Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
180 followers
310 following
47 posts
Professor of Biophysics, Drug Discovery, Photographer, Traveller and a Cultural succupus.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Sep 4
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Aug 27
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Aug 27
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Aug 26
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Aug 18
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Aug 9
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Jul 26
Reposted by Shozeb
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Jun 25
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· Jun 10
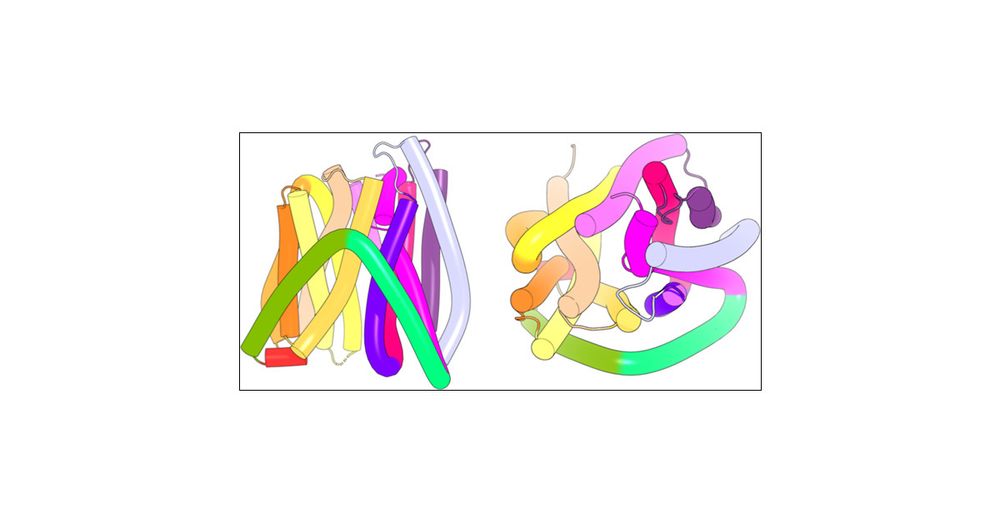
Conformational Landscape of the Di- and Tripeptide Permease A Transport Cycle
Dipeptide and tripeptide permease A (DtpA) transporter is a bacterial homologue of the human PepT that is responsible for the uptake of di- and tripeptides from the small intestine and transports them...
pubs.acs.org
Reposted by Shozeb
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· May 28

SAND: a comprehensive annotation of class D β-lactamases using structural alignment-based numbering | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Class D β-lactamases (DBLs) form a large family with nearly 1,300 identified members in the β-Lactamase Database (Fig. S1, www.bldb.euhttp://www.bldb.eu/) (1). They are produced mainly by Gram-negative bacteria, with some by Gram-positive bacteria (2). DBLs are an important mechanism of resistance to β-lactam antibiotics, including carbapenems, one of last resort treatments to infections in hospitalized patients (3). The production of class D β-lactamases is a major public health concern, as they can often transfer between different bacterial species, allowing resistance to spread quickly and widely. Some members were found to be membrane-bound and are secreted via outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) to contribute further in antimicrobial resistance dissemination (4). Their mechanism of action involves a catalytic serine, as in classes A and C β-lactamases, since all share the conserved SXXK tetrad and KXG triad (3).
journals.asm.org
Shozeb
@shozebhaider.bsky.social
· May 28

SAND: a comprehensive annotation of class D β-lactamases using structural alignment-based numbering | Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy
Class D β-lactamases (DBLs) form a large family with nearly 1,300 identified members in the β-Lactamase Database (Fig. S1, www.bldb.euhttp://www.bldb.eu/) (1). They are produced mainly by Gram-negative bacteria, with some by Gram-positive bacteria (2). DBLs are an important mechanism of resistance to β-lactam antibiotics, including carbapenems, one of last resort treatments to infections in hospitalized patients (3). The production of class D β-lactamases is a major public health concern, as they can often transfer between different bacterial species, allowing resistance to spread quickly and widely. Some members were found to be membrane-bound and are secreted via outer membrane vesicles (OMVs) to contribute further in antimicrobial resistance dissemination (4). Their mechanism of action involves a catalytic serine, as in classes A and C β-lactamases, since all share the conserved SXXK tetrad and KXG triad (3).
journals.asm.org