John Butts
@j-c-butts.bsky.social
52 followers
52 following
11 posts
Biomedical Sciences PhD Candidate at The University of Maine and The Jackson Laboratory
Genetics. Music. Tennis. (Not necessarily in that order)
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
John Butts
@j-c-butts.bsky.social
· Apr 23
John Butts
@j-c-butts.bsky.social
· Apr 23
John Butts
@j-c-butts.bsky.social
· Apr 23
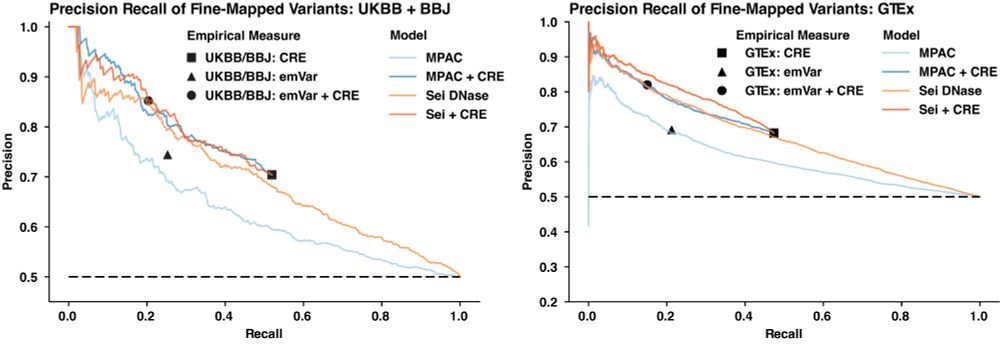
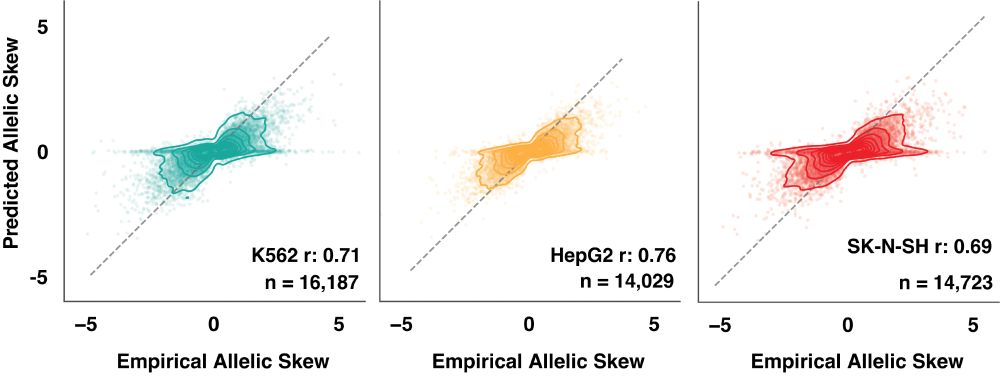
Identifying non-coding variant effects at scale via machine learning models of cis-regulatory reporter assays
Supplemental data and resources for "Identifying non-coding variant effects at scale via machine learning models of cis-regulatory reporter assays" Including: MPAC predictions for: Siraj 2024 (UKBB/BB...
zenodo.org