Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by wnoble.bsky.social
Reposted by wnoble.bsky.social
Michael MacCoss
@maccoss.bsky.social
· Jun 16
Nature Methods
@natmethods.nature.com
· Jun 16
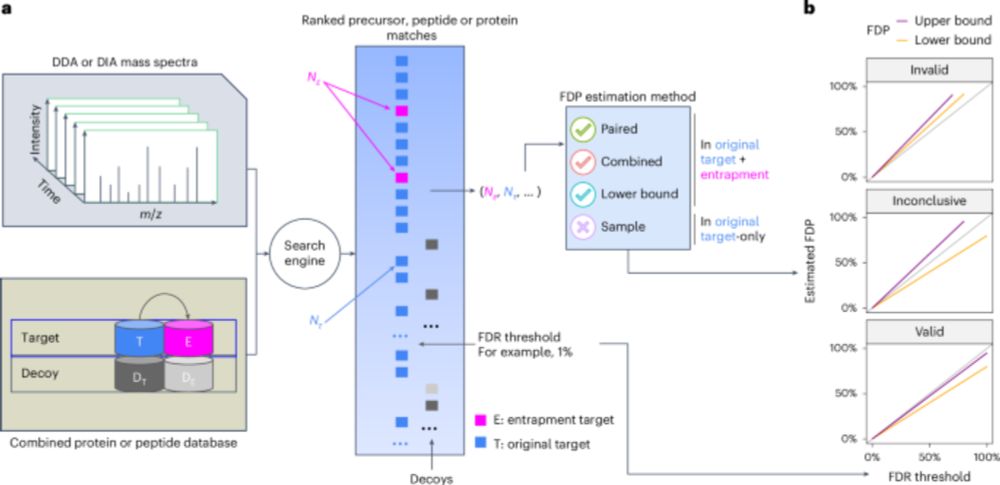
Assessment of false discovery rate control in tandem mass spectrometry analysis using entrapment - Nature Methods
A theoretical foundation for entrapment methods is presented, along with a method that enables more accurate evaluation of false discovery rate (FDR) control in proteomics mass spectrometry analysis p...
www.nature.com
wnoble.bsky.social
@wnoble.bsky.social
· Jun 16
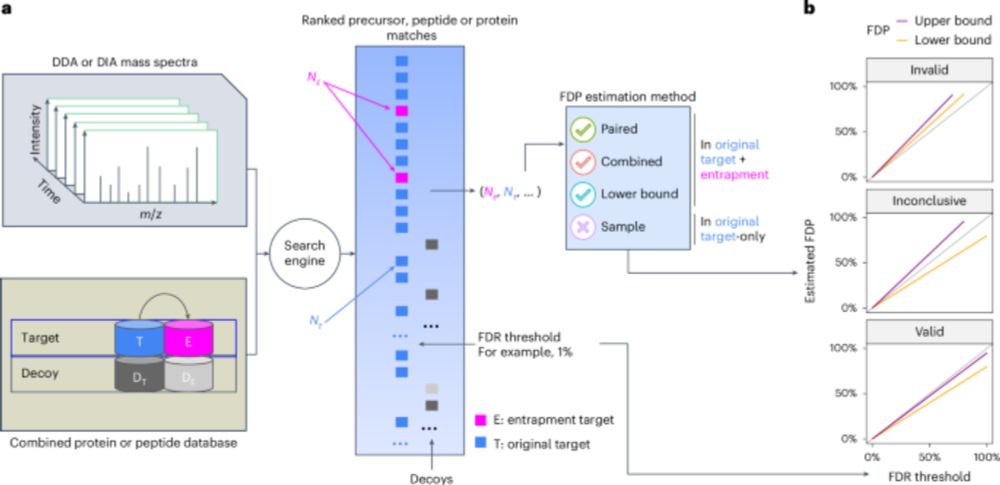
Assessment of false discovery rate control in tandem mass spectrometry analysis using entrapment - Nature Methods
A theoretical foundation for entrapment methods is presented, along with a method that enables more accurate evaluation of false discovery rate (FDR) control in proteomics mass spectrometry analysis p...
www.nature.com
wnoble.bsky.social
@wnoble.bsky.social
· May 22

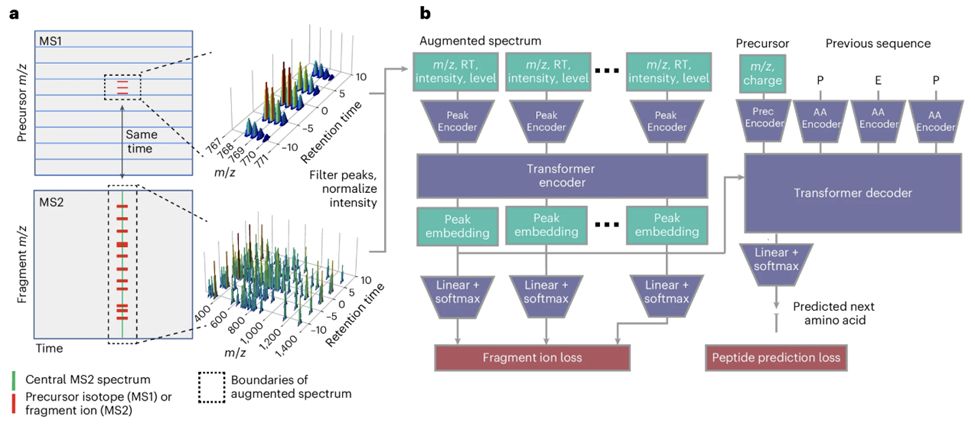
Foundation model for mass spectrometry proteomics
Mass spectrometry is the dominant technology in the field of proteomics, enabling high-throughput analysis of the protein content of complex biological samples. Due to the complexity of the instrument...
arxiv.org
Reposted by wnoble.bsky.social
wnoble.bsky.social
@wnoble.bsky.social
· Dec 21

A generalizable Hi-C foundation model for chromatin architecture, single-cell and multi-omics analysis across species
Nuclear DNA is organized into a compact three-dimensional (3D) structure that impacts critical cellular processes. High-throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) is the most widely used method...
tinyurl.com
wnoble.bsky.social
@wnoble.bsky.social
· Nov 12
Wrangling a de novo sequencing benchmark
In any machine learning study, high quality data for training and validating the model is critical. This paper describes the result of an iterative process of data wrangling and quality control, which...
communities.springernature.com
wnoble.bsky.social
@wnoble.bsky.social
· Oct 26