Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
9 followers
9 following
24 posts
neurology @unipd.bsky.social
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Aug 13

Non-native entanglement protein misfolding observed in all-atom simulations and supported by experimental structural ensembles
All-atom simulations populate a predicted class of misfolding, and ensembles are proposed based on structural mass spectrometry.
www.science.org
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Jul 19
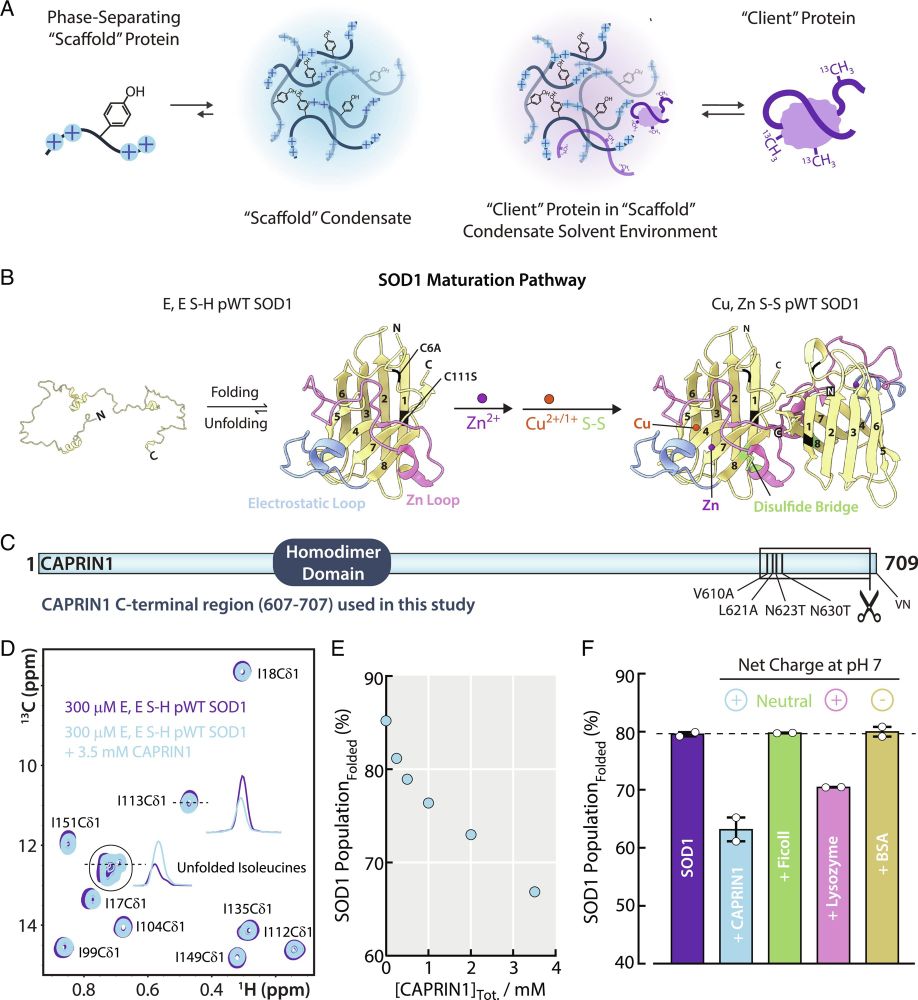
Atomic resolution map of the solvent interactions driving SOD1 unfolding in CAPRIN1 condensates | PNAS
Biomolecules can be sequestered into membrane-less compartments, referred to as biomolecular
condensates. Experimental and computational methods ha...
www.pnas.org
Reposted by Emanuele Lamberti
Nature
@nature.com
· Jul 9
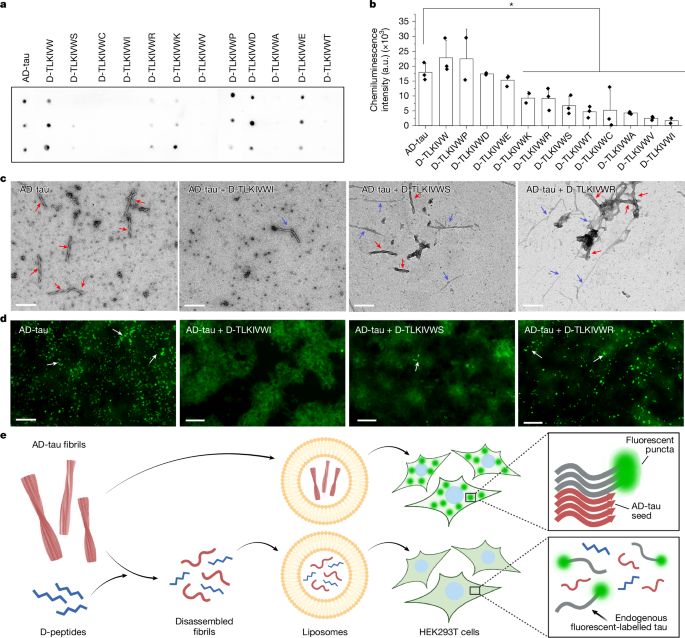
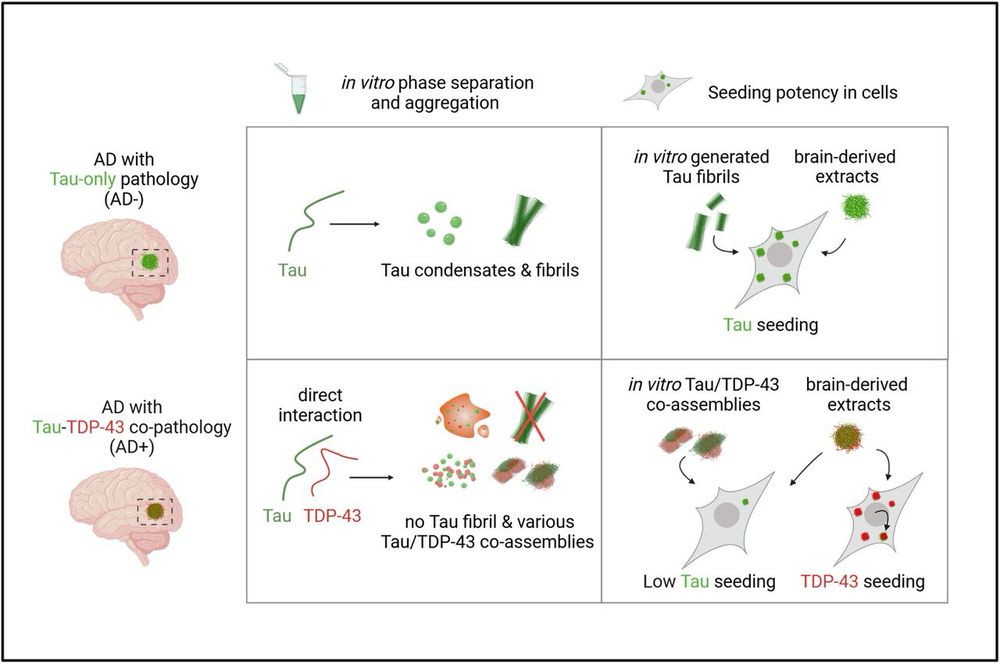
How short peptides disassemble tau fibrils in Alzheimer’s disease - Nature
Cryo-electron and atomic force microscopy shed light on how fibrils of the protein tau, which accumulate in the brain of people with Alzheimer’s disease, can be disassembled by short peptides, providing a possible route towards developing treatments.
go.nature.com
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Jun 15
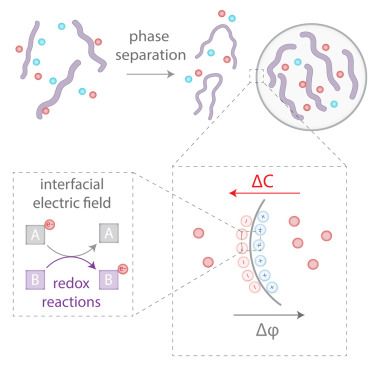
Network-forming phase separation of oppositely charged polyelectrolytes forming coacervates in a solvent
Nature Communications - The formation of coacervates through phase separation of oppositely charged polyelectrolytes (PEs) is critical for understanding biological condensates and developing...
rdcu.be
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· May 17
Small-molecule dissolution of stress granules by redox modulation benefits ALS models
Nature Chemical Biology - Uechi et al. found that a small-molecule lipoamide dissolves stress granules (SGs) by targeting SFPQ, a redox-sensitive disordered SG protein, alleviating pathological...
rdcu.be
Reposted by Emanuele Lamberti
BioMassSpec
@realbiomassspec.bsky.social
· May 10
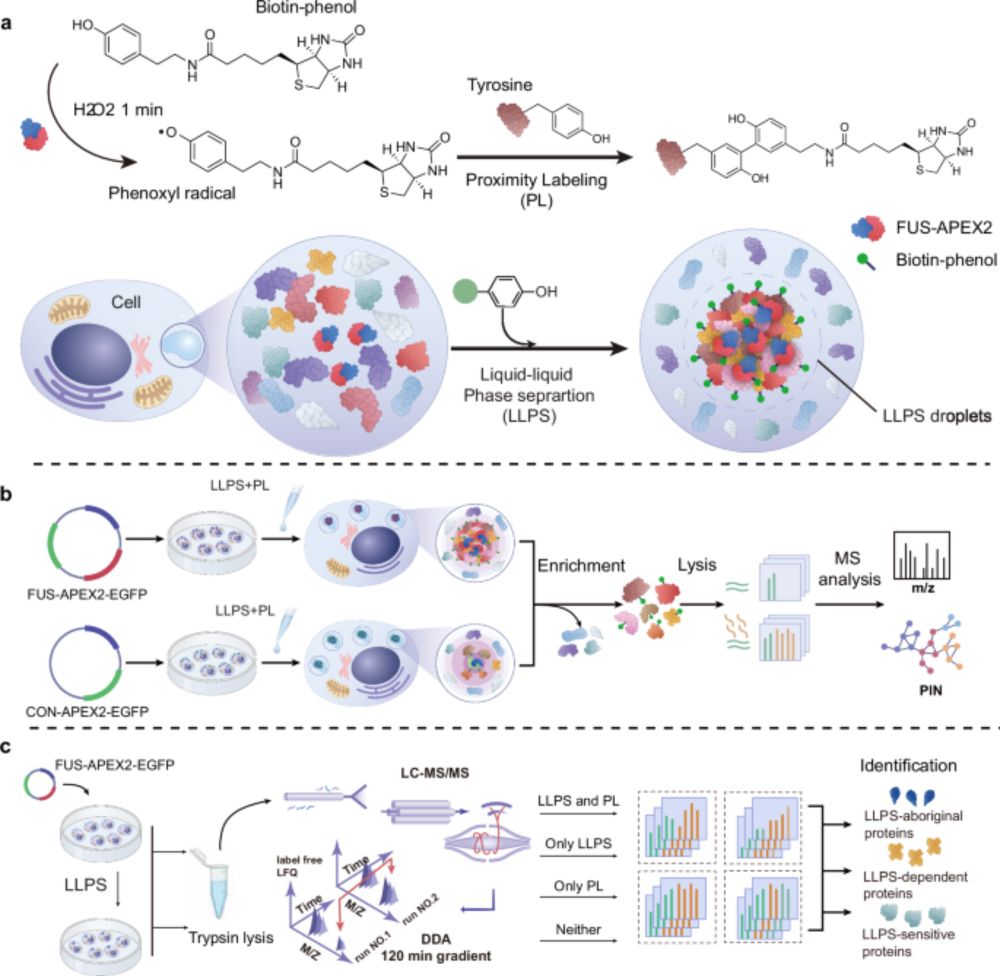
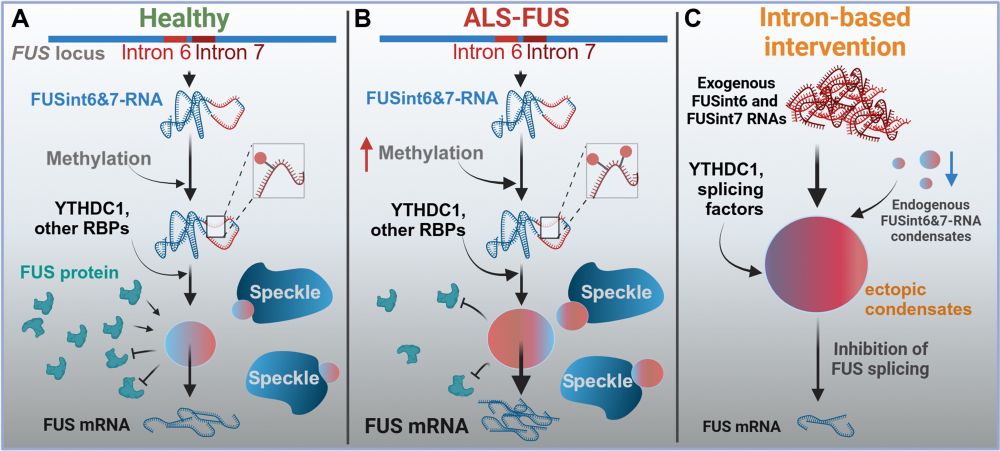
Spatiotemporal deciphering of dynamic the FUS interactome during liquid-liquid phase separation in living cells - Nature Communications
CLAPM uses proximity labeling mass spectrometry to monitor proteomes within phase-separated droplets. This approach identifies condensate-specific proteins to assess proteome dynamics in various cell ...
www.nature.com
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Mar 17
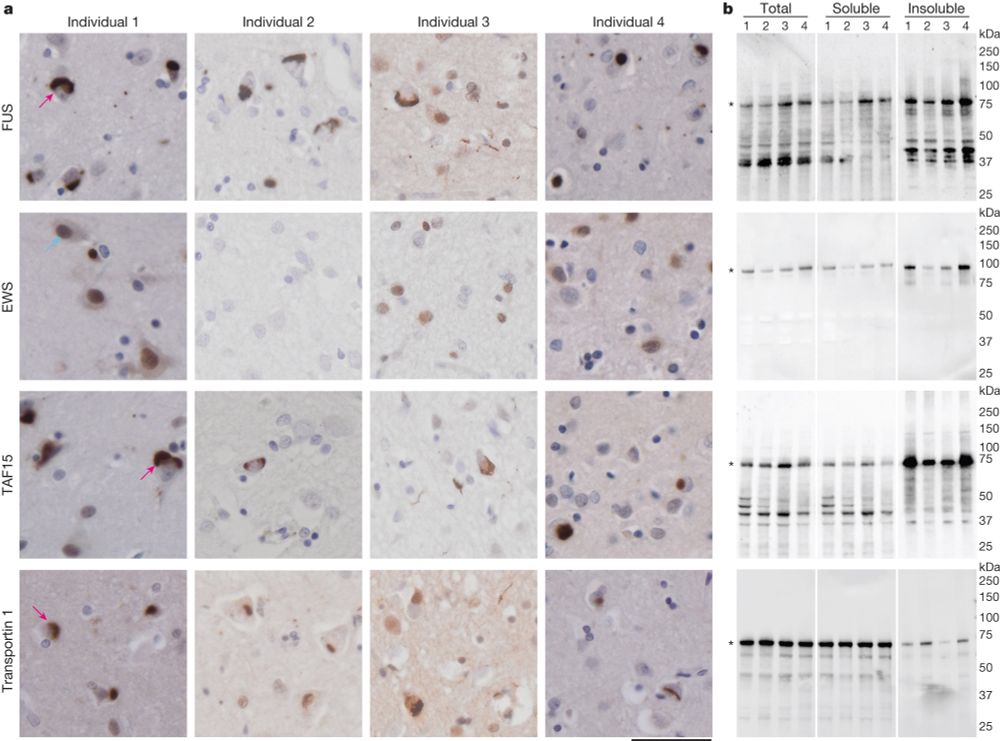
TAF15 amyloid filaments in frontotemporal lobar degeneration
Nature - Cryogenic electron microscopy structures of amyloid filaments extracted from patient brains reveal that the protein TAF15 forms filaments that characterize certain cases of frontotemporal...
rdcu.be
Reposted by Emanuele Lamberti
Rohit V. Pappu
@rohitpappu68.bsky.social
· Feb 27

Nuclear speckle proteins form intrinsic and MALAT1-dependent microphases
Nuclear speckles are enriched in serine / arginine rich splicing factors (SRSFs), such as SRSF1. Splicing factors and proteins such as TDP43 concentrate into distinct speckle territories to enable pre...
www.biorxiv.org
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Jan 26
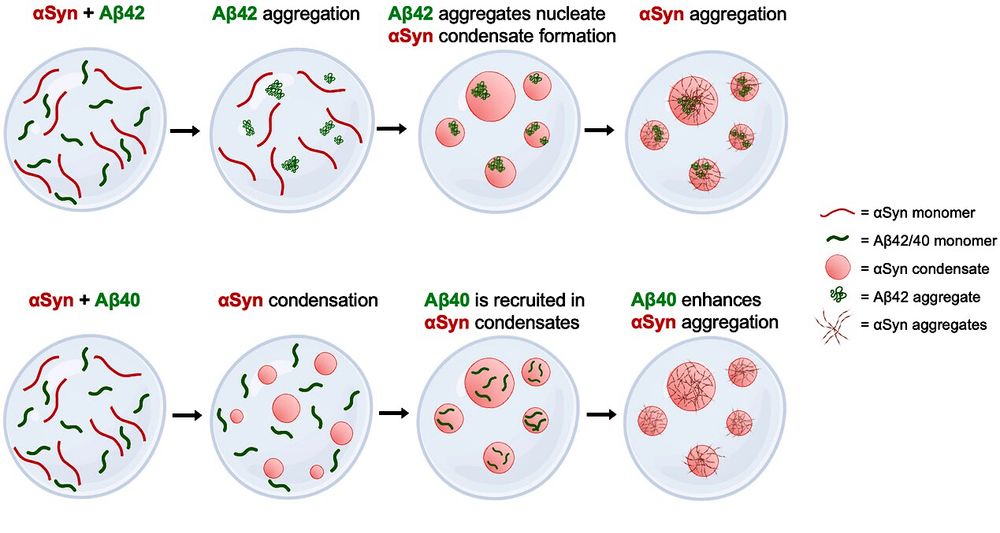
MOAG-4 promotes the aggregation of α-synuclein by competing with self-protective electrostatic interactions
Aberrant protein aggregation underlies a variety of age-related neurodegenerative
disorders, including Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases. Little is known, however,
about the molecular mechanisms th...
www.jbc.org
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Jan 19
Simple Model of the Effect of Solution Conditions on the Nucleation of Amyloid Fibrils
It is well known that peptide and protein fibrillation is strongly affected by the solution conditions, but a fundamental understanding of how amyloid fibril nucleation depends on solution pH, salt concentration, and solvent is absent. Here, we use expressions from Debye–Hückel theory to describe the interactions between charged amino acids in combination with our recently developed nonstandard nucleation theory to predict the concentration dependence of the fibril nucleation rate under different solvent conditions. The general rule that emerges from these considerations is that changes in solution pH, salt concentration, and solvent that increase the bonding energy between the fibril building blocks decrease the fibril solubility and promote fibril nucleation, in line with experimental observations. The simple analytical relations among the nucleation rate, fibril solubility, and binding energies provide a tool to controlling and understanding amyloid fibril formation by changing the solution conditions.
pubs.acs.org
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Jan 14
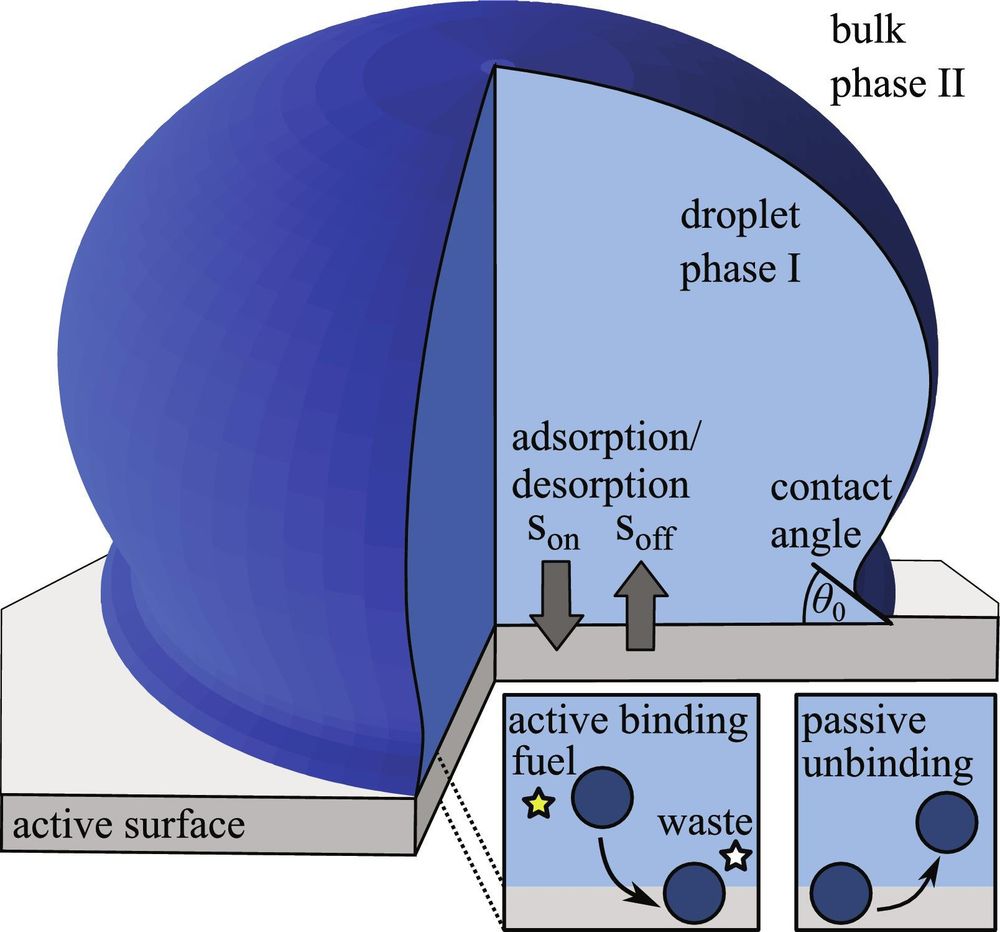
Glutamate helps unmask the differences in driving forces for phase separation versus clustering of FET family proteins in sub-saturated solutions
Multivalent proteins undergo coupled segregative and associative phase transitions. Phase separation, a segregative transition, is driven by macromolecular solubility, and this leads to coexisting pha...
www.researchsquare.com
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Jan 13
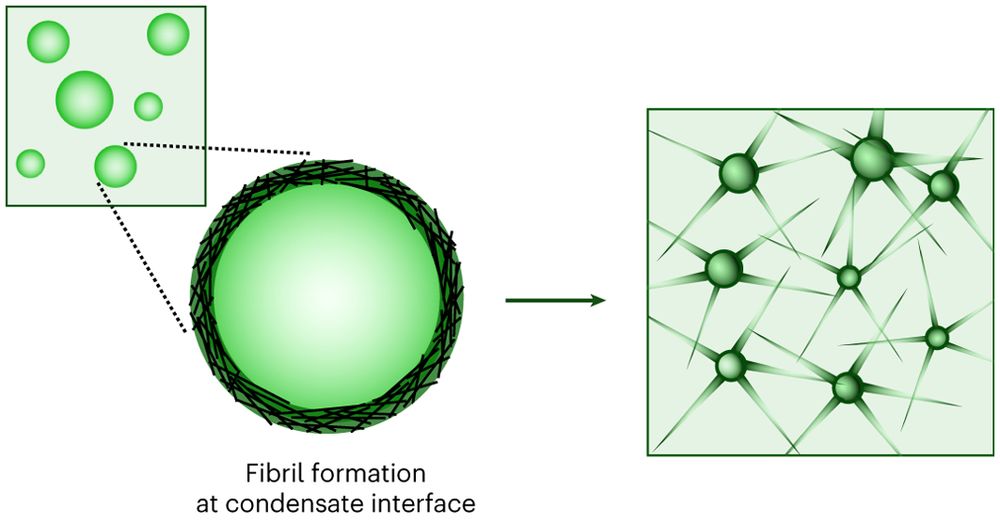
The interface of condensates of the hnRNPA1 low-complexity domain promotes formation of amyloid fibrils
Nature Chemistry - Understanding of the molecular mechanisms underlying the maturation of protein condensates into amyloid fibrils associated with neurodegenerative diseases has so far remained...
rdcu.be
Emanuele Lamberti
@elamberti.bsky.social
· Jan 11
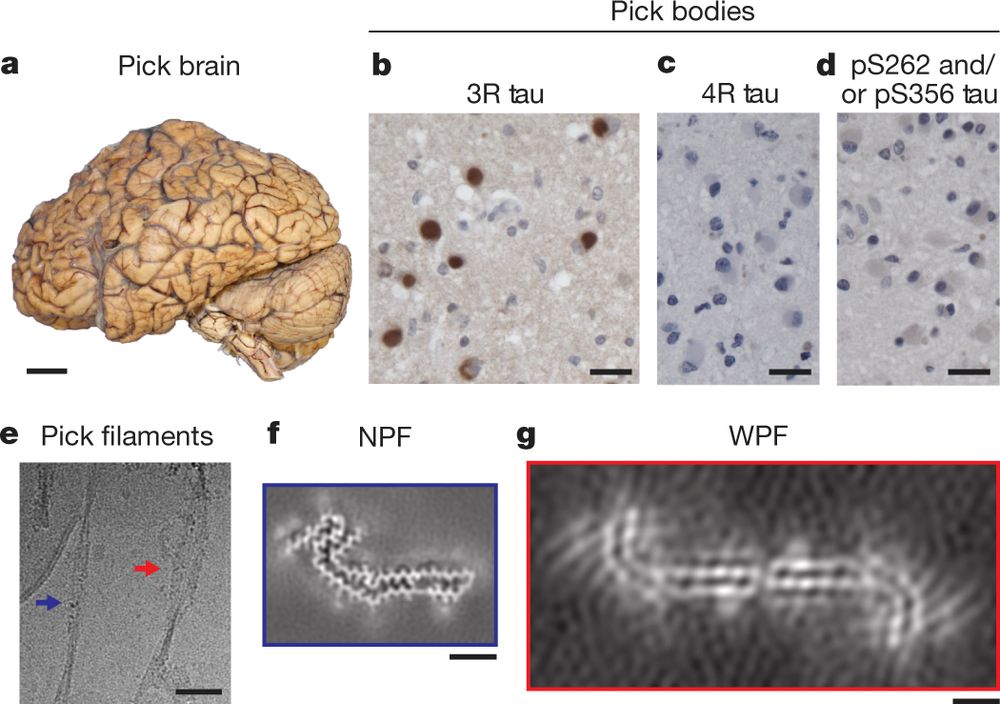
Structures of filaments from Pick’s disease reveal a novel tau protein fold
Nature - The structures of tau filaments from patients with the neurodegenerative disorder Pick’s disease show that the filament fold is different from that of the tau filaments found in...
rdcu.be