Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
480 followers
1.1K following
27 posts
Junior Research Group Leader @LMU Munich, interested in vascular biology with a focus on platelets and immunothrombosis
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jun 22
Reposted by Leo Nicolai
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Apr 24
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Apr 24
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Apr 24
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Apr 24
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Apr 24
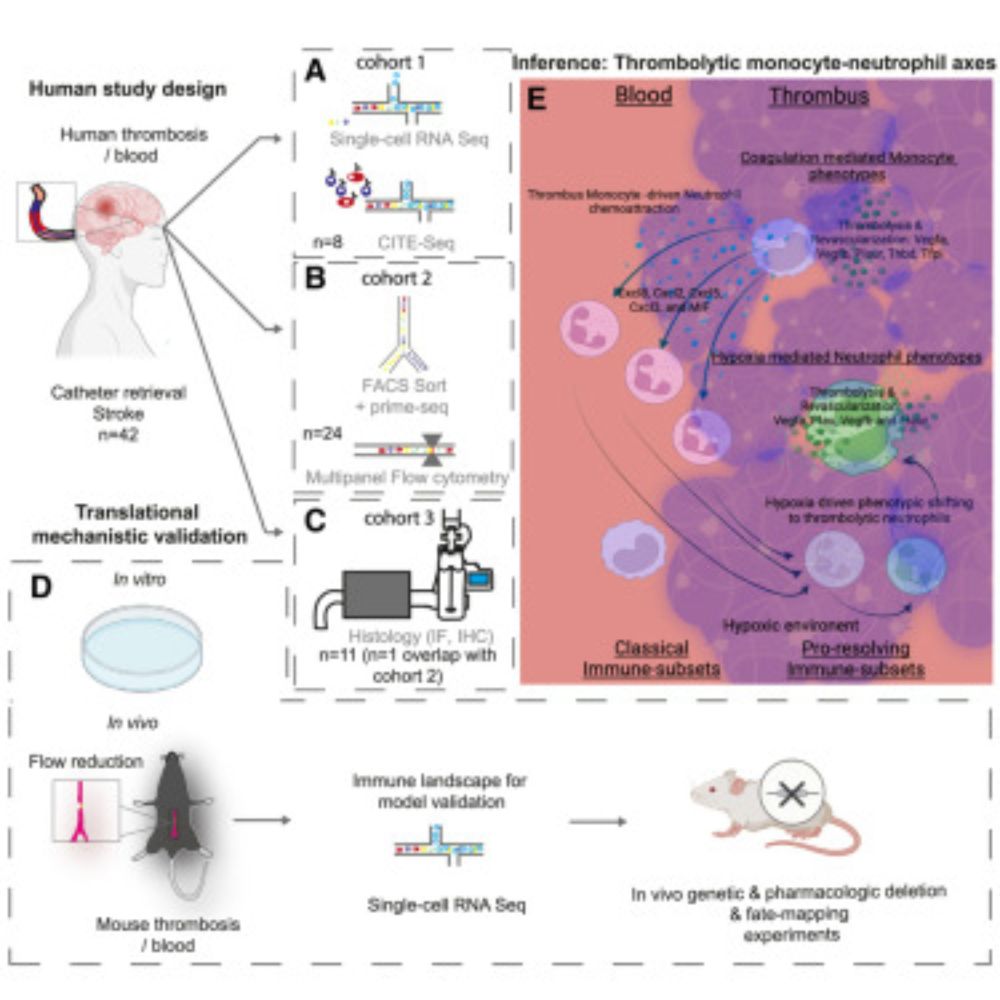
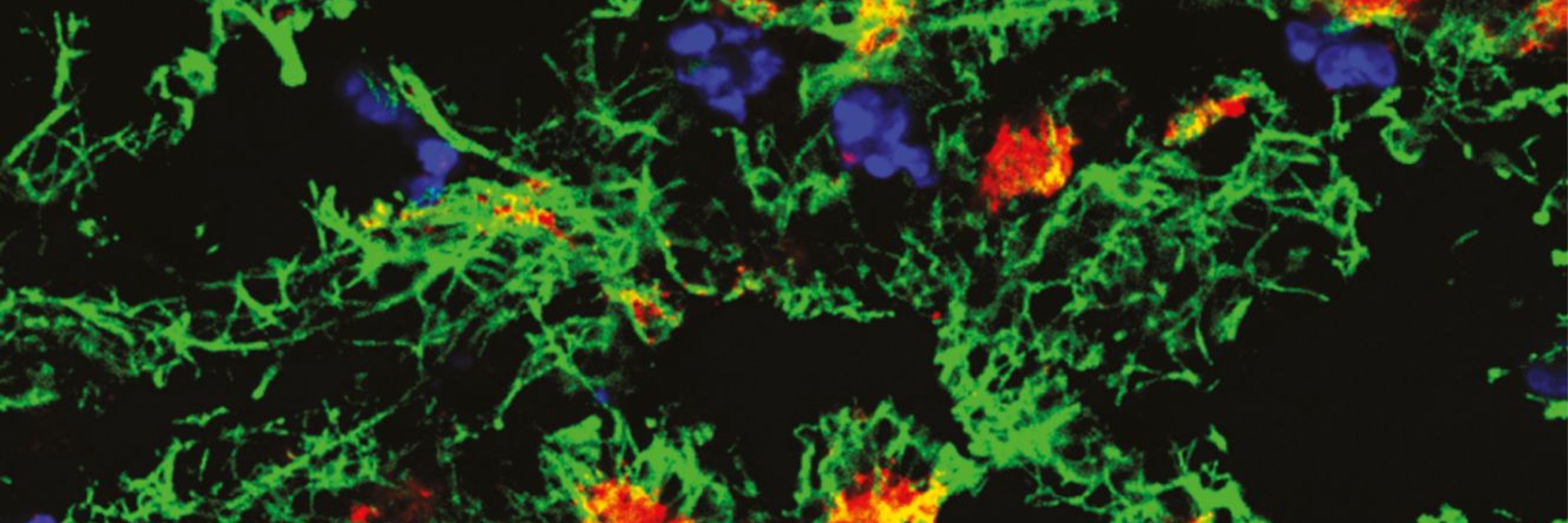
Immunothrombolytic monocyte-neutrophil axes dominate the single-cell landscape of human thrombosis and correlate with thrombus resolution
Thrombotic diseases remain the major cause of death and disability worldwide, and the contribution of inflammation is increasingly recognized. Thrombo…
www.sciencedirect.com
Reposted by Leo Nicolai
Ivan Zanoni
@lozanzi.bsky.social
· Apr 24

Immunothrombolytic monocyte-neutrophil axes dominate the single-cell landscape of human thrombosis and correlate with thrombus resolution
Thrombotic diseases remain the major cause of death and disability worldwide, and the contribution of inflammation is increasingly recognized. Thrombo…
www.sciencedirect.com
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jan 25
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jan 25
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jan 25
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jan 23
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jan 23
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jan 23
Leo Nicolai
@immunothrombosis.bsky.social
· Jan 23