
https://joshuacfowler.github.io/
🔗 buff.ly/b7IL4MJ
@joshuacfowler.bsky.social @jmoutouama.bsky.social

🔗 buff.ly/b7IL4MJ
@joshuacfowler.bsky.social @jmoutouama.bsky.social

@meafkhami.bsky.social
@kerricrawford.bsky.social
@aclassen.bsky.social
@johnstinchcombe.bsky.social
@damianmicroeco.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1111/nph....

@meafkhami.bsky.social
@kerricrawford.bsky.social
@aclassen.bsky.social
@johnstinchcombe.bsky.social
@damianmicroeco.bsky.social
doi.org/10.1111/nph....
We use a model legume to assess how plant host genotype and microbes non-additively interact to shape plant growth and disease ecology.
Check it out here: doi.org/10.1111/pce....
We use a model legume to assess how plant host genotype and microbes non-additively interact to shape plant growth and disease ecology.
Check it out here: doi.org/10.1111/pce....
Climate change may push dioecious plants toward female-biased sex ratios which will impair seed production. Ignoring this feedback underestimates range shifts. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

Climate change may push dioecious plants toward female-biased sex ratios which will impair seed production. Ignoring this feedback underestimates range shifts. www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...

doi.org/10.1111/oik....
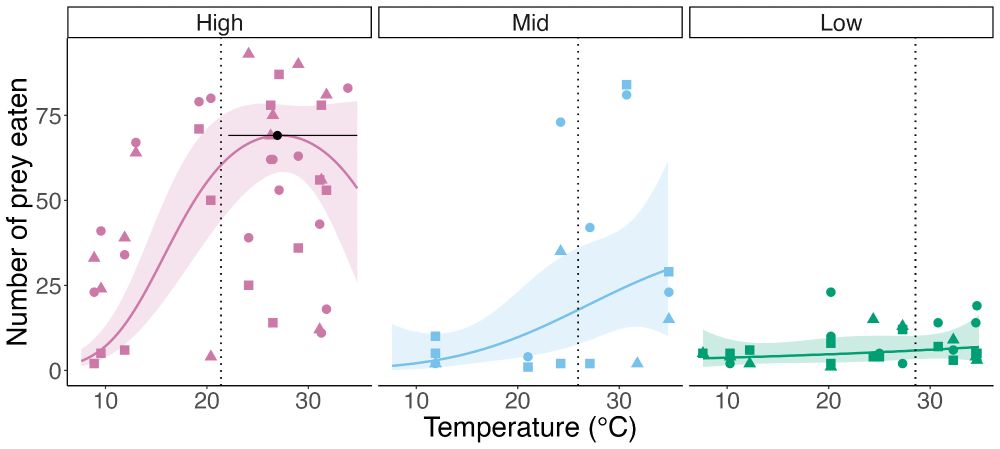
doi.org/10.1111/oik....
We tested microbiome network theory empirically in nature and found central early colonisers significantly (1) enhanced biodiversity, (2) reshaped assembly trajectories and (3) increased recruitment of non-peripheral microbes.
doi.org/10.1111/ele....

We tested microbiome network theory empirically in nature and found central early colonisers significantly (1) enhanced biodiversity, (2) reshaped assembly trajectories and (3) increased recruitment of non-peripheral microbes.
doi.org/10.1111/ele....

