Christoph Kaleta
@kaletalab.bsky.social
460 followers
510 following
83 posts
Medical Systems Biology research group - Constraint-based modelling - Modelling of host-microbiome-interactions - Systems Biology of Aging
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Christoph Kaleta
@kaletalab.bsky.social
· May 27

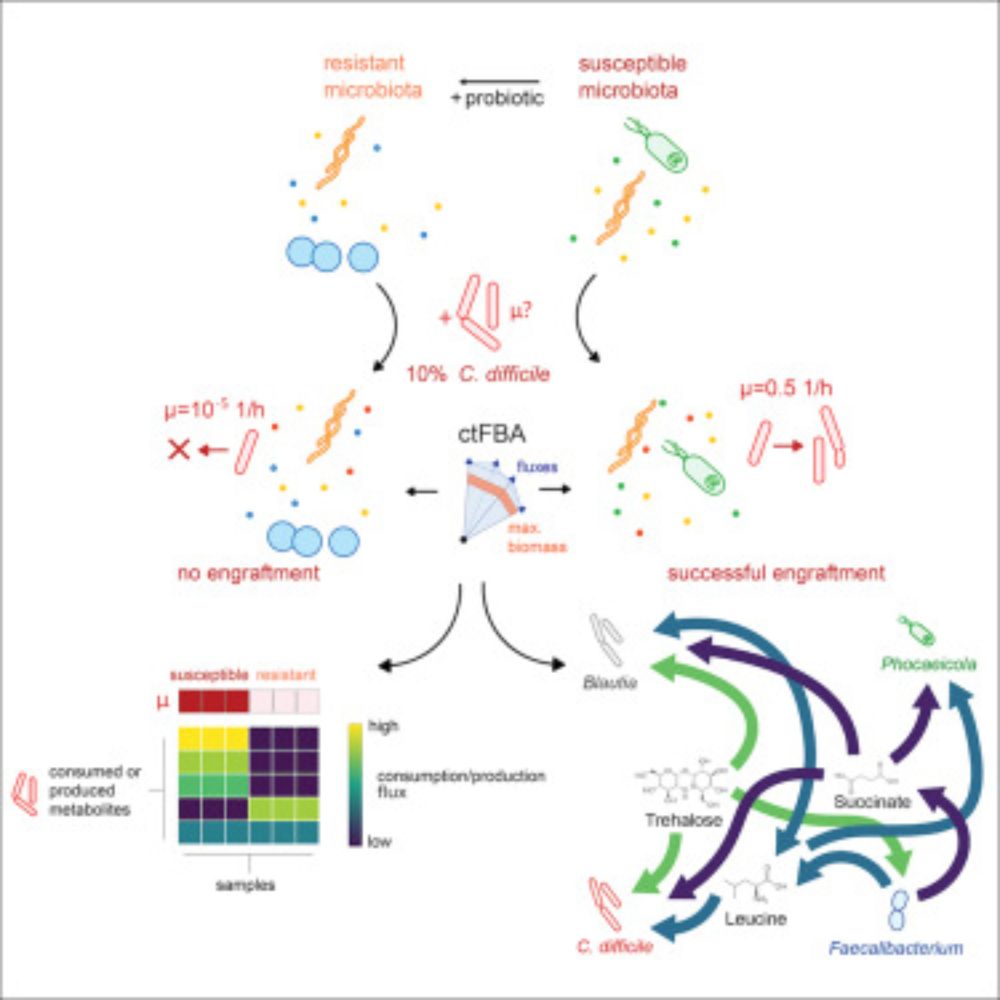
Metabolic modeling elucidates phenformin and atpenin A5 as broad-spectrum antiviral drugs against RNA viruses
Communications Biology - A metabolic modeling approach reveals druggable host cell pathways essential for viral replication across various viruses with minimal cytotoxicity. These findings...
rdcu.be
Reposted by Christoph Kaleta
Reposted by Christoph Kaleta
Reposted by Christoph Kaleta
Reposted by Christoph Kaleta
Reposted by Christoph Kaleta
Sean Gibbons 🦠💩
@gibbological.bsky.social
· Jul 31
Metagenomic estimation of absolute bacterial biomass in the mammalian gut through host-derived read normalization | mSystems
In this study, we asked whether normalization by host reads alone was sufficient to
estimate absolute bacterial biomass directly from stool metagenomic data, without
the need for synthetic spike-ins, ...
journals.asm.org
Christoph Kaleta
@kaletalab.bsky.social
· Jul 22