Samuel Hewitt, PhD
@samuelhewitt.bsky.social
920 followers
580 following
88 posts
Machine Learning Engineer at Limbic
Building AI therapy
Previously, Max Planck Centre for Computational Psychiatry @ UCL
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Samuel Hewitt, PhD
Tobias Hauser
@tobiasuhauser.bsky.social
· May 14

Brain Explorer - Test your brain power
The brain explorer app for Apple and Android tests your brain functions and helps researchers to understand the brain. Explore your brain power and how brain functions are important for mental health.
www.brainexplorer.net
Reposted by Samuel Hewitt, PhD
Reposted by Samuel Hewitt, PhD
Jade Duffy
@jduffy9.bsky.social
· Mar 24
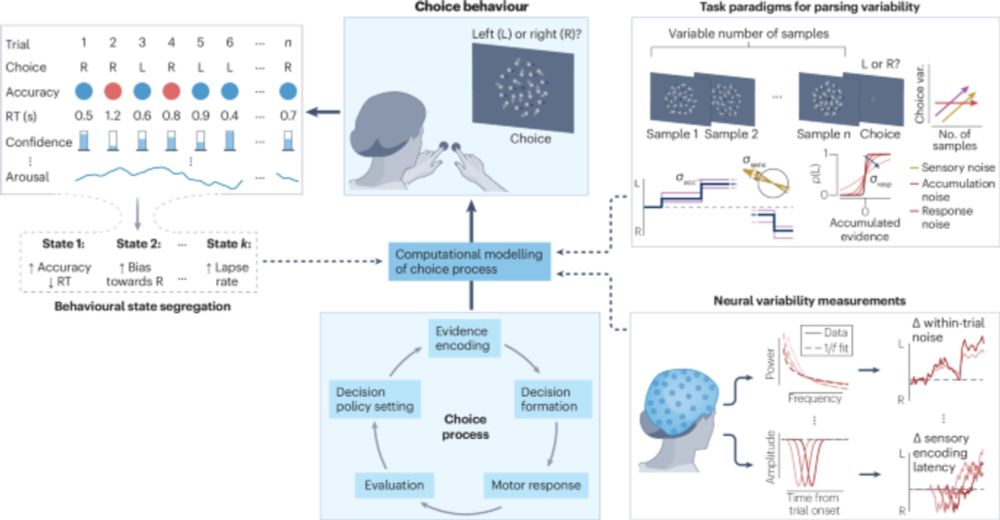
Disentangling sources of variability in decision-making - Nature Reviews Neuroscience
Identifying the psychological and neurobiological processes underpinning intra-individual variations in choice behaviour presents a formidable challenge. In this Review, Duffy et al. discuss how algor...
www.nature.com
Reposted by Samuel Hewitt, PhD
Quentin Huys
@docqhuys.bsky.social
· Mar 18










