LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
720 followers
450 following
44 posts
Structure-function relationship on transport proteins. Fluorescence, cryo-EM and molecular pharmacology on neurotransmitter:sodium symporters.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
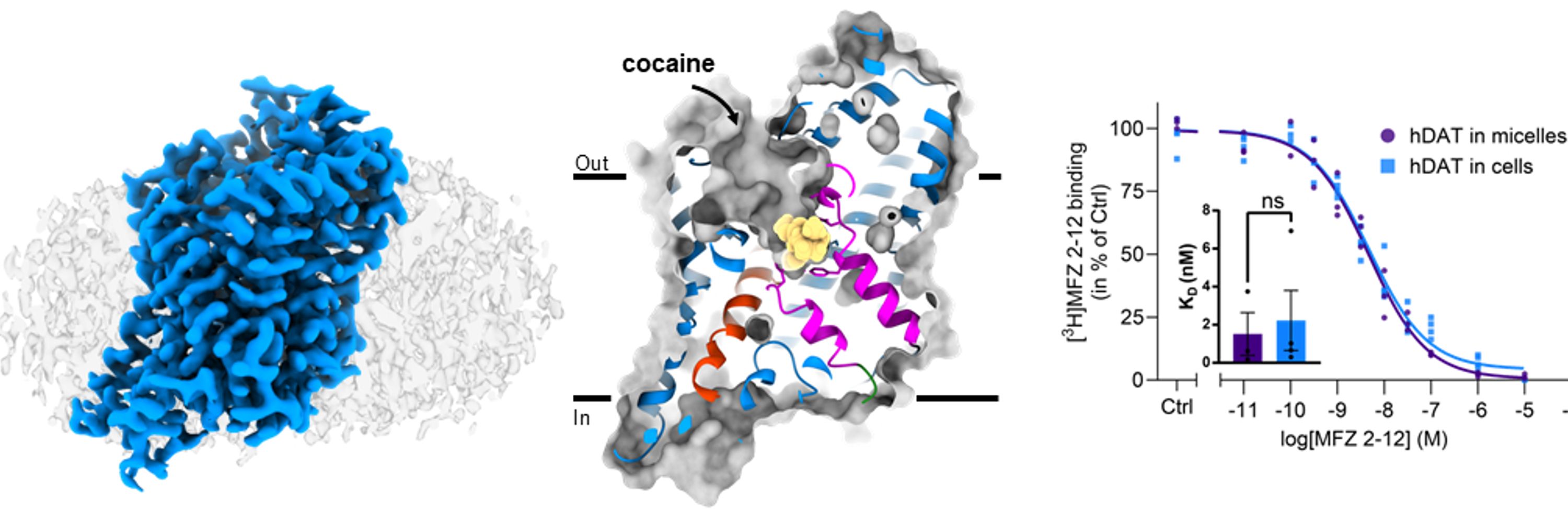
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Nov 23
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Feb 12
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Feb 2
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 28

Squeeze pumping of lipids and insecticides by ABCH transporter
High-resolution cryo-EM structures and biochemical data reveal the dynamic process by which the ABCH transporter binds and transports lipid substrates and insecticides across cell membranes while detoxifying insecticides, providing atomic-level insights for the development of arthropod pest control agents and strategies for managing pesticide resistance.
www.cell.com
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 26

Trapping of spermine, Kukoamine A, and polyamine toxin blockers in GluK2 kainate receptor channels - Nature Communications
Kainate receptors (KARs) contribute to excitatory neurotransmission, neuronal plasticity and neurological disorders. Here, Gangwar et al. present KAR structures in complex with channel blockers NpTx8,...
www.nature.com
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 15
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 11
A sodium channel mutant removes fast inactivation with the inactivation particle bound | Journal of General Physiology | Rockefeller University Press
In this work, Liu and Bezanilla describe a voltage-gated sodium channel mutant that removes fast inactivation while the fast inactivation particle, the IFM
rupress.org
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 11

Ion coupling and inhibitory mechanisms of the human presynaptic high-affinity choline transporter CHT1
Qiu et al. report the cryo-EM structures of the human high-affinity choline transporter 1 (CHT1) with bound inhibitors, the substrate choline, and a substrate-free state. These structures reveal the binding modes of inhibitors with different chemical structures and shed light on the ion-coupled substrate transport mechanism of CHT1.
www.cell.com
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 9

GABAA receptor π forms channels that stimulate ERK through a G-protein-dependent pathway
GABAA receptor π (GABRP) can form homopentameric channel-like structures, similar to the more common heteromeric type-A GABA receptor channels. However, GABRP activation by GABA uniquely induces a G-protein-signaling pathway rather than allowing chloride passage. Selective inhibition of GABRP signaling may hold therapeutic promise for GABRP-associated cancers.
www.cell.com
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 9

Substrate translocation and inhibition in human dicarboxylate transporter NaDC3
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology - The authors show cryo-electron microscopy structures of the human high-affinity sodium–dicarboxylate cotransporter, responsible for dicarboxylate...
rdcu.be
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 7

Insights into the distinct membrane targeting mechanisms of WDR91 family proteins
Proteins from the WDR91 family control phosphoinositide conversion required for endosome maturation. By combining structural, biochemical, and cellular data, Ma et al. provide evidence that two representative members of this family WDR91 and SORF1 either use the Rab7-binding WD40 domain or an amphipathic helix for membrane targeting.
www.cell.com
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 7

De novo variants in LRRC8C resulting in constitutive channel activation cause a human multisystem disorder | The EMBO Journal
imageimageVolume-regulated ion channels (VRACs) open in response to hypotonic stress and protect against excessive cell swelling and bursting. This study describes two patient variants in a VRAC subunit that cause a severe pleiotropic disorder ...
www.embopress.org
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 7
LolandLab
@lolandlab.bsky.social
· Dec 7