
Kevin Zemaitis
@kevinzemaitis.bsky.social
84 followers
130 following
39 posts
Staff scientist @EMSL within @PNNL originally from @UBChemistry. Spatial multiomics by mass spectrometry (FTMS rules, everything else drools). Tweets are mine, and are random.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Kevin Zemaitis
@kevinzemaitis.bsky.social
· May 23
Kevin Zemaitis
@kevinzemaitis.bsky.social
· Apr 14
Advanced multi-modal mass spectrometry imaging reveals functional differences of placental villous compartments at microscale resolution #NatCommun www.nature.com/articles/s41...

Advanced multi-modal mass spectrometry imaging reveals functional differences of placental villous compartments at microscale resolution - Nature Communications
Spatial multi-omics methodologies are essential for capturing the molecular heterogeneity of complex biological systems. In this study, the authors introduce a multi-omics imaging workflow capable of ...
www.nature.com
Kevin Zemaitis
@kevinzemaitis.bsky.social
· Jan 28
Kevin Zemaitis
@kevinzemaitis.bsky.social
· Dec 26
Reposted by Kevin Zemaitis
Chris Anderton ⚜️
@anderton.bsky.social
· Dec 22
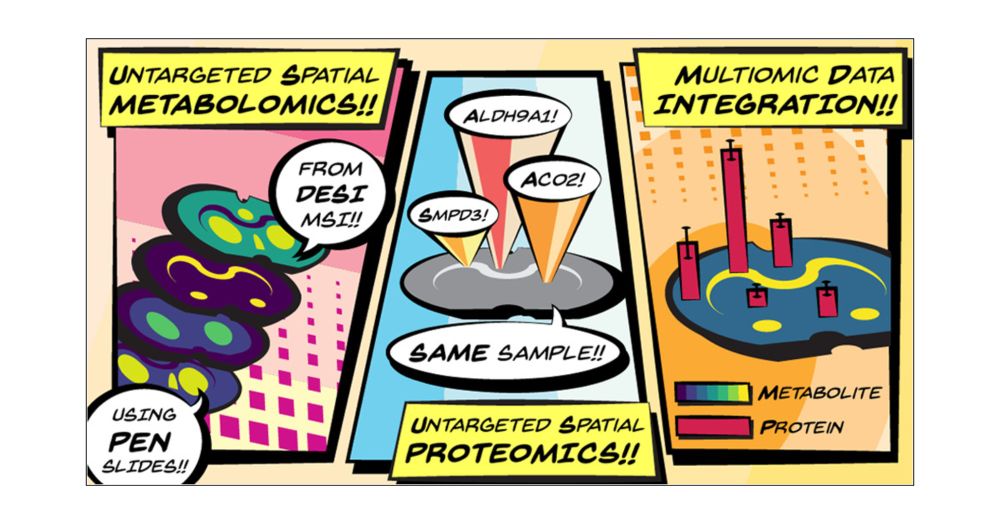
Untargeted Spatial Metabolomics and Spatial Proteomics on the Same Tissue Section
An increasing number of spatial multiomic workflows have recently been developed. Some of these approaches have leveraged initial mass spectrometry imaging (MSI)-based spatial metabolomics to inform the region of interest (ROI) selection for downstream spatial proteomics. However, these workflows have been limited by varied substrate requirements between modalities or have required analyzing serial sections (i.e., one section per modality). To mitigate these issues, we present a new multiomic workflow that uses desorption electrospray ionization (DESI)-MSI to identify representative spatial metabolite patterns on-tissue prior to spatial proteomic analyses on the same tissue section. This workflow is demonstrated here with a model mammalian tissue (coronal rat brain section) mounted on a poly(ethylene naphthalate)-membrane slide. Initial DESI-MSI resulted in 160 annotations (SwissLipids) within the METASPACE platform (≤20% false discovery rate). A segmentation map from the annotated ion images informed the downstream ROI selection for spatial proteomics characterization from the same sample. The unspecific substrate requirements and minimal sample disruption inherent to DESI-MSI allowed for an optimized, downstream spatial proteomics assay, resulting in 3888 ± 240 to 4717 ± 48 proteins being confidently directed per ROI (200 μm × 200 μm). Finally, we demonstrate the integration of multiomic information, where we found ceramide localization to be correlated with SMPD3 abundance (ceramide synthesis protein), and we also utilized protein abundance to resolve metabolite isomeric ambiguity. Overall, the integration of DESI-MSI into the multiomic workflow allows for complementary spatial- and molecular-level information to be achieved from optimized implementations of each MS assay inherent to the workflow itself.
pubs.acs.org























