link.springer.com/article/10.1...

link.springer.com/article/10.1...
jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...

jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...
www.nfid.org/infectious-d...

www.nfid.org/infectious-d...
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...

www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

www.nature.com/articles/d41...
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...

www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...

www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...

www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
academic.oup.com/jac/advance-...

academic.oup.com/jac/advance-...
aricjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

aricjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
aricjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

aricjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
www.nature.com/articles/s44...

www.nature.com/articles/s44...
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
academic.oup.com/jac/advance-...

academic.oup.com/jac/advance-...
aricjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

aricjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...

journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/...
jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...

jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...
#PITT_IDFall25
www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10....

#PITT_IDFall25
www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10....
#PITT_IDFall25
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...

#PITT_IDFall25
www.thelancet.com/journals/lan...
www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/14...
www.mdpi.com/2079-6382/14...
jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...

jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...
bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....

bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10....
#PITT_IDFall2025
www.nature.com/articles/s44...

#PITT_IDFall2025
www.nature.com/articles/s44...
jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...
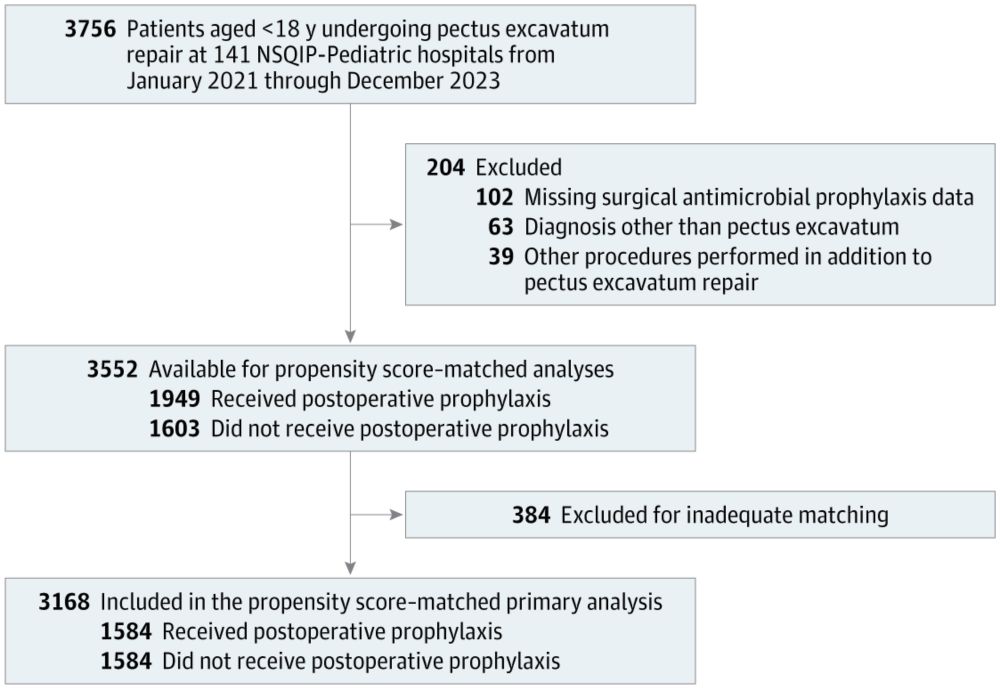
jamanetwork.com/journals/jam...

