Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
68 followers
81 following
26 posts
Group Leader, Uppsala University 🇸🇪 |
Studying brain tumor evolution and treatment resistance
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Veronica Rendo
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Mar 19
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Mar 19
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Mar 19
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Mar 19
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Mar 19
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Mar 19
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Mar 19

Recurrent breakpoints in the BRD4 locus reduce toxicity associated with gene amplification
Wala et al. identify recurrent focal BRD4 deletions in tumors harboring larger amplifications,
suggesting that these deletions may serve to limit toxic BRD4 overexpression. A CRISPR-Cas9
cell line mod...
www.cell.com
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Feb 27
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Feb 27
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Feb 19
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Feb 19
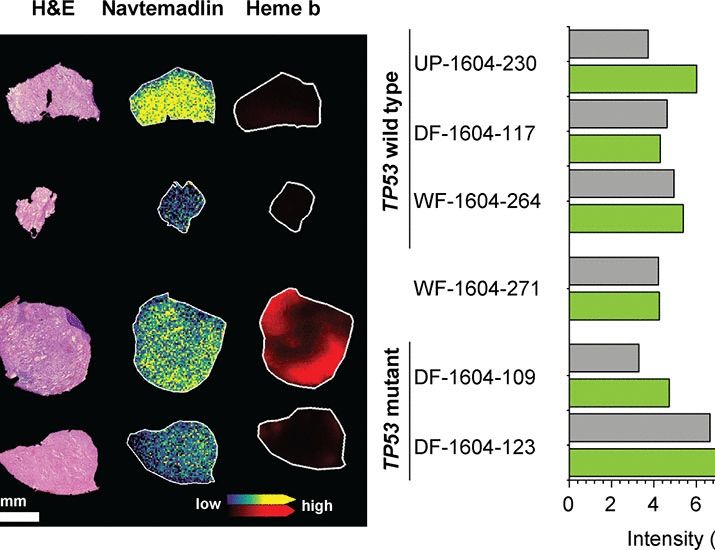
A window-of-opportunity trial reveals mechanisms of response and resistance to navtemadlin in patients with recurrent glioblastoma
In patients with glioblastoma, navtemadlin resistance is not mediated by TP53-inactivating mutations, and combination with TMZ may improve efficacy.
www.science.org
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Jan 27
Veronica Rendo
@vrendo.bsky.social
· Jan 27