Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
430 followers
1.1K following
28 posts
The goal of our research is to understand how brain states shape decision-making, and how this process goes awry in certain neurological & psychiatric disorders
| tobiasdonner.net | University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf, Germany
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14

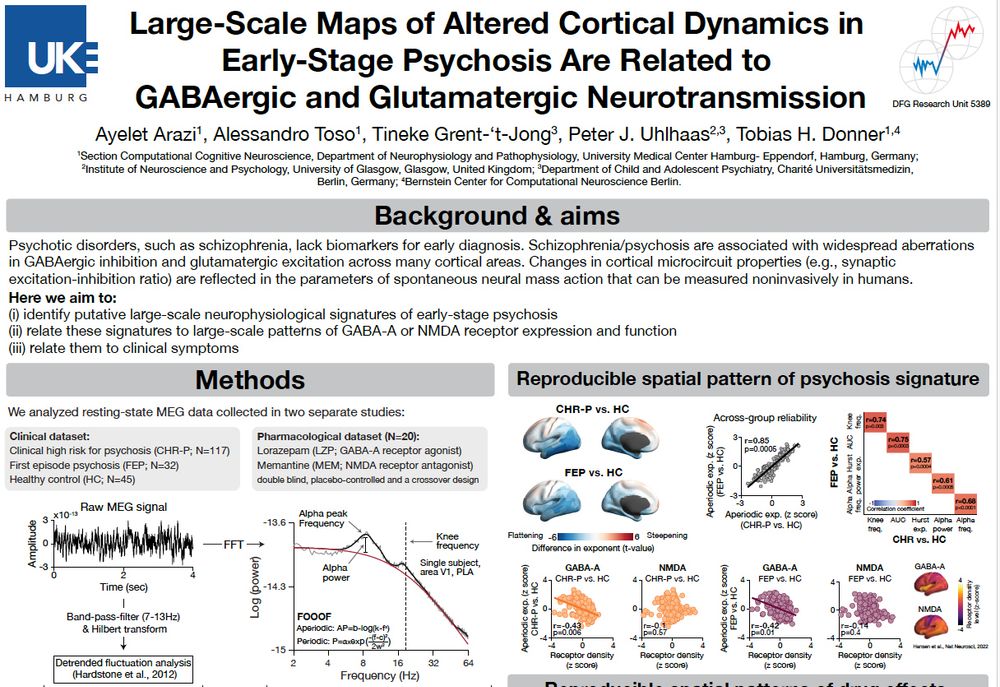
Large-scale maps of altered cortical dynamics in early-stage psychosis are related to GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission
Cortex-wide changes in neural dynamics in early-stage psychosis relate to GABA-A or NMDA receptors and clinical symptoms.
www.science.org
Reposted by Donner Lab
de Gee lab
@degeelab.bsky.social
· Sep 5
Reposted by Donner Lab
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 14

Large-scale maps of altered cortical dynamics in early-stage psychosis are related to GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission
Cortex-wide changes in neural dynamics in early-stage psychosis relate to GABA-A or NMDA receptors and clinical symptoms.
www.science.org
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Jul 12
Reposted by Donner Lab
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Jun 27
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Jun 27
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Jun 27
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Jun 27
Donner Lab
@donnerlab.bsky.social
· Jun 27