Viet Anh Khoa Tran
@ktran.de
130 followers
910 following
8 posts
PhD student on Dendritic Learning/NeuroAI with Willem Wybo,
at Emre Neftci's lab (@fz-juelich.de).
ktran.de
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Viet Anh Khoa Tran
@ktran.de
· Jun 10

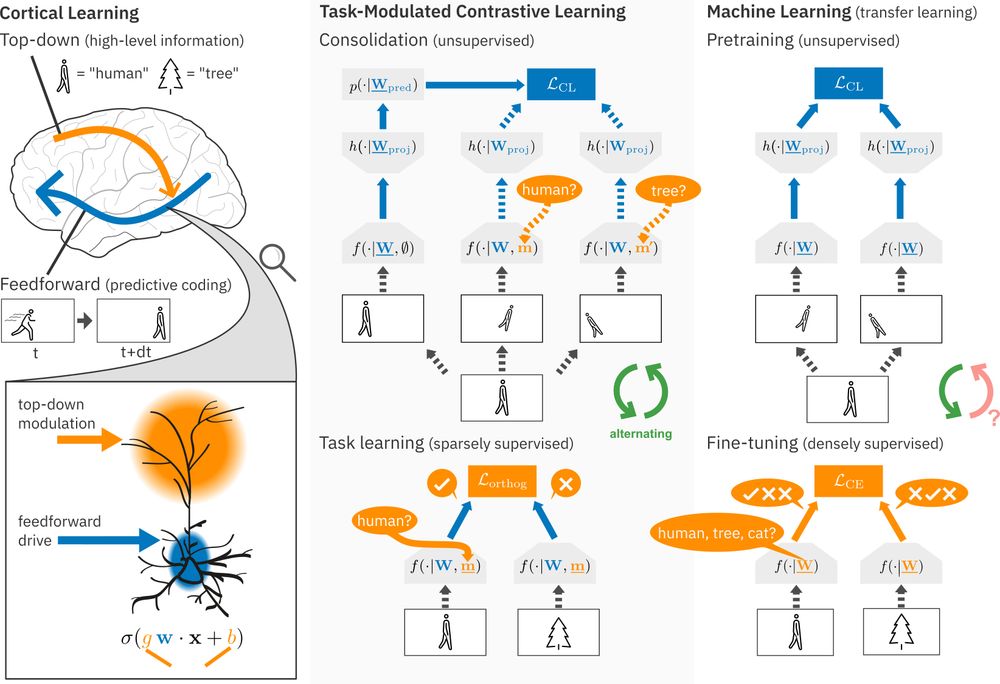
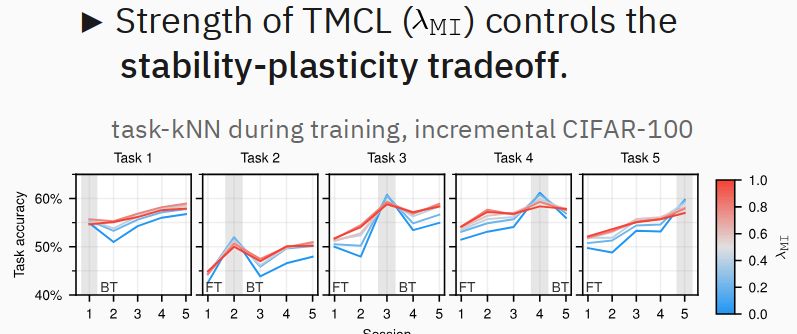
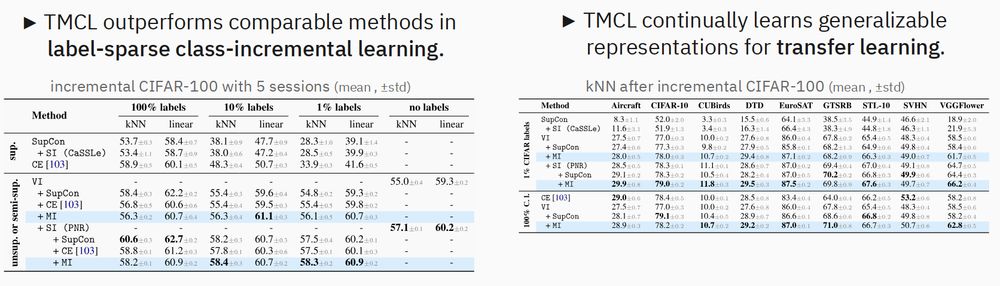
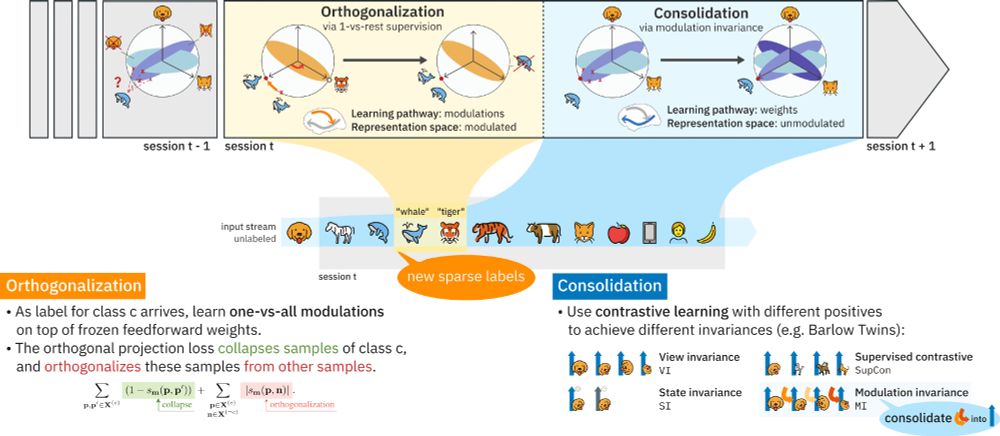
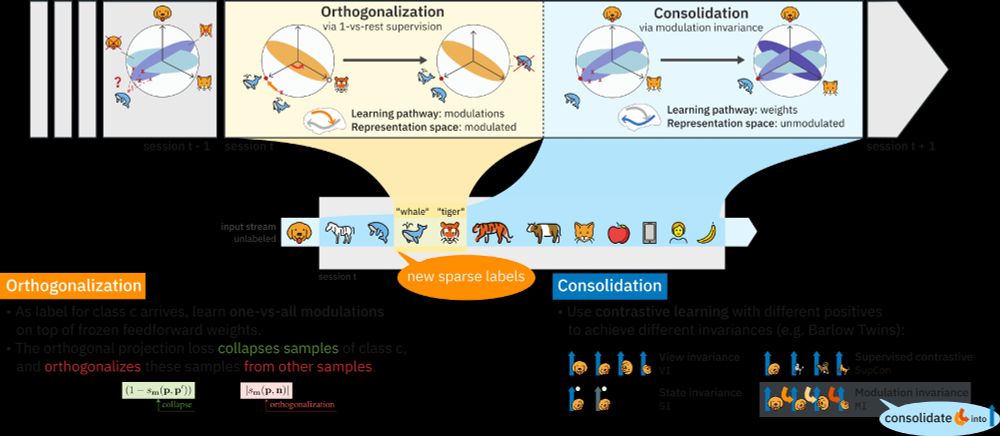
Contrastive Consolidation of Top-Down Modulations Achieves Sparsely Supervised Continual Learning
Biological brains learn continually from a stream of unlabeled data, while integrating specialized information from sparsely labeled examples without compromising their ability to generalize. Meanwhil...
arxiv.org
Viet Anh Khoa Tran
@ktran.de
· Jun 10