Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Yasin El Abiead
@yelabiead.bsky.social
· Aug 23

A Perspective on Unintentional Fragments and their Impact on the Dark Metabolome, Untargeted Profiling, Molecular Networking, Public Data, and Repository Scale Analysis.
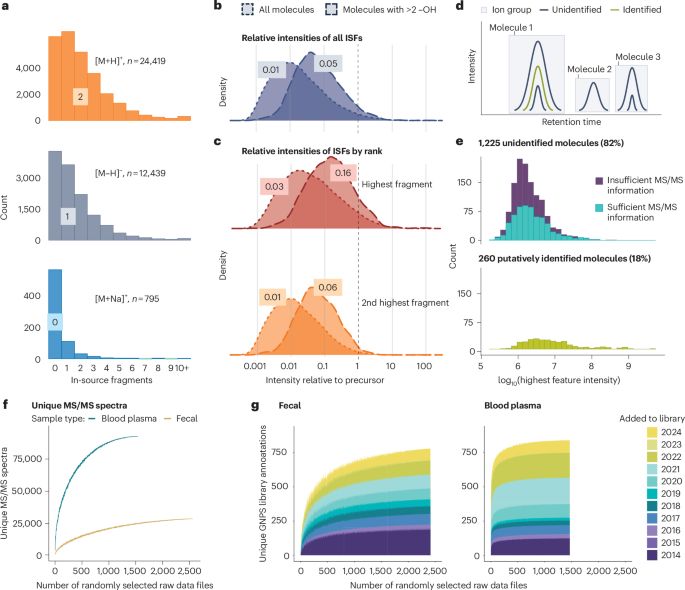
In/post-source fragments (ISFs) arise during electrospray ionization or ion transfer in mass spectrometry when molecular bonds break, generating ions that can complicate data interpretation. Although ISFs have been recognized for decades, their contribution to untargeted metabolomics - particularly in the context of the so-called “dark matter” (unannotated MS or MS/MS spectra) and the “dark metabolome” (unannotated molecules) - remains unsettled. This ongoing debate reflects a central tension: while some caution against overinterpreting unidentified signals lacking biological evidence, others argue that dismissing them too quickly risks overlooking genuine molecular discoveries. These discussions also raise a deeper question: what exactly should be considered part of the metabolome? As metabolomics advances toward large-scale data mining and high-throughput computational analysis, resolving these conceptual and methodological ambiguities has become essential. In this perspective, we propose a refined definition of the “dark metabolome” and present a systematic overview of ISFs and related ion forms, including adducts and multimers. We examine their impact on metabolite annotation, experimental design, statistical analysis, computational workflows, and repository-scale data mining. Finally, we provide practical recommendations - including a set of dos and don’ts for researchers and reviewers - and discuss the broader implications of ISFs for how the field explores unknown molecular space. By embracing a more nuanced understanding of ISFs, metabolomics can achieve greater rigor, reduce misinterpretation, and unlock new opportunities for discovery.
doi.org
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Adriano Rutz
@adafede.bsky.social
· Jul 18
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Steffen Neumann
@sneumann.bsky.social
· Jul 16
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Reposted by Adriano Rutz
Mingxun Wang
@mingxunwang.bsky.social
· Mar 5
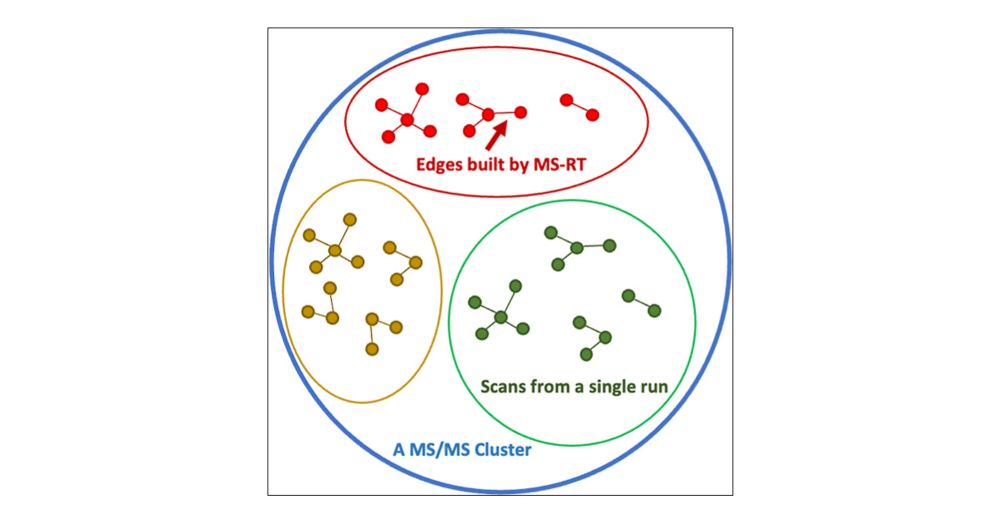
MS-RT: A Method for Evaluating MS/MS Clustering Performance for Metabolomics Data
The clustering of tandem mass spectra (MS/MS) is a crucial computational step to deduplicate repeated acquisitions in data-dependent experiments. This technique is essential in untargeted metabolomics, particularly with high-throughput mass spectrometers capable of generating hundreds of MS/MS spectra per second. Despite advancements in MS/MS clustering algorithms in proteomics, their performance in metabolomics has not been extensively evaluated due to the lack of database search tools with false discovery rate control for molecule identification. To bridge this gap, this study introduces the MS1-retention time (MS-RT) method to assess MS/MS clustering performance in metabolomics data sets. Here, we validate MS-RT by comparing MS-RT to established proteomics clustering evaluation approaches that utilize database search identifications. Additionally, we evaluate the performance of several MS/MS clustering tools on metabolomics data sets, highlighting their advantages and drawbacks. This MS-RT method and the MS/MS clustering tool benchmarking will provide valuable real world practical recommendations for tools and set the stage for future advancements in metabolomics MS/MS clustering.
doi.org