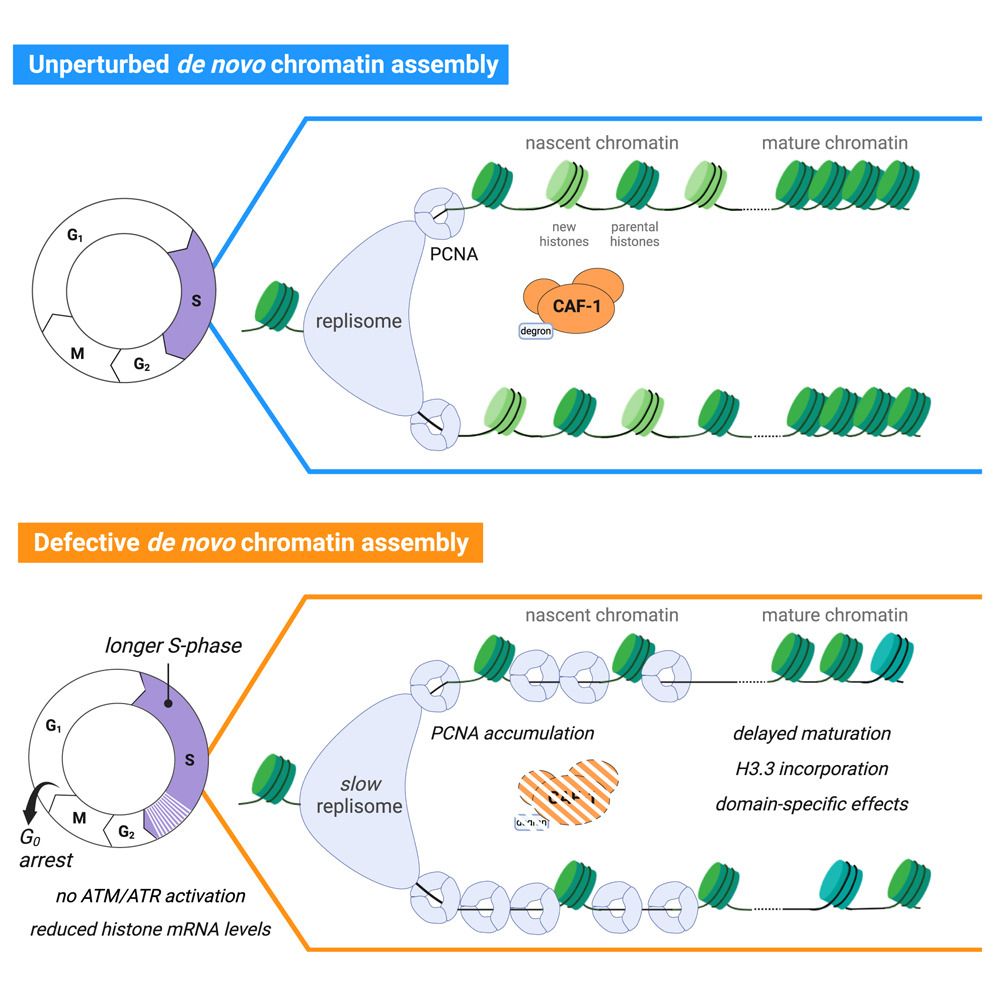
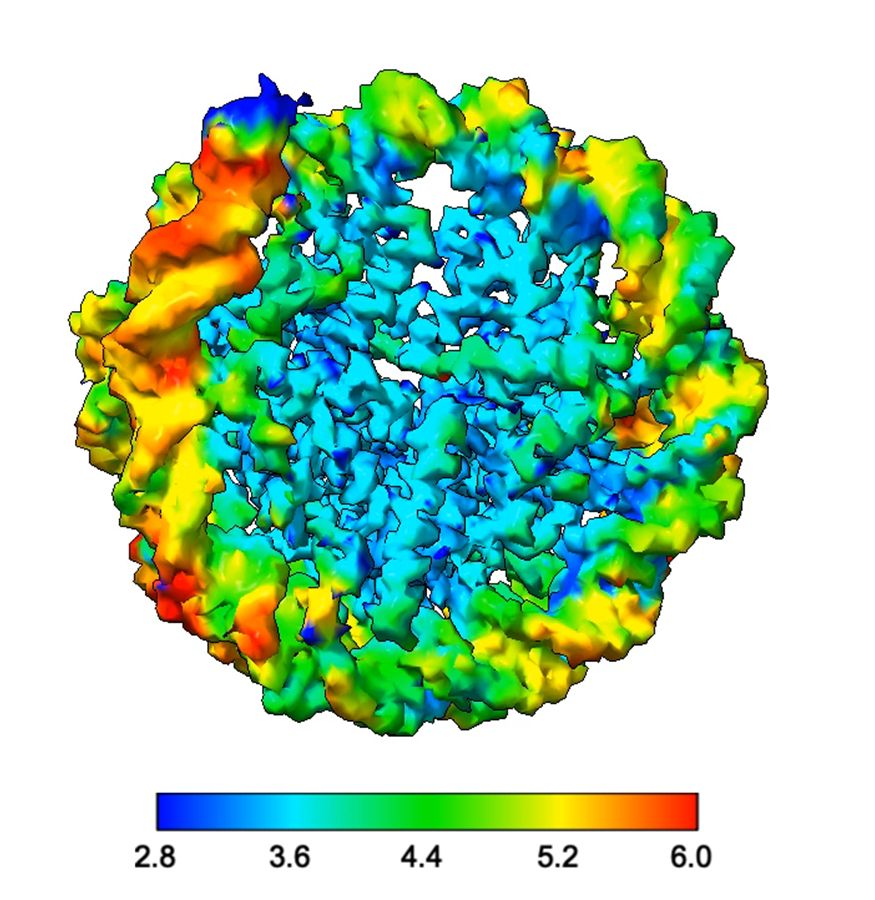
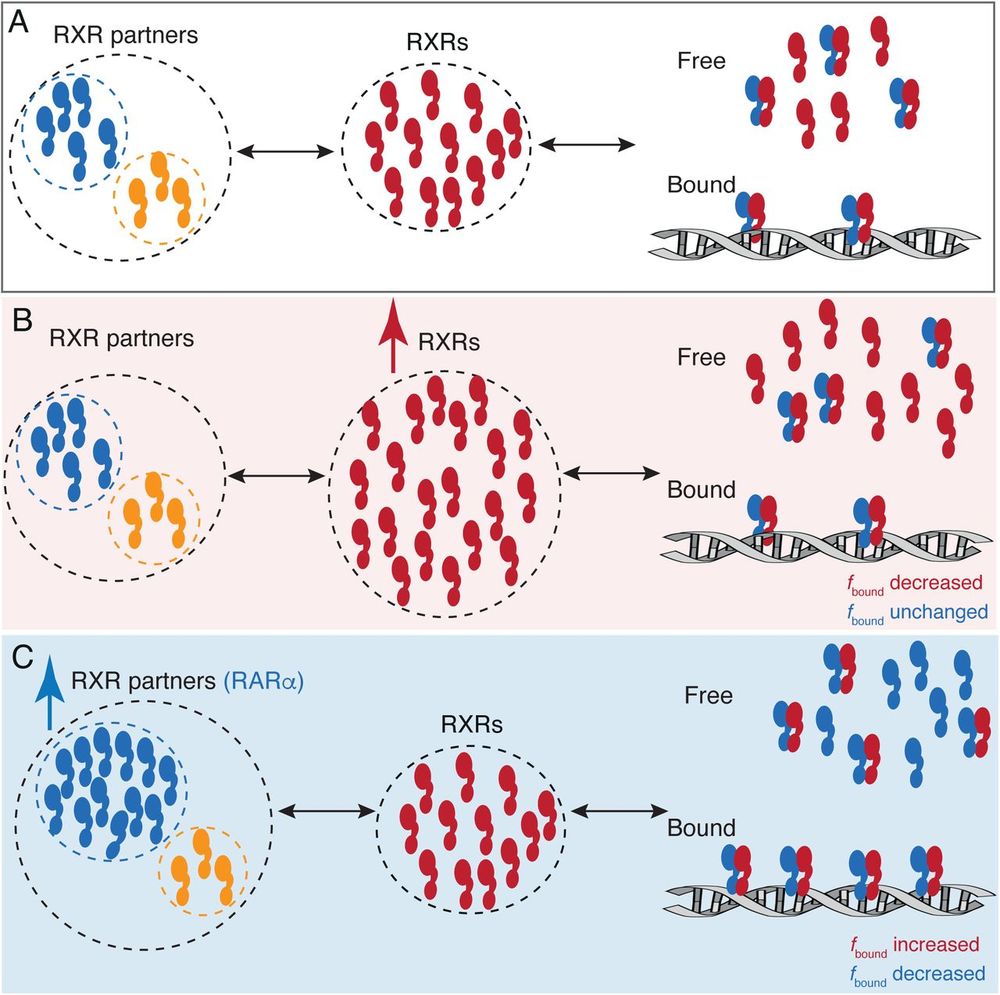
Chromatin Haiku
@chromatinhaiku.bsky.social
1.2K followers
33 following
11 posts
Nuclear events
Narratives in chromatin
By haiku, of course
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs