Knowledge, attitudes, and practices (KAP) regarding nutrition among bodybuilders of Zanjan, Northwest of Iran: a cross-sectional study - BMC Sports Science, Medicine and Rehabilitation
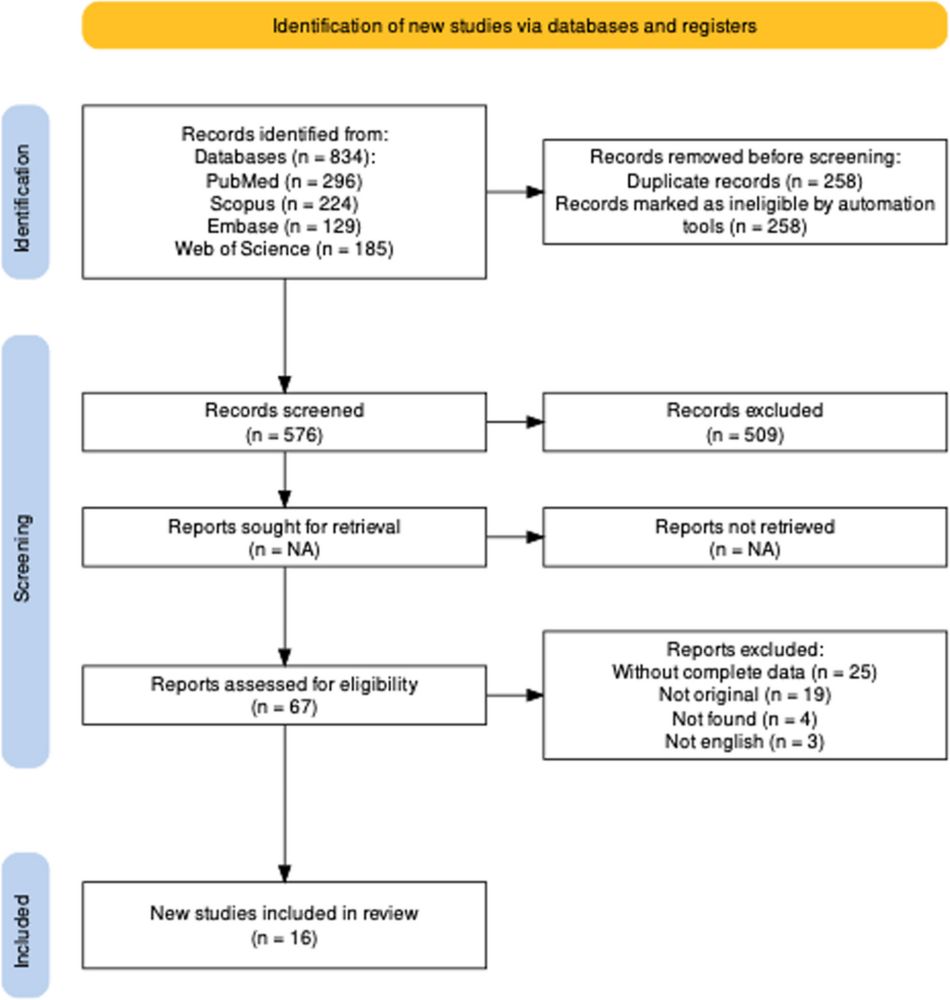
Our study aimed to investigate the relationship of knowledge, attitude, and practice towards nutrition (KAP) with socio-demographic and anthropometric factors among bodybuilders in Zanjan, Iran, in 2019. In three parts, we performed a cross-sectional study of 220 male bodybuilders across Zanjan City, Iran. First, we assessed the KAP of our athletes with a standard survey questionnaire of KAP. Subsequently, socio-demographic variables were assessed using a self-reported questionnaire, while anthropometric measurements, including height, weight, and BMI, were obtained through standardized and. A total of 220 male bodybuilders participated in our study. The mean nutrition knowledge (NK) score was 86.33, indicating a good level of knowledge among participants. Marital status and education, use of supplements, supplement usage, nutritional interventions provided by a registered nutritionist, bodybuilding history, and smoking had no significant relationship with KAP. Alcohol consumption showed no significant correlation with knowledge, attitude, or practice. Age was positively correlated with attitude, while no significant correlation was found with knowledge or practice. BMI exhibited a significant inverse correlation with practice, but no significant correlation was observed with knowledge or attitude. Our results showed that the NK of bodybuilders in Zanjan city of Iran was good, and there was no significant relevance between socio-demographic factors and KAP, except for alcohol consumption. This demonstrates a substantial NK gap among bodybuilders regarding alcohol use and supplement use, necessitating nutritional education programs for athletes. Not applicable.