Here, we reveal the unique, molecular mechanism by which USP1/UAF1 cleaves ubiquitin chains on PCNA, which may direct DNA damage tolerance.
doi.org/10.1038/s414...
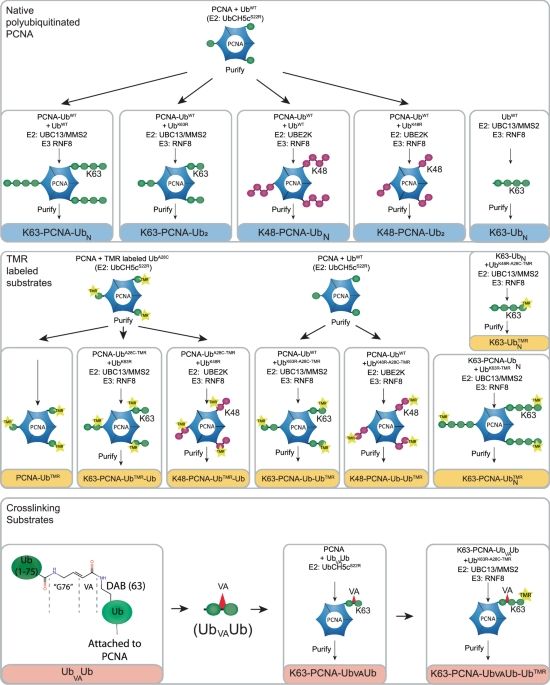
Here, we reveal the unique, molecular mechanism by which USP1/UAF1 cleaves ubiquitin chains on PCNA, which may direct DNA damage tolerance.
doi.org/10.1038/s414...
USP1/UAF1's exo-cleavage mechanism, and its preference for polyubiquitinated PCNA, may drive DNA damage tolerance pathway choice by enriching for monoubiquitinated PCNA.
Read our preprint for our full analysis:
doi.org/10.1101/2024...
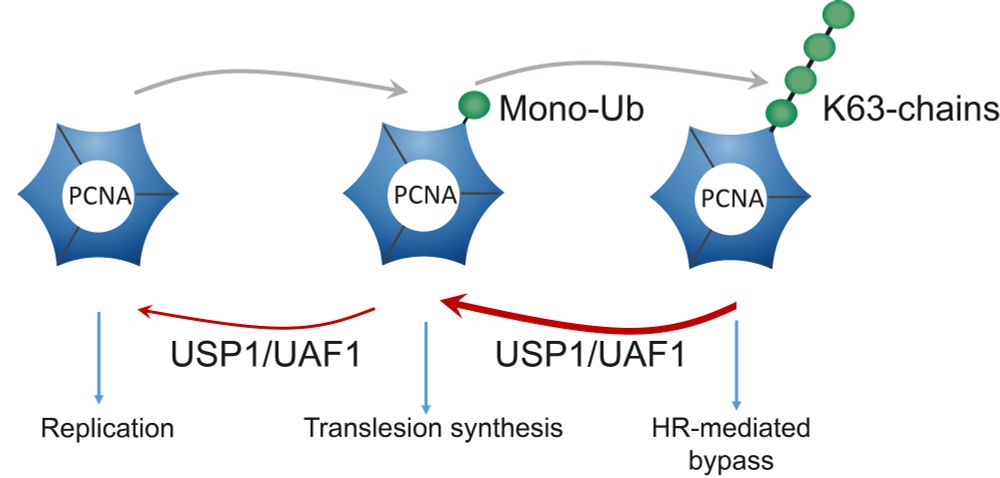
USP1/UAF1's exo-cleavage mechanism, and its preference for polyubiquitinated PCNA, may drive DNA damage tolerance pathway choice by enriching for monoubiquitinated PCNA.
Read our preprint for our full analysis:
doi.org/10.1101/2024...
Here we reveal USP1/UAF1 as a highly efficient DUB for K63- and K48 polyubiquitinated PCNA and give detailed insights into its mechanism that may drive pathway choice in DNA damage tolerance.
Preprint is available now:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Here we reveal USP1/UAF1 as a highly efficient DUB for K63- and K48 polyubiquitinated PCNA and give detailed insights into its mechanism that may drive pathway choice in DNA damage tolerance.
Preprint is available now:
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

