
📖 nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
by Franklin et al.
@mjonikas.bsky.social @ericfranklin.bsky.social @WileyPlantSci

📖 nph.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/...
by Franklin et al.
@mjonikas.bsky.social @ericfranklin.bsky.social @WileyPlantSci
🌿 Un estudio del #CSIC muestra cómo la activación de una proteína interviene en el crecimiento celular de organismos fotosintéticos
➡️http://tiny.cc/164i001
🌿 Un estudio del #CSIC muestra cómo la activación de una proteína interviene en el crecimiento celular de organismos fotosintéticos
➡️http://tiny.cc/164i001
@ibvf-sevilla.bsky.social #PlantScience ⬇️
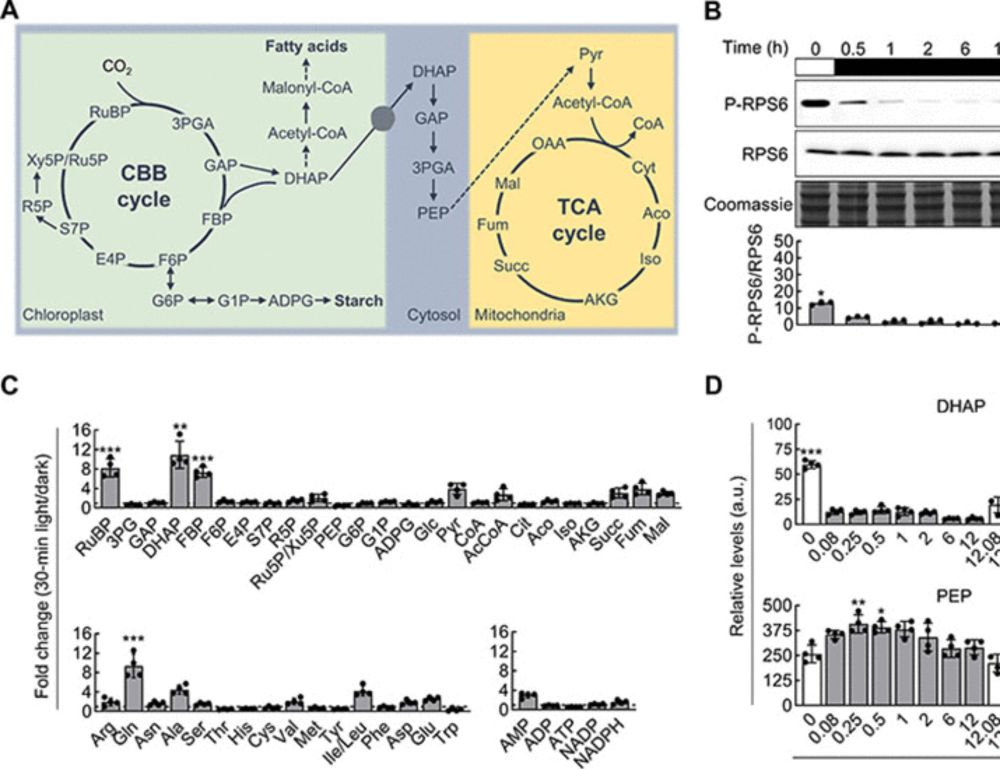
![Fig 3E. Proposed model for the regulation of target of rapamycin (TOR) activity by dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) in the model green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii.
Photosynthesis provides reducing power [NADPH (reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate)] and energy [ATP (adenosine 5′-triphosphate)] for CO2 fixation and the biosynthesis of organic carbon compounds. DHAP is synthesized in the chloroplast and exported to the cytoplasm through the TPT3 transporter. The abundance of cytoplasmic DHAP is transmitted to TOR to modulate its activity.](https://cdn.bsky.app/img/feed_thumbnail/plain/did:plc:tfidqyziwn7mqcunvhghjcno/bafkreidgr5dwszoxph6imyae7jpolneks7yh3vdhnyzeur2acgqz5dhrhi@jpeg)


@ibvf-sevilla.bsky.social #PlantScience ⬇️



