Fiona H. Marshall
Fiona Hamilton Marshall is a British pharmacologist, biotech-founder and President of Biomedical Research at Novartis. She founded and previously served… more
Source: Wikipedia

H-index:
60
Pleased to see this academic-industry collaboration lead to a new, AI-enabled view of MS disease progression that could potentially accelerate drug development and enhance the precision of clinical treatments for patients living with this disease. #AI www.nature.com/articles/s41...

AI-driven reclassification of multiple sclerosis progression - Nature Medicine
Using large cohorts from published clinical trials involving more than 8,000 patients with multiple sclerosis, a probabilistic machine learning model reconstructs the transition probabilities from dat...
www.nature.com
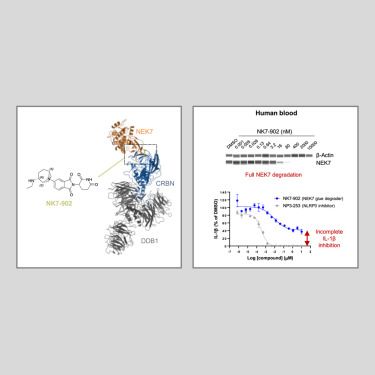
Congratulations to the Novartis-led research team behind this @cp-cellchembiol.bsky.social paper. Their findings shed light on the context-specific nature of NEK7 inhibition of the NLRP3 #inflammasome via a novel molecular glue degrader. #TPD
Excited to see this work in @natchembio.nature.com from our Novartis teams. They report the discovery of a small molecule that binds pVHL, functioning as a molecular glue degrader. The findings suggest new opportunities to leverage VHL molecular glues.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#SciSky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
#SciSky

A small-molecule VHL molecular glue degrader for cysteine dioxygenase 1 - Nature Chemical Biology
High-content protein arrays were used to identify cysteine dioxygenase (CDO1) as a small-molecule glue target for the von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) E3 ubiquitin ligase and induces VHL-dependent proteasomal ...
www.nature.com
Recent findings from our Oncology group in @nature.com point to potential new therapeutic possibilities for targeting RAS signalling. Fascinating work that advances understanding of this critical pathway. #SciSky #MedSky
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
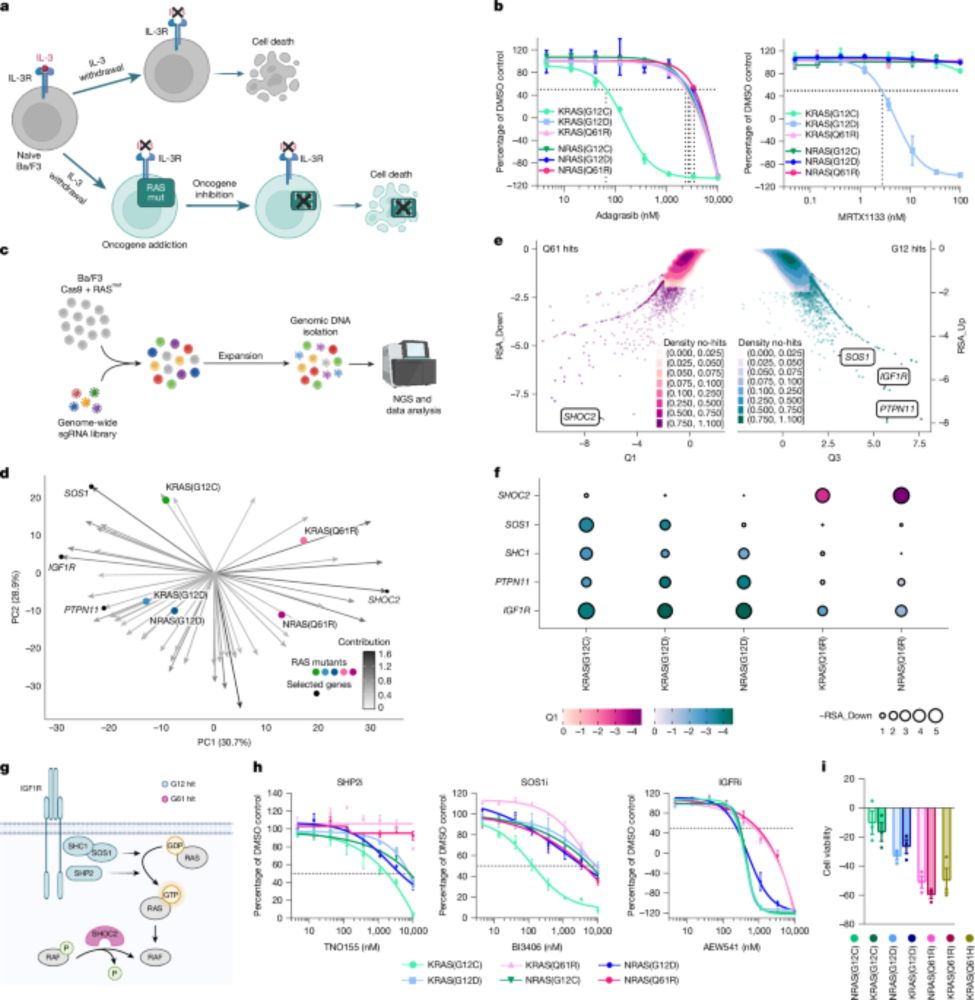
Targeting the SHOC2–RAS interaction in RAS-mutant cancers - Nature
A study of dependencies associated with cancer-causing mutations has identified a small molecule that binds to SHOC2 and inhibits RAS signalling in cells carrying NRAS Q61 mutations, a common onc...
www.nature.com
Intriguing @nature.com perspective piece from @uoft.bsky.social and academic collaborators on the promise of multimodal models. Truly highlights the potential of recent breakthroughs in computational modeling to harness multi-omics datasets and accelerate discovery. www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Towards multimodal foundation models in molecular cell biology - Nature
The development of multimodal foundation models, pretrained on diverse omics datasets, to unravel the intricate complexities of molecular cell biology is envisioned.
www.nature.com
Cell paper revealing a fascinating mechanism of HECT E3 ligase inhibition through an allosteric pocket - great combination of HTS and structure based design - shows the power of scientific collaboration. www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...

Therapeutic potential of allosteric HECT E3 ligase inhibition
A large, unbiased biochemical screen discovers inhibitors of SMURF1 that reverse established
pulmonary arterial hypertension by extending an α helix over a conserved glycine hinge
to restrict the esse...
www.cell.com
Congratulations to the authors of this paper investigating mGluR5 inhibition as a potential clinical approach in cocaine use disorder. Great science and important findings the research community can build on to further understand glutamate signaling in abuse disorders www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
New insights on the mechanisms underlying GPCR specificity in this paper from Science Advances, with relevance to ligand design and drug development targeting GPCR subtypes. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

Structure and dynamics determine G protein coupling specificity at a class A GPCR
Structural and conformational changes determine GPCR signaling bias and G protein coupling specificity.
www.science.org
Well worth spending time studying this paper which highlights key role of microglia in Alzheimer’s disease.
Reposted by: Fiona H. Marshall
A study in Nature Medicine shows the mechanisms driving amyloid-β clearance in both passively and actively Aβ immunized patients with Alzheimer’s disease. #alzsky 🧪
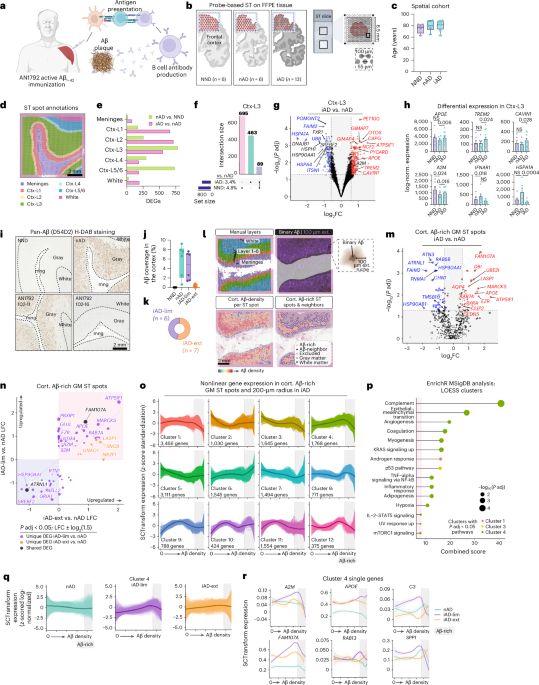
Microglial mechanisms drive amyloid-β clearance in immunized patients with Alzheimer’s disease - Nature Medicine
Spatial transcriptomics reveals distinct microglial mechanisms driving amyloid-β clearance in both passively and actively immunized patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
go.nature.com
I’m excited to share this excellent @natrevimmunol.bsky.social article from our Novartis Immunology team and colleagues on immune reset, its evolution and outlook in #therapeutics. Thank you to Richard Siegel and Tobias Junt for spearheading this important publication. www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Defining immune reset: achieving sustained remission in autoimmune diseases - Nature Reviews Immunology
New immunotherapies have the potential to mediate a sustained remission from certain autoimmune diseases. This has been referred to as achieving an ‘immune reset’ in patients. Here, Junt and colleague...
www.nature.com
Fascinating insight that AFib has a strong genetic component - opening up potential new therapeutic approaches. Congratulations to our own Steven Lubitz and all the other collaborators on this important paper. www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Sequencing in over 50,000 cases identifies coding and structural variation underlying atrial fibrillation risk - Nature Genetics
Analyses of genome and exome sequencing data identify rare coding and structural variants associated with atrial fibrillation and highlight genetic links between atrial fibrillation and cardiomyopathi...
www.nature.com
Excellent new review from David Gloriam shows why GPCRs continue to be of great interest for drug discovery. Therapies directed at 30 novel targets now in clinical trials.

GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications - Nature Reviews Drug Discovery
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are one of the largest families of drug targets. This Review analyses drug discovery trends for GPCRs, covering compounds, targets and indications that have reached...
www.nature.com
Another UK Biobank data analysis investigates the impact of environmental and genetic factors on aging and age related diseases.
bsky.app/profile/mrcl... Excited to see a new spin out from @mrclmb.bsky.social
UK Biobank data continues to provide useful insight into difficult to treat diseases. Could these very early markers point to strategies for disease prevention?

Large-scale proteomic analyses of incident Parkinson’s disease reveal new pathophysiological insights and potential biomarkers - Nature Aging
The early pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease is not well understood. Here the authors perform large-scale proteomic analyses of incident Parkinson’s disease to reveal pathophysiological insights a...
www.nature.com
Reposted by: Fiona H. Marshall
New UK-based LMB spinout company, Sortera Bio, launched to realise the therapeutic potential of Deep Screening technology developed by Ben Porebski and Philipp Holliger.
Read more: www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/sortera-bio-...
#LMBNews #drugdiscovery #therapeutics #spinout
Read more: www2.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/sortera-bio-...
#LMBNews #drugdiscovery #therapeutics #spinout