

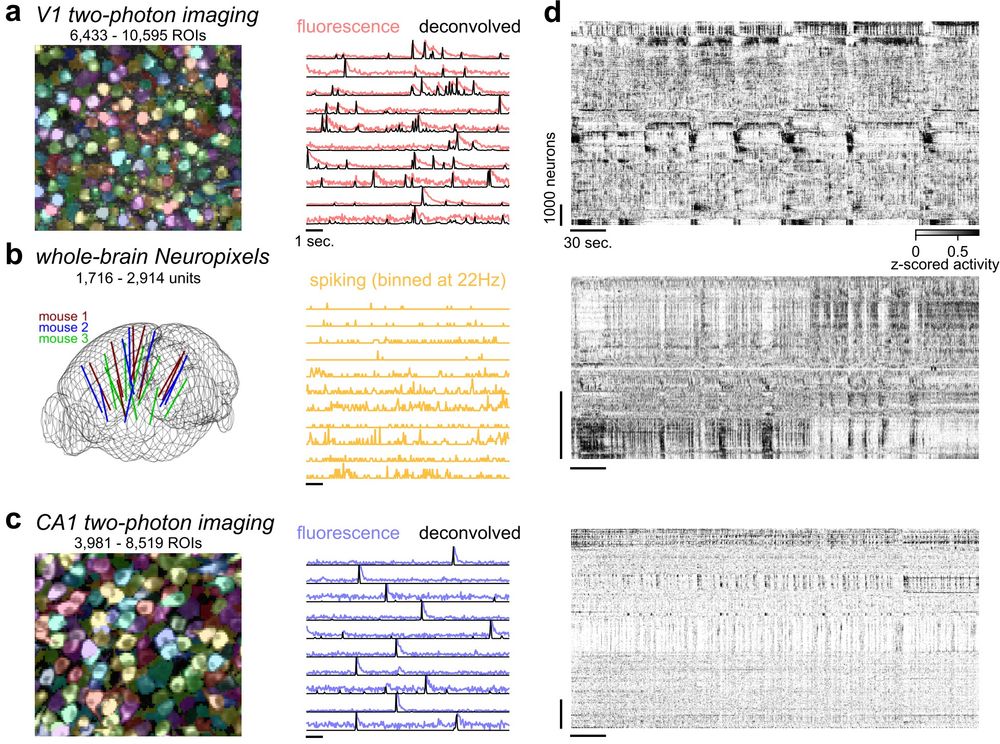
www.vox.com/future-perfe...

www.vox.com/future-perfe...
news.ucsc.edu/2025/10/lear...

news.ucsc.edu/2025/10/lear...
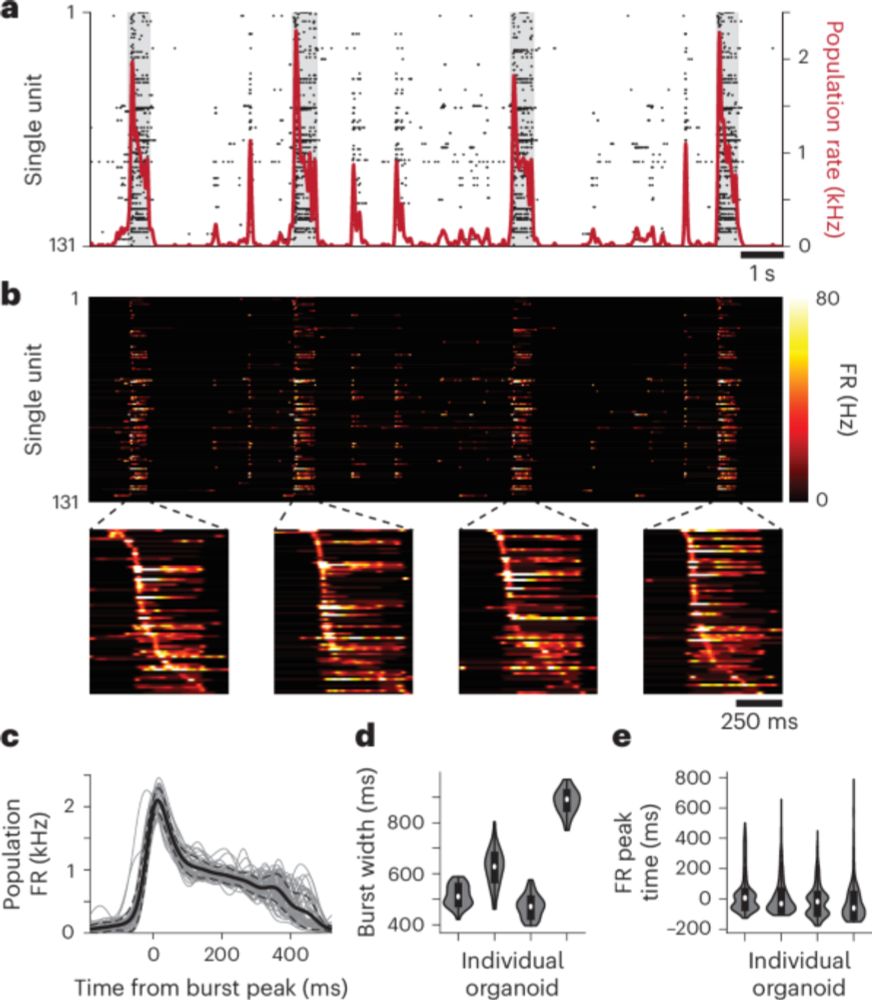
Goal-directed learning in cortical #organoids
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...

Goal-directed learning in cortical #organoids
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...


