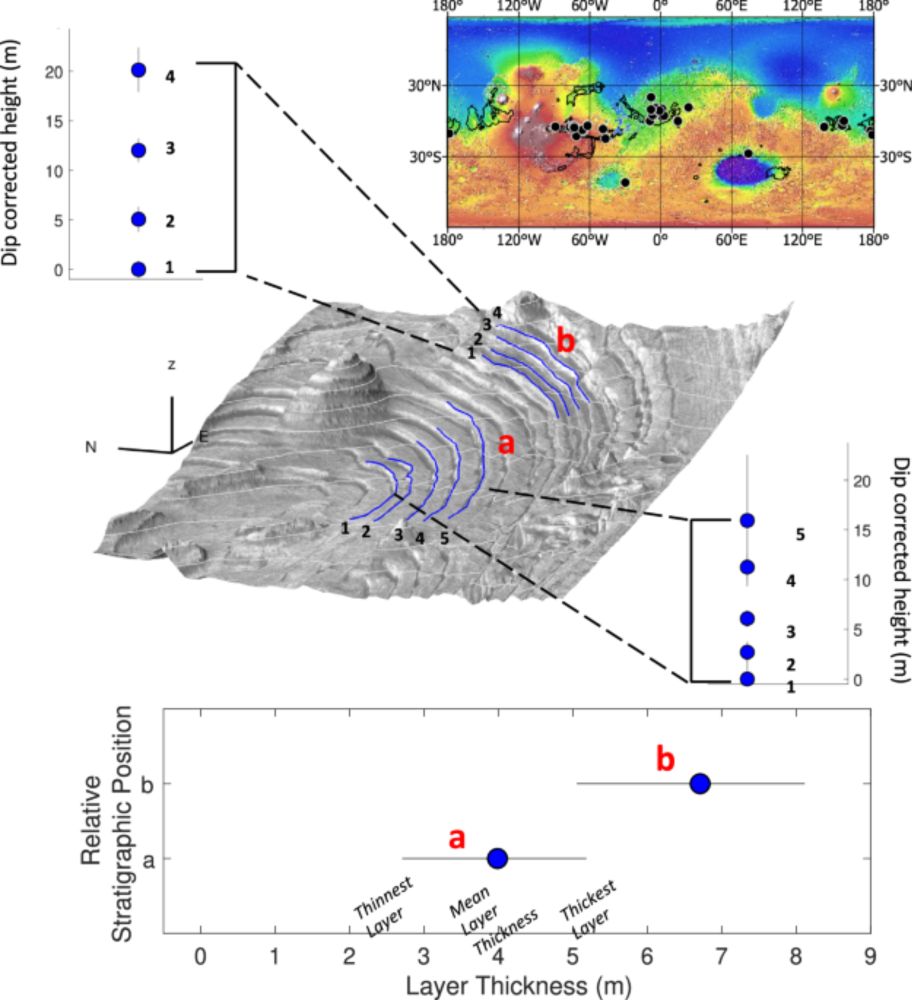
Madison Turner et al., "Early thinning, late persistence, diachronous boundaries, and a regional dichotomy in Mars' young sedimentary rocks", Communications Earth and Environment: (open access link) www.nature.com/articles/s43...
Madison Turner et al., "Early thinning, late persistence, diachronous boundaries, and a regional dichotomy in Mars' young sedimentary rocks", Communications Earth and Environment: (open access link) www.nature.com/articles/s43...

Madison Turner et al., "Early thinning, late persistence, diachronous boundaries, and a regional dichotomy in Mars' young sedimentary rocks", Communications Earth and Environment: (open access link) www.nature.com/articles/s43...
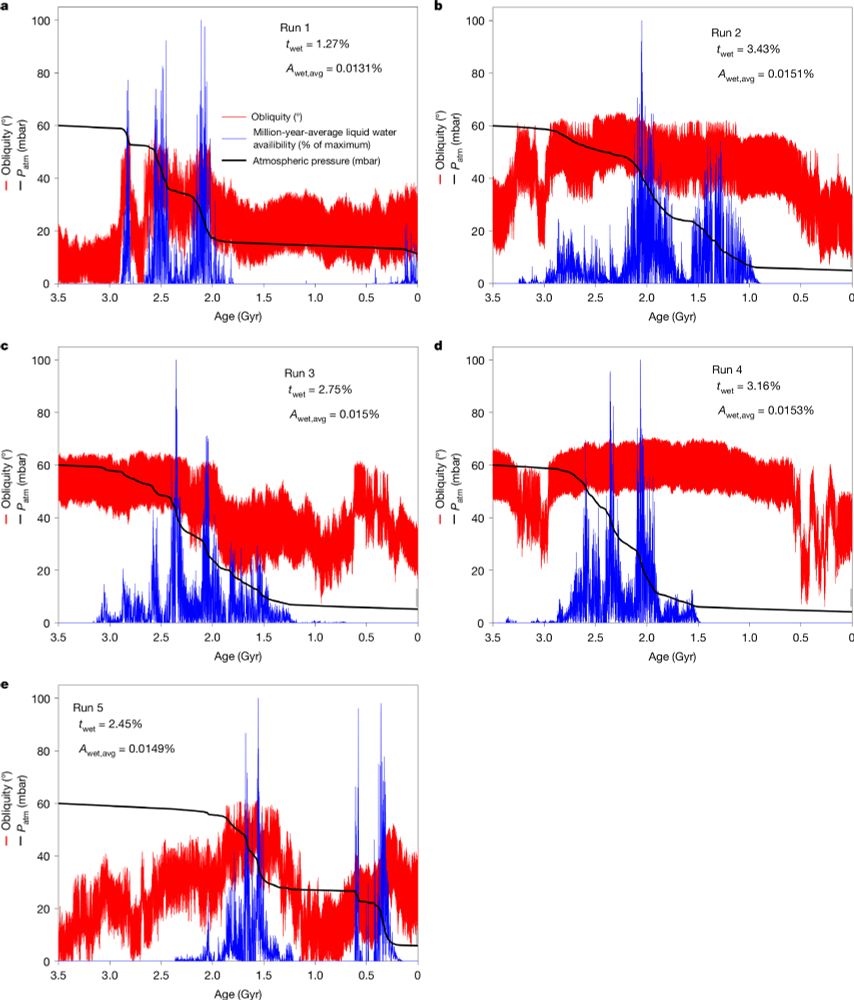
arxiv.org/abs/2510.07344

arxiv.org/abs/2510.07344
— @rdword.bsky.social
#spacetravel #spaceexploration #rovers

— @rdword.bsky.social
#spacetravel #spaceexploration #rovers
arxiv.org/abs/2510.07344

arxiv.org/abs/2510.07344
news.uchicago.edu/big-brains-p... 🧪🔭 #Mars

news.uchicago.edu/big-brains-p... 🧪🔭 #Mars
Brandon Park Coy et al., "The Role of Tectonic Luck in Long-Term Habitability of Abiotic Earth-like Planets" (accepted by PSJ):
arxiv.org/abs/2507.23124

Brandon Park Coy et al., "The Role of Tectonic Luck in Long-Term Habitability of Abiotic Earth-like Planets" (accepted by PSJ):
arxiv.org/abs/2507.23124
To submit an abstract, please visit
agu.confex.com/agu/agu25/pr...

To submit an abstract, please visit
agu.confex.com/agu/agu25/pr...
To submit an abstract, please visit
agu.confex.com/agu/agu25/pr...

To submit an abstract, please visit
agu.confex.com/agu/agu25/pr...
www.erikadebenedictis.com/s/The-case-f...

www.erikadebenedictis.com/s/The-case-f...
Mars could be green in MY lifetime. 🚀 🌼
What’s stopping us? We need a lot more real research into how to do it right. Don’t nuke Mars!
👇
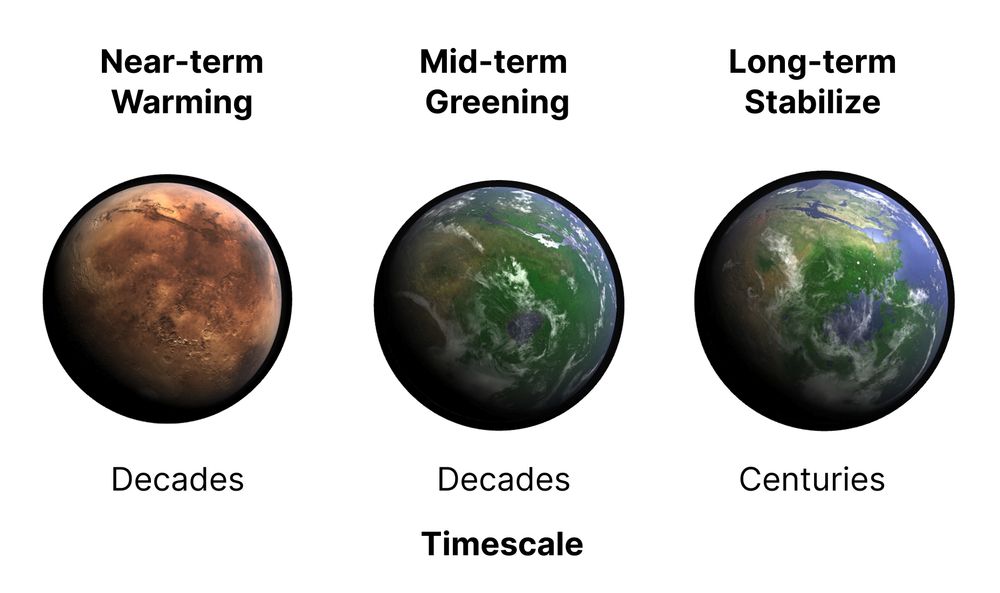
Mars could be green in MY lifetime. 🚀 🌼
What’s stopping us? We need a lot more real research into how to do it right. Don’t nuke Mars!
👇
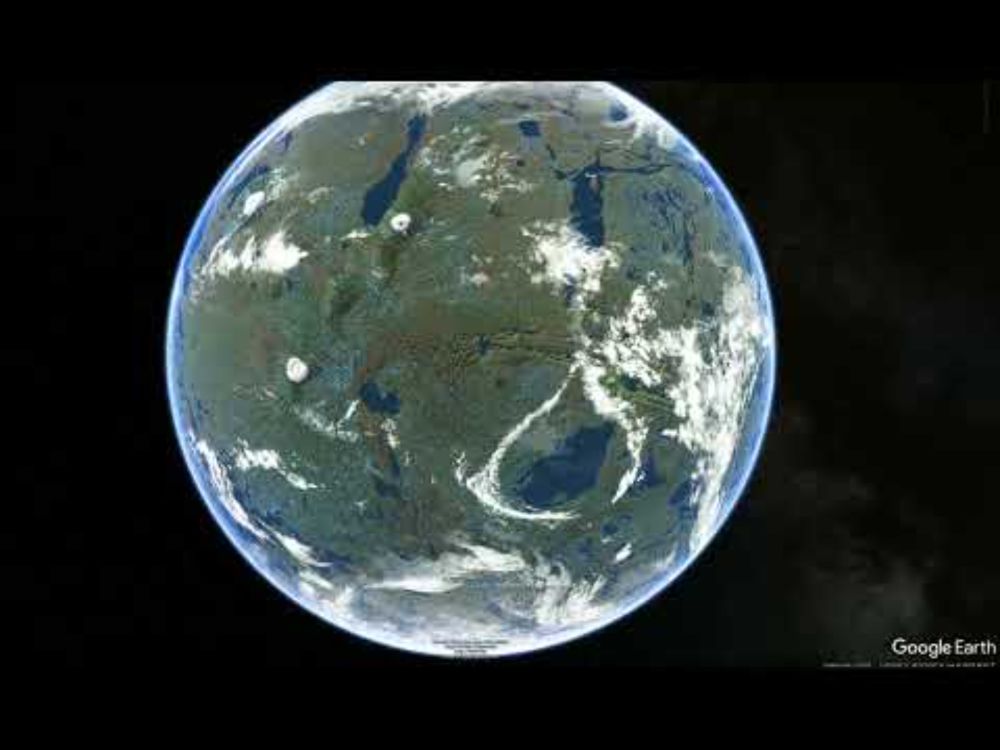








asteriskmag.com/issues/09/gr...

asteriskmag.com/issues/09/gr...
Will anything grow in this media? Stay tuned!
💧+ 🪨 → 🌱 ?
open.substack.com/pub/pioneerl...
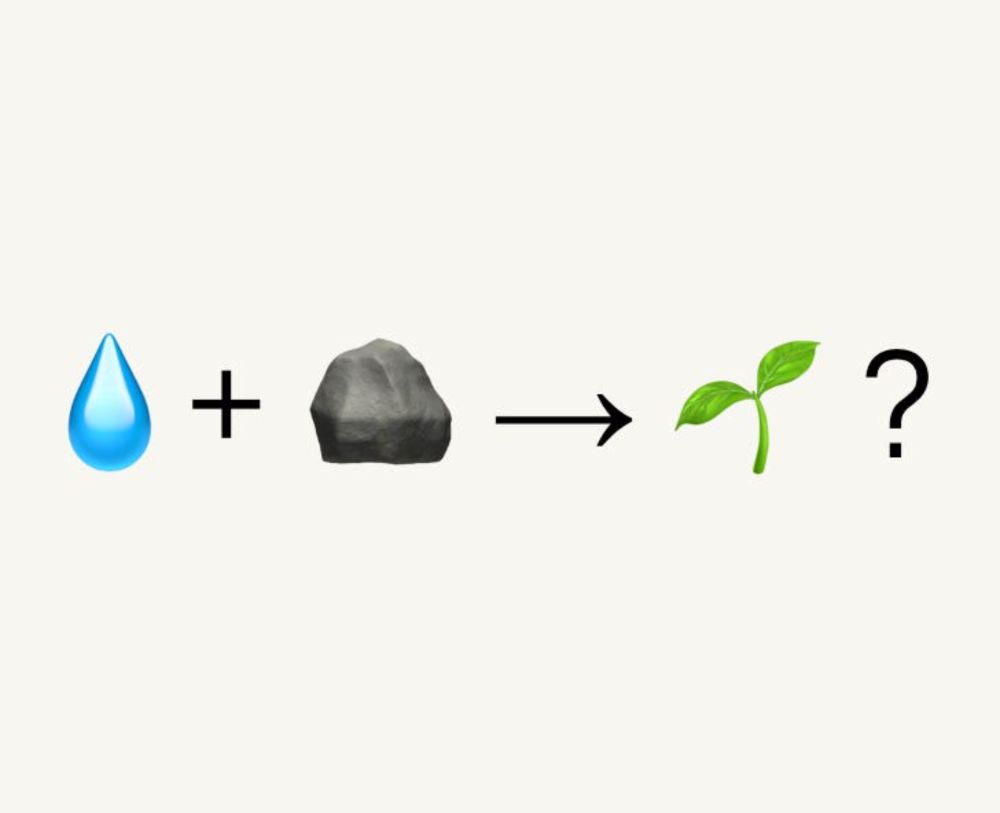

Will anything grow in this media? Stay tuned!
💧+ 🪨 → 🌱 ?
open.substack.com/pub/pioneerl...



