Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
80 followers
52 following
92 posts
Q-Chem provides a comprehensive ab initio quantum chemistry program, allowing scientists worldwide to model chemical problems quickly and accurately.
http://q-chem.com/
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Sep 3

Ultrafast Transversal CISS Effect Observed in a Chiral Photoswitching Molecule
Progress in the fundamental understanding of the chirality-induced spin-selectivity (CISS) effect is hindered by complexity of the systems that have been characterized experimentally. With the goal of...
doi.org
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Aug 28

John Herbert receives the 2024-2025 Diversity Enhancement Faculty Award
2024-2025 Diversity Enhancement Faculty Award This award recognizes a faculty member from within The Ohio State University College of Arts and Sciences whose research, teaching and/or service/outreach...
chemistry.osu.edu
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Aug 25

Instability of the Octahedral Symmetry in Si8O12H8 and Ge8O12H8: A Consequence of the Pseudo-Jahn–Teller Effect - Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials
The symmetry breaking in octahedral silsesquioxane and its germanium analogues (Si8O12H8 and Ge8O12H8) has been investigated using the M06-2X/6-31++G(3df, 3pd) method and group theory. Both structures...
doi.org
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Aug 22

Rationalising Exciton Interactions in Aggregates Based on the Transition Density
Exciton coupling in organic chromophores is revisited through the lens of the transition density. The presented formalism gives insight into the strength and sign of the coupling based on the relativ...
doi.org
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Aug 18

Development of a Spectroscopic Map to Explain the Broad Raman Peak for Alkynes Solvated in Triethylamine
The terminal alkyne C≡C stretch has a large Raman scattering cross section in the “silent” region for biomolecules. Experimental work taking advantage of this property provide an impetus for the development of theoretical tools addressing the vibration. In prior work, we have developed a localized normal mode method for computing terminal alkyne vibrational frequencies using a discrete variable representation of the potential energy surface. Using this method and molecular dynamics simulations, we interpret the unusually broad Raman spectrum of alkynes solvated in triethylamine. Energy decomposition analysis is performed on alkyne-triethylamine dimers to determine that charge transfer, electrostatics, and Pauli repulsion have large effects on the frequency. Molecular dynamics simulations of triethylamine-solvated alkynes are performed and uncover that the terminal alkyne hydrogen interacts strongly with the triethylamine nitrogen. Interactions persist for 3–10 ps. Using this data, a spectroscopic map for terminal alkynes is developed and used to compute Raman spectra for alkynes in triethylamine. We find that the broad experimental spectra result from the combination of a population of alkynes associated with the solvent nitrogens and a population not associated with those nitrogens. This work sets the stage for investigations of alkynes in more complex environments like proteins and nanomaterial surfaces.
pubs.acs.org
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Aug 5
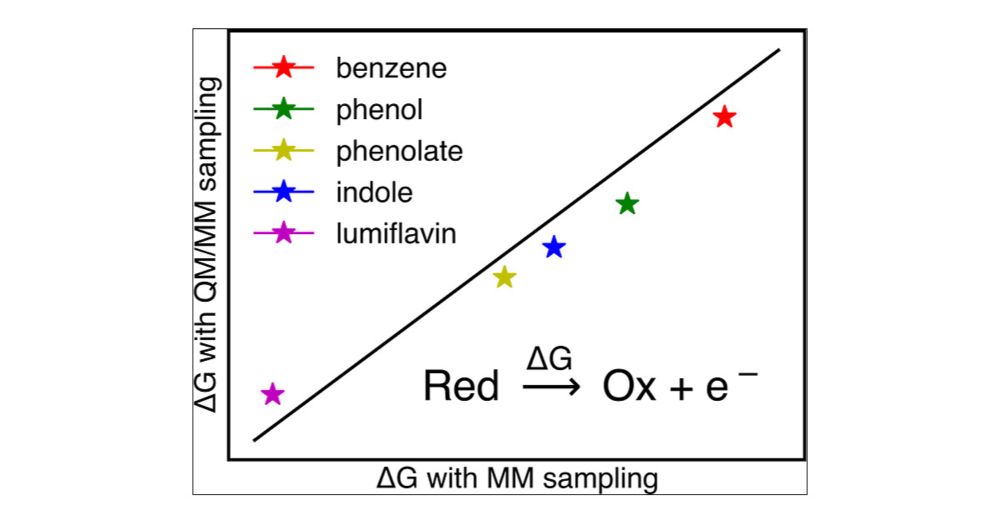
Effects of Conformational Sampling on Computing Redox Properties Using Linear Response Approach
Redox processes are an important step in many chemical and biochemical reactions. One simple approach to calculate the free energy change of a redox process is linear response approximation (LRA). However, variability in conformational and energy-gap sampling poses a challenge in balancing computational cost and accuracy. Herein, we calculate the redox properties of the one-electron oxidation processes for small, biologically relevant redox-active molecules (e.g., phenol, phenolate, benzene, indole, lumiflavin) in aqueous solution using two conformational sampling strategies. We sampled the conformations using molecular mechanics (MM) and hybrid quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics (QM/MM) simulations to investigate how these techniques affect redox properties. We also performed QM/MM energy-gap sampling while varying the QM region to investigate its impact on overall redox behavior. We observed free energy of oxidation, and consequently, oxidation potential differs consistently by ∼0.2–0.4 V between QM/MM and MM sampling for the molecules under investigation. Overall, we infer that computationally cheaper MM sampling would be adequate for computing the redox properties of small molecules when corrected by a system-specific correction factor.
doi.org
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Aug 1
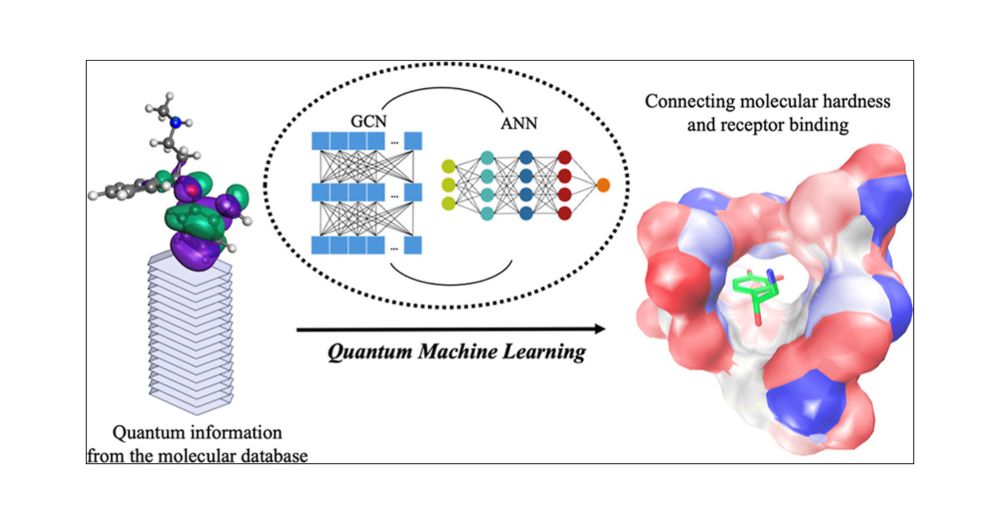
Graph Convolutional Neural Network-Enabled Frontier Molecular Orbital Prediction: A Case Study with Neurotransmitters and Antidepressants
With the advancement of artificial intelligence-embedded methodologies, their application to predict fundamental molecular properties has become increasingly prevalent. In this study, a graph convolut...
doi.org
Q-Chem
@qchemsoftware.bsky.social
· Jul 21
Revisiting a large and diverse data set for barrier heights and reaction energies: best practices in density functional theory calculations for chemical kinetics
Accurate prediction of barrier heights and reaction energies is of paramount importance for reaction kinetics. For computational efficiency, such calculations are typically performed with density func...
doi.org