
Thanks to wonderful coauthors/collaborators/friends, the whole @doudna-lab.bsky.social and everyone at @innovativegenomics.bsky.social

A new study from the Alex Gao lab. The scope of this work is incredible!!!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

A new study from the Alex Gao lab. The scope of this work is incredible!!!
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
In this preprint, Lucas Paoli et al, ask what shapes antiphage systems expression in native contexts.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

In this preprint, Lucas Paoli et al, ask what shapes antiphage systems expression in native contexts.
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
@cp-cellhostmicrobe.bsky.social
this morning from Chrishan Fernando & Nicole D. Marino! www.cell.com/cell-host-mi...

@cp-cellhostmicrobe.bsky.social
this morning from Chrishan Fernando & Nicole D. Marino! www.cell.com/cell-host-mi...
🧵1/4 Excited to share our work on AI-guided design of minimal RNA-guided nucleases. Amazing work by @petrskopintsev.bsky.social @isabelesain.bsky.social @evandeturk.bsky.social et al!
Multi-lab collaboration @banfieldlab.bsky.social @jhdcate.bsky.social @jacobsenucla.bsky.social🧬
🔗👇
🧵1/4 Excited to share our work on AI-guided design of minimal RNA-guided nucleases. Amazing work by @petrskopintsev.bsky.social @isabelesain.bsky.social @evandeturk.bsky.social et al!
Multi-lab collaboration @banfieldlab.bsky.social @jhdcate.bsky.social @jacobsenucla.bsky.social🧬
🔗👇
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.6...
Our HIDEN-SEQ links the "dark matter" genes of your favorite phage to any selectable phenotype, guiding the path from fun observations to molecular mechanisms.
A thread 1/8

Our HIDEN-SEQ links the "dark matter" genes of your favorite phage to any selectable phenotype, guiding the path from fun observations to molecular mechanisms.
A thread 1/8
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Thanks to wonderful coauthors/collaborators/friends, the whole @doudna-lab.bsky.social and everyone at @innovativegenomics.bsky.social

Thanks to wonderful coauthors/collaborators/friends, the whole @doudna-lab.bsky.social and everyone at @innovativegenomics.bsky.social

Thanks to wonderful coauthors/collaborators/friends, the whole @doudna-lab.bsky.social and everyone at @innovativegenomics.bsky.social
nature.com/articles/s41...
PhD graduate and now post-doc Sofia Dahlman, along with co-senior author Sam Forster from The Hudson and other researchers from our lab and others.

nature.com/articles/s41...
PhD graduate and now post-doc Sofia Dahlman, along with co-senior author Sam Forster from The Hudson and other researchers from our lab and others.
Plasmid genomes were resolved using #PacBio HiFi sequencing with hifiasm-meta for #metagenome assembly. Host association was detected using epigenetic signals.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

Plasmid genomes were resolved using #PacBio HiFi sequencing with hifiasm-meta for #metagenome assembly. Host association was detected using epigenetic signals.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...
Check out @erinedoherty.bsky.social and my work from @doudna-lab.bsky.social lab here:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Check out @erinedoherty.bsky.social and my work from @doudna-lab.bsky.social lab here:
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...


Here we reveal an exceptional diversity of viral 2H phosphodiesterases (PDEs) that enable immune evasion by selectively degrading oligonucleotide-based messengers. This 2H PDE fold has evolved striking substrate breath & specificity.

Here we reveal an exceptional diversity of viral 2H phosphodiesterases (PDEs) that enable immune evasion by selectively degrading oligonucleotide-based messengers. This 2H PDE fold has evolved striking substrate breath & specificity.
More information: www.oeaw.ac.at/aithyra/rese... #AITHYRA #StartingPI

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Was fun to write this piece with Dina Hochhauser!
Here is a thread to explain the premises
1/
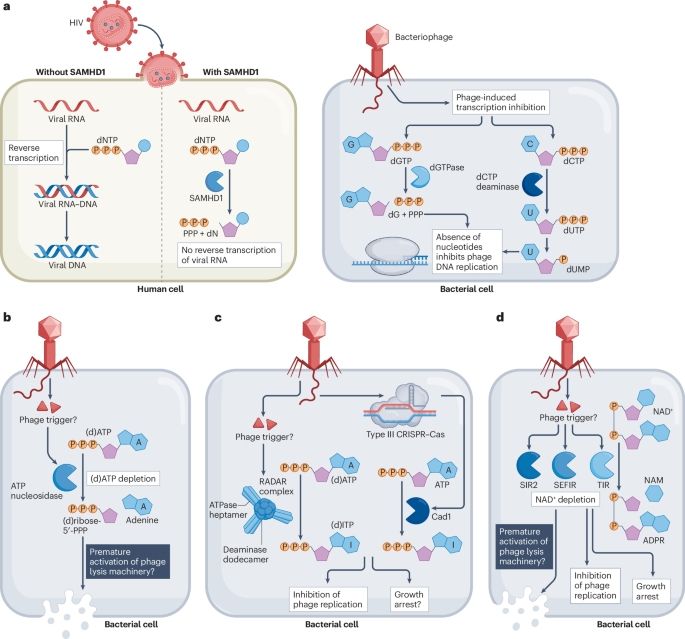
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
Was fun to write this piece with Dina Hochhauser!
Here is a thread to explain the premises
1/
We noticed a pair of genes - a nuclease and a protease - shuffles between antiviral systems. We show how proteolysis activates the nuclease, triggering defense in known and unknown immune contexts.
tinyurl.com/2uwwy4ty

We noticed a pair of genes - a nuclease and a protease - shuffles between antiviral systems. We show how proteolysis activates the nuclease, triggering defense in known and unknown immune contexts.
tinyurl.com/2uwwy4ty

We noticed a pair of genes - a nuclease and a protease - shuffles between antiviral systems. We show how proteolysis activates the nuclease, triggering defense in known and unknown immune contexts.
tinyurl.com/2uwwy4ty
Muntathar Al-Shimary, @doudna-lab.bsky.social , @cresslab.bsky.social and I present a gene knockdown tool that works in diverse bacteriophages: CRISPRi through antisense RNA Targeting (CRISPRi-ART)!
Check it out @naturemicrobiol.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
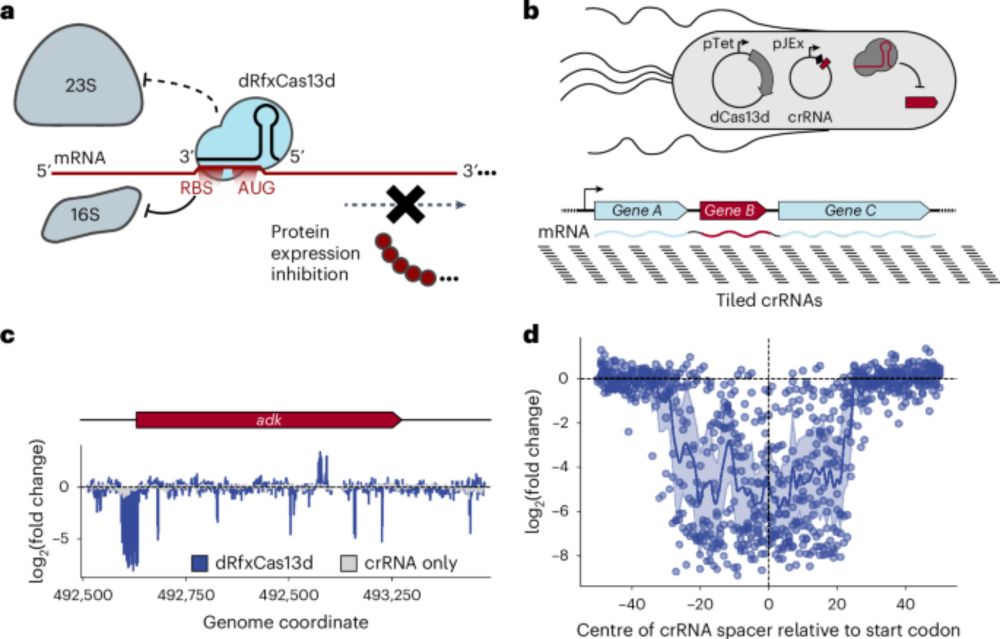
Muntathar Al-Shimary, @doudna-lab.bsky.social , @cresslab.bsky.social and I present a gene knockdown tool that works in diverse bacteriophages: CRISPRi through antisense RNA Targeting (CRISPRi-ART)!
Check it out @naturemicrobiol.bsky.social
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
CARDs are essential for caspase recruitment during human inflammasome activation. We now find them in bacterial immune systems
Congrats Tana Wein! Thank you Kranzusch lab!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
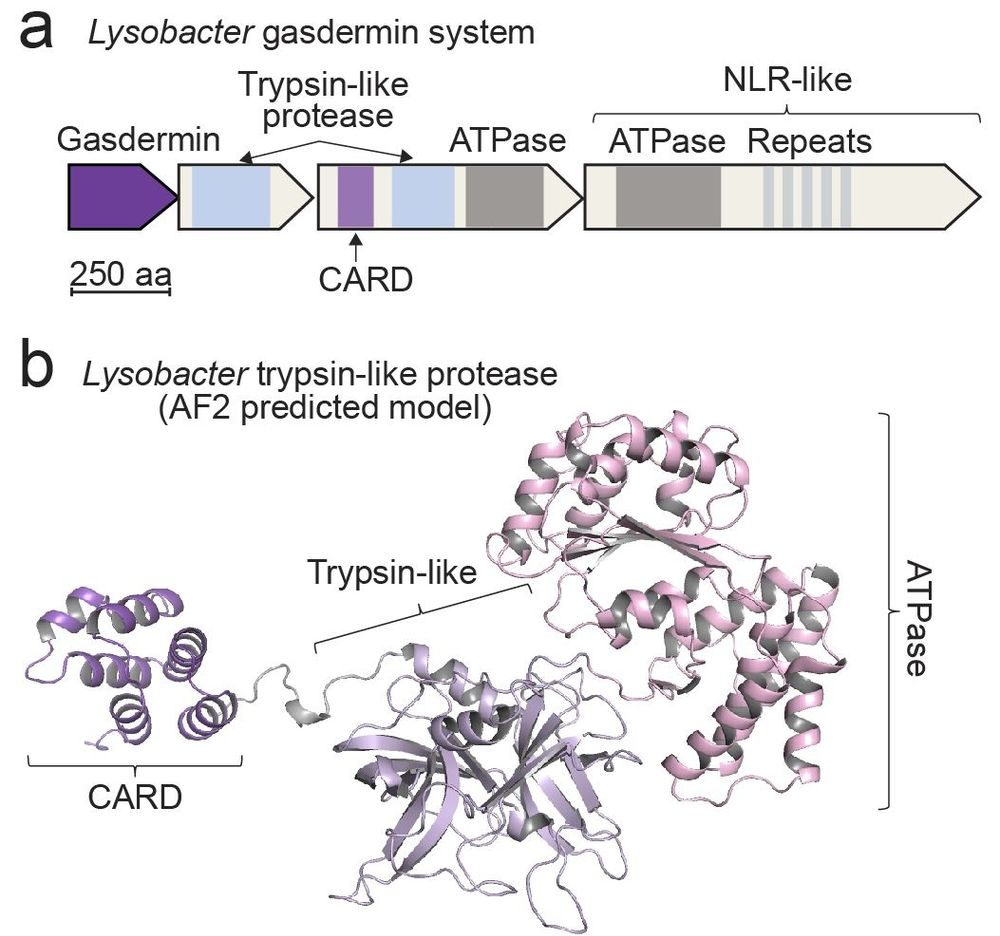
CARDs are essential for caspase recruitment during human inflammasome activation. We now find them in bacterial immune systems
Congrats Tana Wein! Thank you Kranzusch lab!
www.nature.com/articles/s41...


