In this IPD-MA we show that single-gene transcripts are equivalent to multi-gene signatures to Dx subclinical TB
They perform consistently across settings + show potential clinical utility to stratify therapy
#IDsky #TBsky
bit.ly/47jU7GN

In this IPD-MA we show that single-gene transcripts are equivalent to multi-gene signatures to Dx subclinical TB
They perform consistently across settings + show potential clinical utility to stratify therapy
#IDsky #TBsky
bit.ly/47jU7GN
In this IPD-MA we show that single-gene transcripts are equivalent to multi-gene signatures to Dx subclinical TB
They perform consistently across settings + show potential clinical utility to stratify therapy
#IDsky #TBsky
bit.ly/47jU7GN

In this IPD-MA we show that single-gene transcripts are equivalent to multi-gene signatures to Dx subclinical TB
They perform consistently across settings + show potential clinical utility to stratify therapy
#IDsky #TBsky
bit.ly/47jU7GN
#TBSky
#TBSky

Men are at higher risk of #tuberculosis v women- but unclear how much driven by higher infection vs progression to disease. We meta-analysed Mtb immunoreactivity surveys to find out more🧵 #tbsky
Men are at higher risk of #tuberculosis v women- but unclear how much driven by higher infection vs progression to disease. We meta-analysed Mtb immunoreactivity surveys to find out more🧵 #tbsky
Worrying stuff
#TBSky #IDSky @nejm.org
www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/...
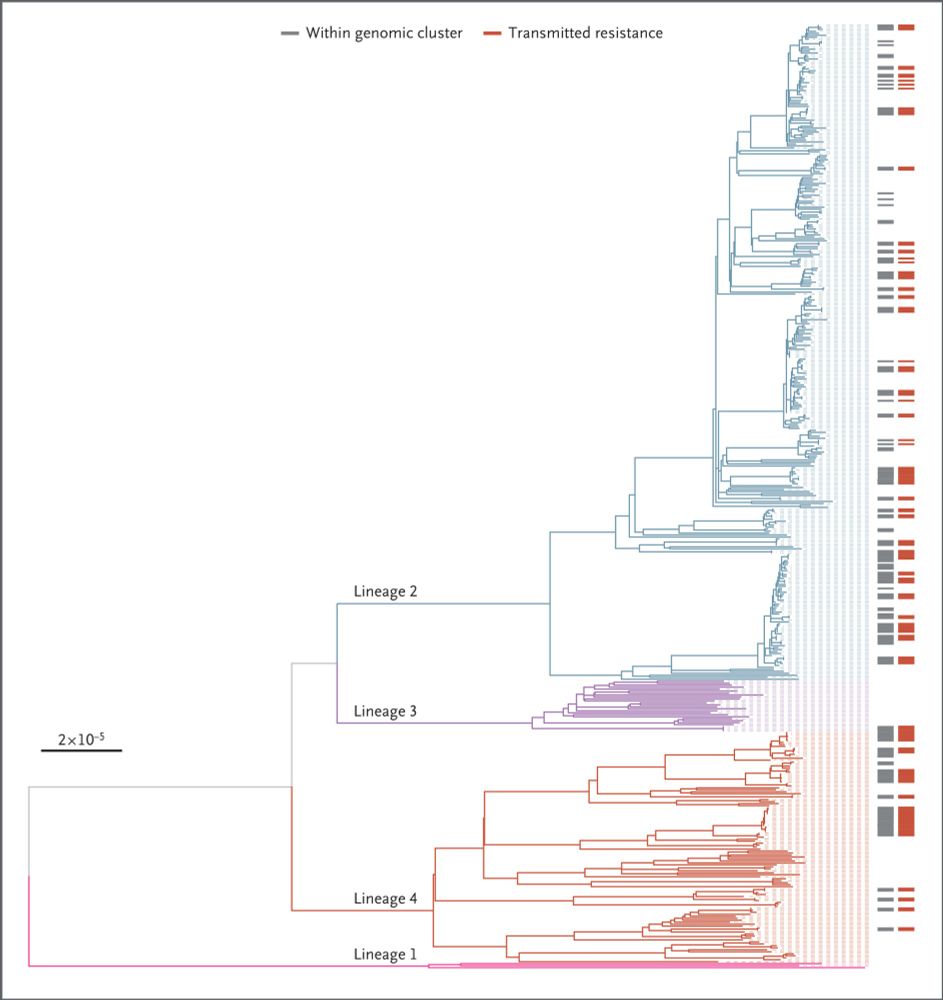
Worrying stuff
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
CRP achieved marginal albeit statistically significant discrimination/AUROC 0.69(95%CI 0.52–0.87) #idsky #medsky #tbsky
publications.ersnet.org/content/erj/...

CRP achieved marginal albeit statistically significant discrimination/AUROC 0.69(95%CI 0.52–0.87) #idsky #medsky #tbsky
publications.ersnet.org/content/erj/...

MX1 expression occurred early in infection before PCR detection…potential role to stratify treatment
#IDSky
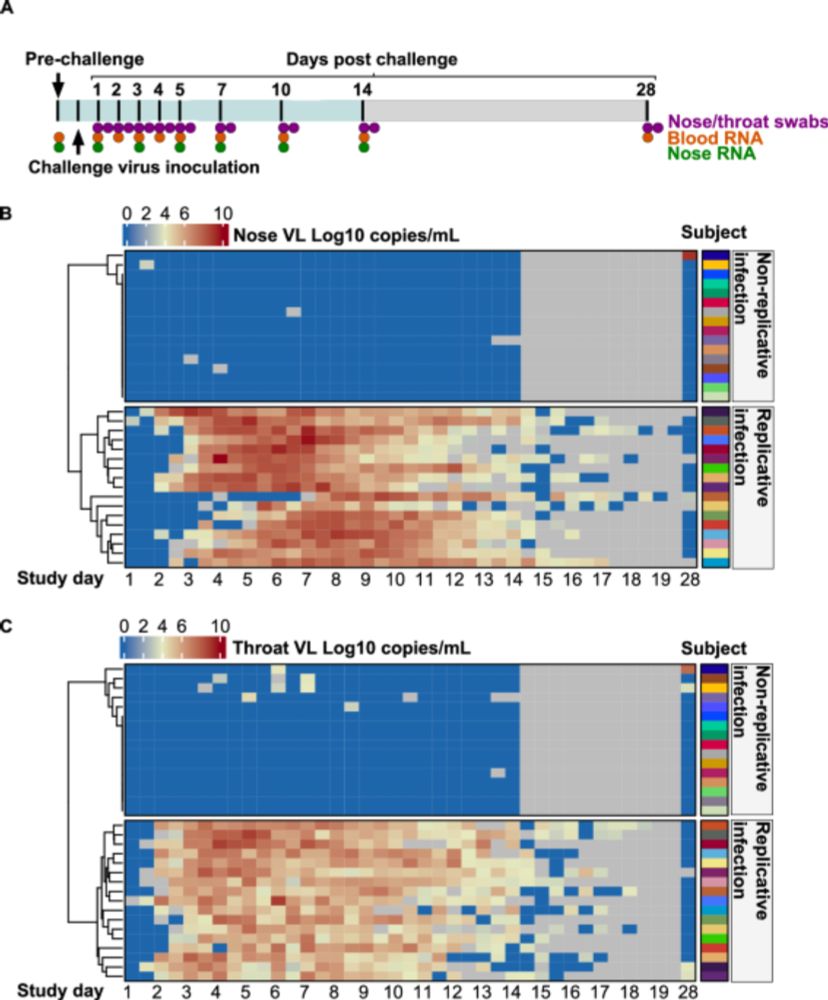
MX1 expression occurred early in infection before PCR detection…potential role to stratify treatment
#IDSky
Very cool study - lots to be learnt from the past…
#TBSky
715,000 people (76% of entire adult population) were X-rayed over just 5 weeks!
In a new study, we looked at the long-term impact of this campaign. journals.plos.org/plosmedicine...
#episky #idsky 🧪🛟

Very cool study - lots to be learnt from the past…
#TBSky
Some personal highlights (in no particular order):
1/10
Some personal highlights (in no particular order):
1/10

