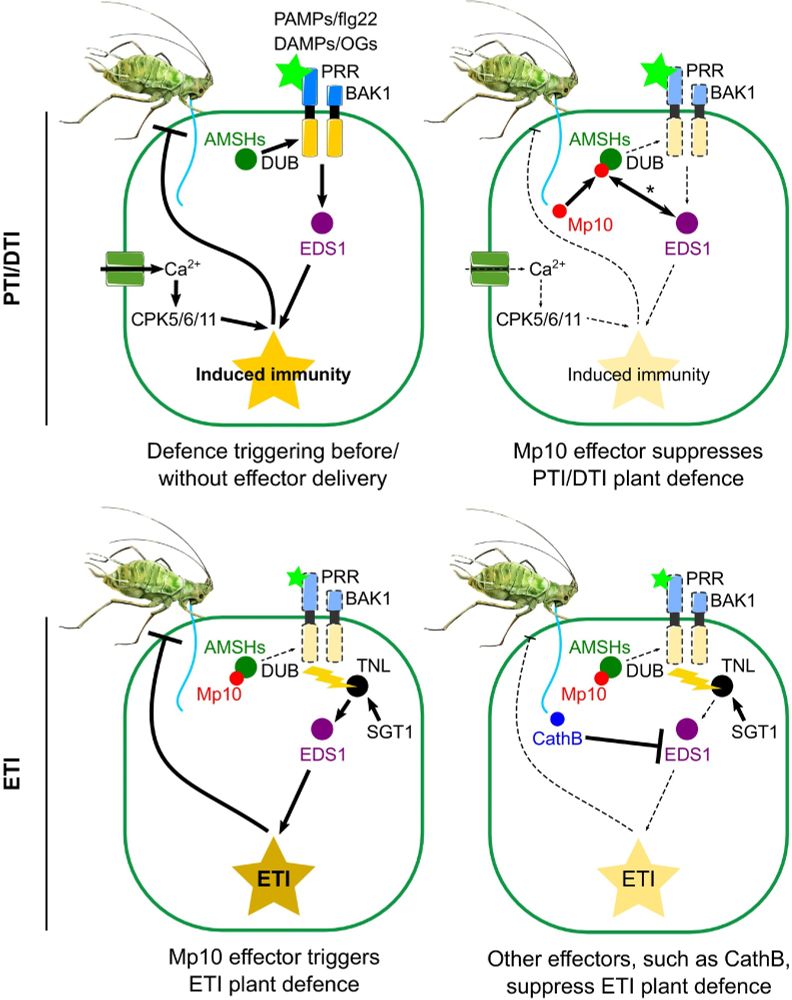
Matteo Gravino
@matteogravino.bsky.social
33 followers
37 following
9 posts
Scientist at the John Innes Centre. Interested in plant-aphid interactions.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Reposted by Matteo Gravino
Sam Mugford
@samtmugford.bsky.social
· Jul 31
Reposted by Matteo Gravino
Sam Mugford
@samtmugford.bsky.social
· Jul 16
Reposted by Matteo Gravino
Baptiste Castel
@baptistebio.bsky.social
· Mar 20

Exploring fern pathosystems and immune receptors to bridge gaps in plant immunity
Land plants include angiosperms, bryophytes, lycophytes and ferns, each of which may deploy distinct strategies to resist pathogens. Here, we investigate fern-pathogen interactions by characterizing n...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Matteo Gravino
Reposted by Matteo Gravino
Sam Mugford
@samtmugford.bsky.social
· Mar 1
Reposted by Matteo Gravino
Sam Mugford
@samtmugford.bsky.social
· Nov 18