Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
190 followers
230 following
20 posts
Group leader at University of Bonn, studying the genomics of birth defects and infectious diseases.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Kerstin Ludwig
Leonard Frach
@leofrach.bsky.social
· Jul 24
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jul 22
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jul 22
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jul 22

Population-scale sequencing resolves correlates and determinants of latent Epstein-Barr Virus infection
Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) is an endemic herpesvirus implicated in autoimmunity, cancer, and neurological disorders. Though primary infection typically resolves with subclinical symptoms, long-term comp...
www.biorxiv.org
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jul 22
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jul 22
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jul 22
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jul 22
Reposted by Kerstin Ludwig
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· Jun 18
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· May 27
Daniel Ibrahim
@danielibrahim.bsky.social
· May 27
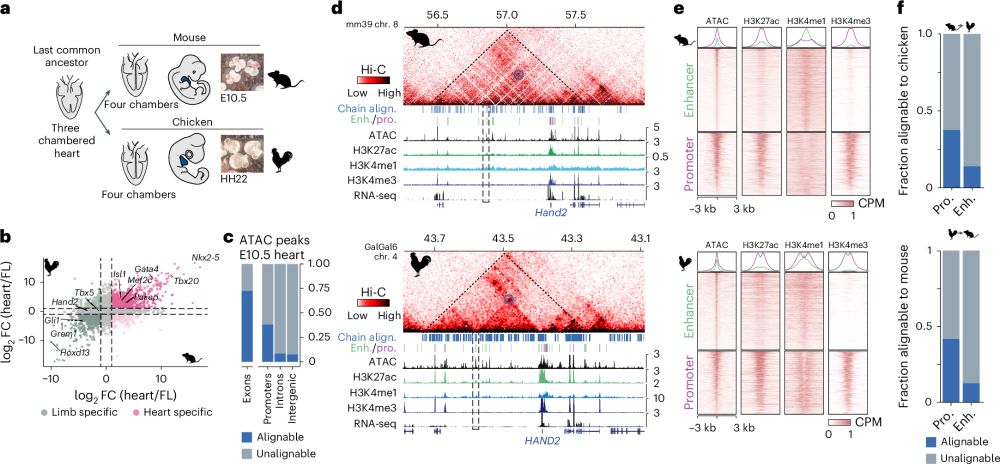
Conservation of regulatory elements with highly diverged sequences across large evolutionary distances
Nature Genetics - Combining functional genomic data from mouse and chicken with a synteny-based strategy identifies positionally conserved cis-regulatory elements in the absence of direct sequence...
rdcu.be
Reposted by Kerstin Ludwig
Kerstin Ludwig
@kuludwig.bsky.social
· May 24
Reposted by Kerstin Ludwig
Reposted by Kerstin Ludwig