
Using deep learning & scATAC-seq, we studied context-specific variants in disease & evolution, and introduce FLARE for de novo mutations—w/ application to autism-affected families.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

The E2G Portal! e2g.stanford.edu
This collates our predictions of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions across >1,600 cell types and tissues.
Uses cases 👇
1/
The E2G Portal! e2g.stanford.edu
This collates our predictions of enhancer-gene regulatory interactions across >1,600 cell types and tissues.
Uses cases 👇
1/

www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....

www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
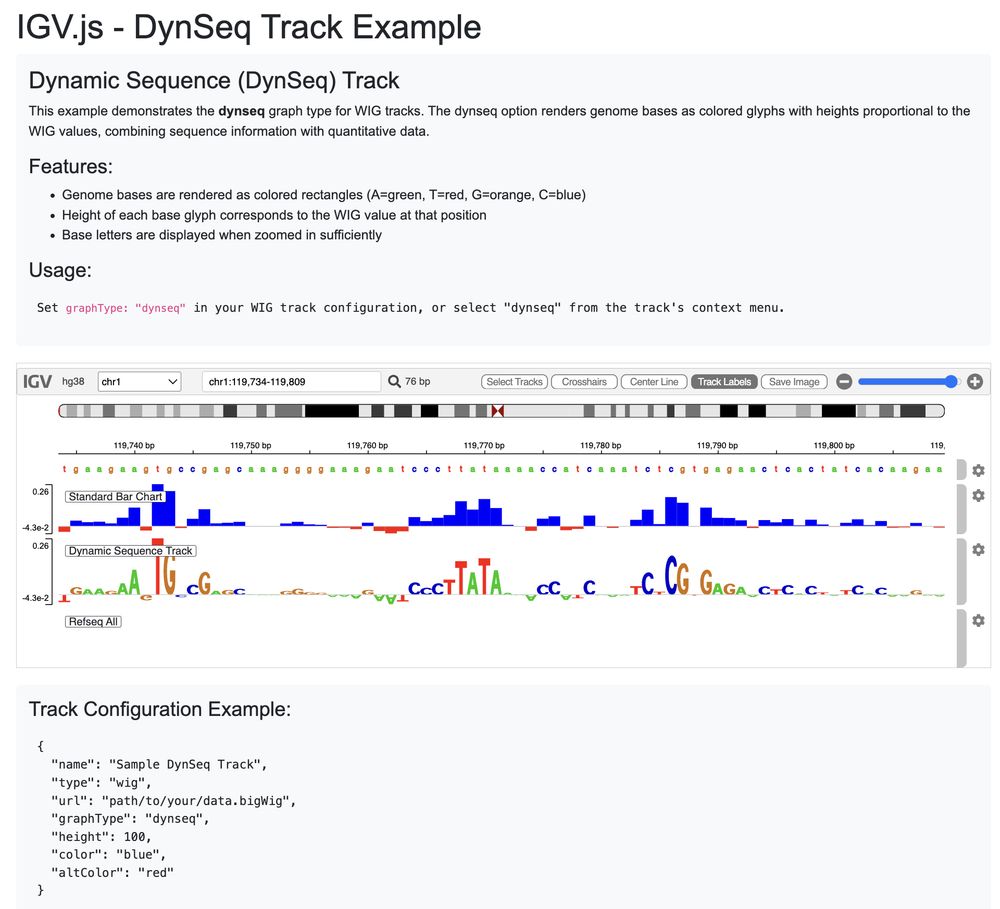
Corgi imitates cellular gene regulation and integrates DNA sequence and trans-regulator information.
This allows Corgi to make accurate predictions in unseen cell types. Also, it can simulate trans-regulator perturbations in silico.

Corgi imitates cellular gene regulation and integrates DNA sequence and trans-regulator information.
This allows Corgi to make accurate predictions in unseen cell types. Also, it can simulate trans-regulator perturbations in silico.

Congrats to DR. Kelly Cochran & DR. @soumyakundu.bsky.social on this momentous achievement.
Brilliant scientists with brilliant futures ahead. 🎉🎉🎉

Congrats to DR. Kelly Cochran & DR. @soumyakundu.bsky.social on this momentous achievement.
Brilliant scientists with brilliant futures ahead. 🎉🎉🎉

Preprint: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
GitHub: github.com/jmschrei/led...

Preprint: www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
GitHub: github.com/jmschrei/led...
#CardioSky
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...

#CardioSky
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
TL;DR: BCRs ARE ALL YOU NEED!
(Well actually .... keep reading) 1/

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
TL;DR: BCRs ARE ALL YOU NEED!
(Well actually .... keep reading) 1/
Using deep learning & scATAC-seq, we studied context-specific variants in disease & evolution, and introduce FLARE for de novo mutations—w/ application to autism-affected families.
doi.org/10.1101/2025...

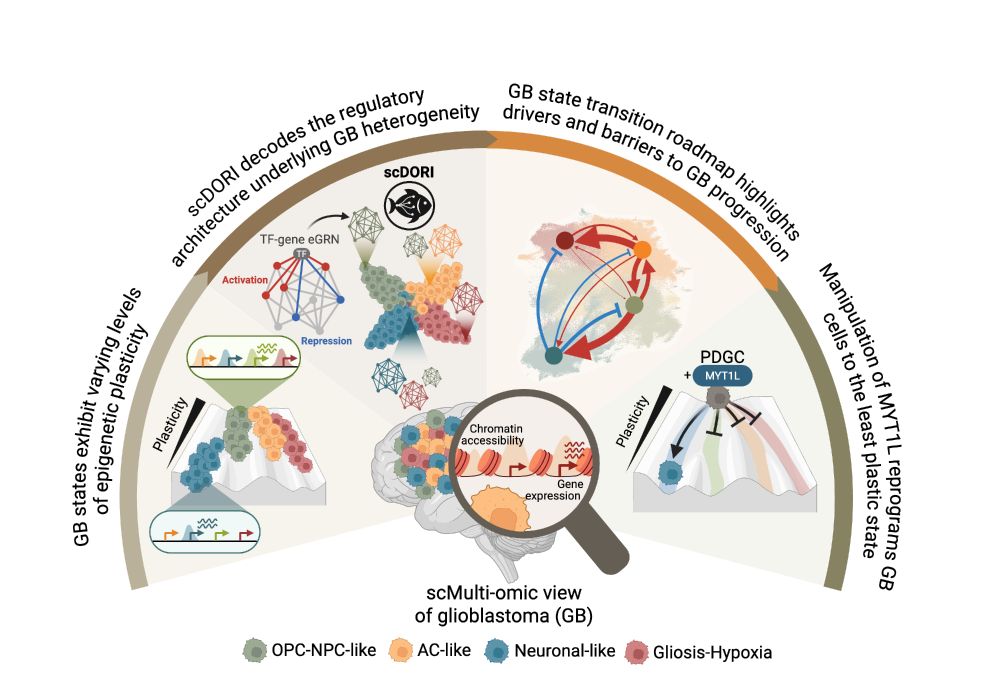
I'm very excited to present our new work combining associations and Perturb-seq to build interpretable causal graphs! A 🧵
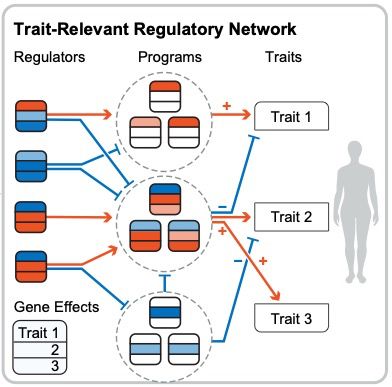
I'm very excited to present our new work combining associations and Perturb-seq to build interpretable causal graphs! A 🧵
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Huge congrats to Anusri! This was quite a slog (for both of us) but we r very proud of this one! It is a long read but worth it IMHO. Methods r in the supp. materials. Bluetorial coming soon below 1/
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
Huge congrats to Anusri! This was quite a slog (for both of us) but we r very proud of this one! It is a long read but worth it IMHO. Methods r in the supp. materials. Bluetorial coming soon below 1/
Paper: doi.org/10.1101/2024.12.20.629764
Code: github.com/saezlab/greta
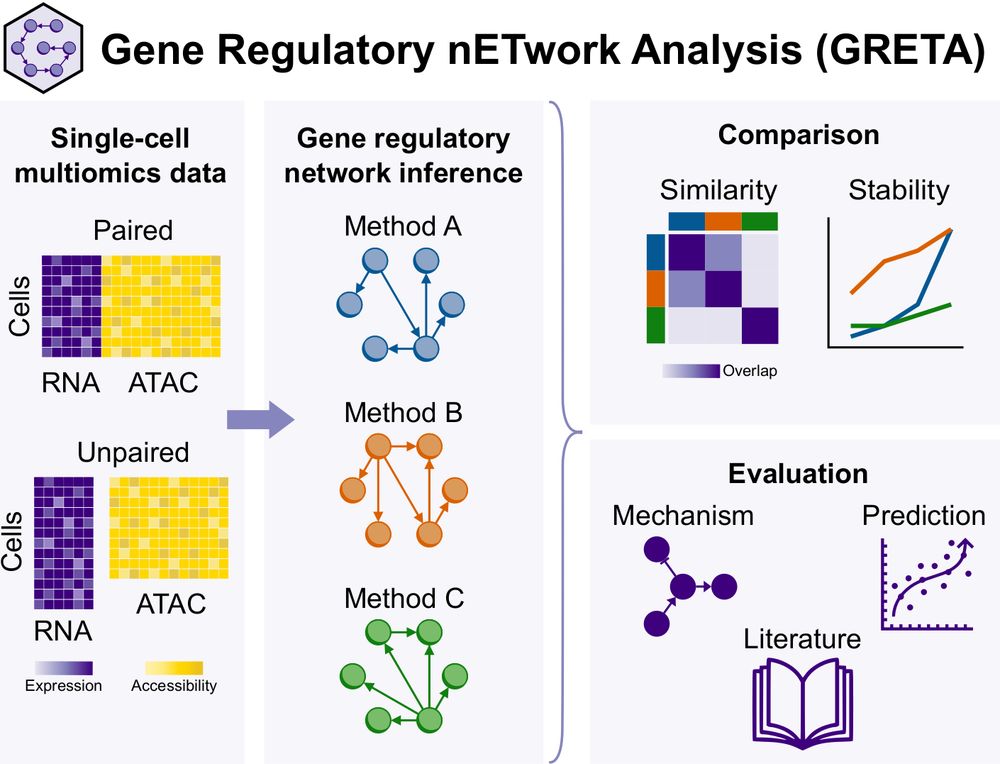
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
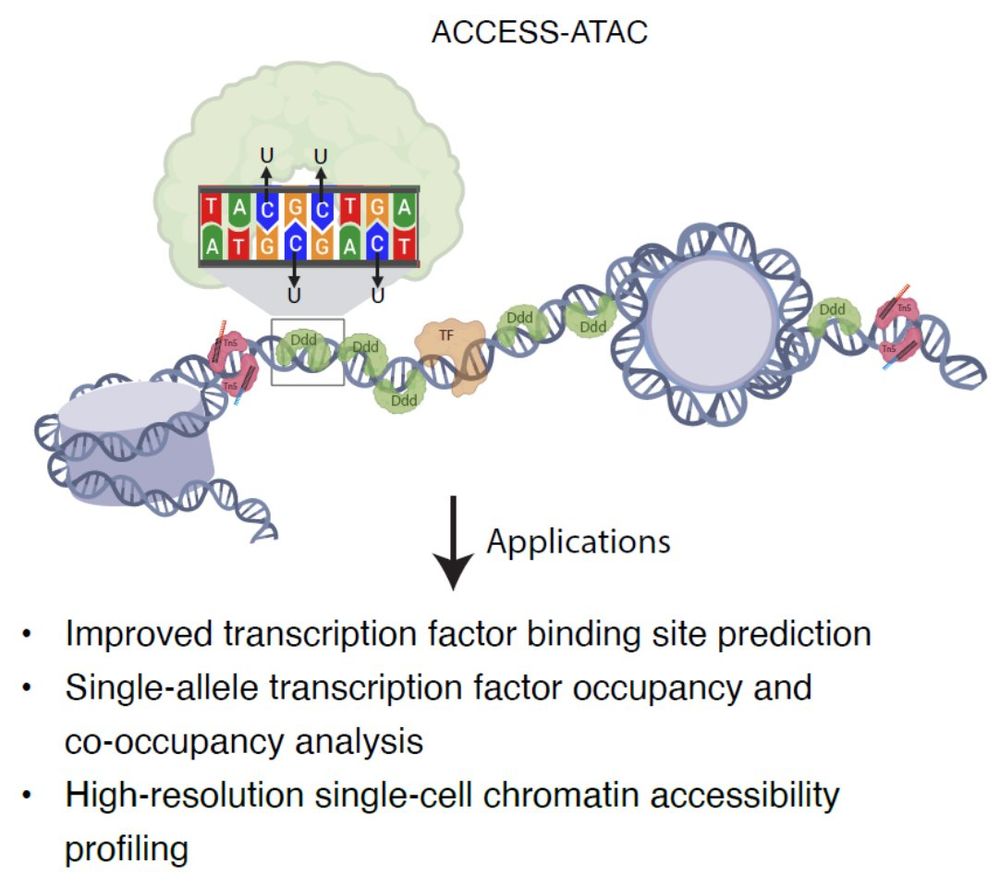
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...


Some new answers in our latest preprint, where we explored:
1). Key cell types contributing to CHD genetics
2). Impact of noncoding variants on CHD risk
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.11.20.24317557v1
Some new answers in our latest preprint, where we explored:
1). Key cell types contributing to CHD genetics
2). Impact of noncoding variants on CHD risk
https://www.medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.11.20.24317557v1
Amazing work led by co-first authors @mayayayas.bsky.social and @613weilin.bsky.social in a great collaboration with @jengreitz.bsky.social's lab
See 🧵 by Wei-Lin ⬇️
Amazing work led by co-first authors @mayayayas.bsky.social and @613weilin.bsky.social in a great collaboration with @jengreitz.bsky.social's lab
See 🧵 by Wei-Lin ⬇️
arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158

arxiv.org/abs/2411.11158

