KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
1.3K followers
290 following
34 posts
Lab of Pekka Katajisto @pekka-katajisto.bsky.social at University of Helsinki and Karolinska Institutet. We study stem cells, aging, metabolism, organelle age and niche interactions https://www.katajisto-lab.com
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Jul 14
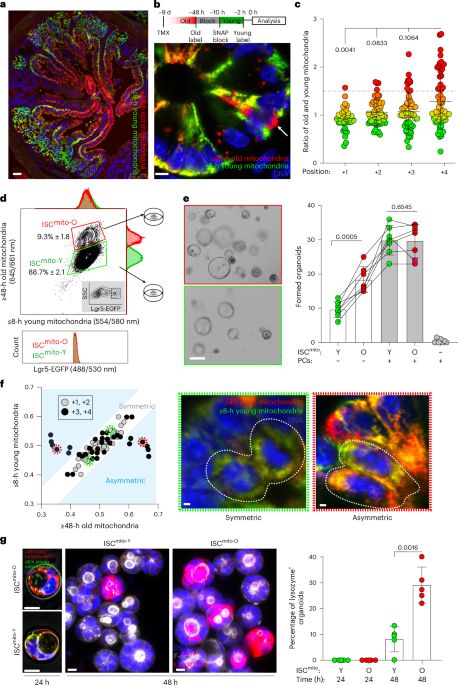
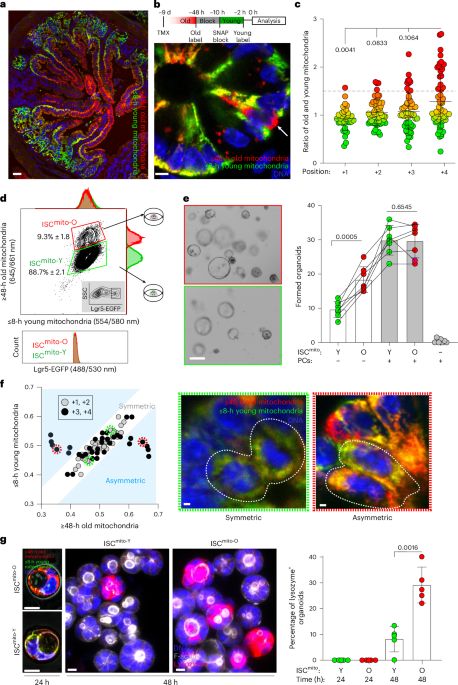
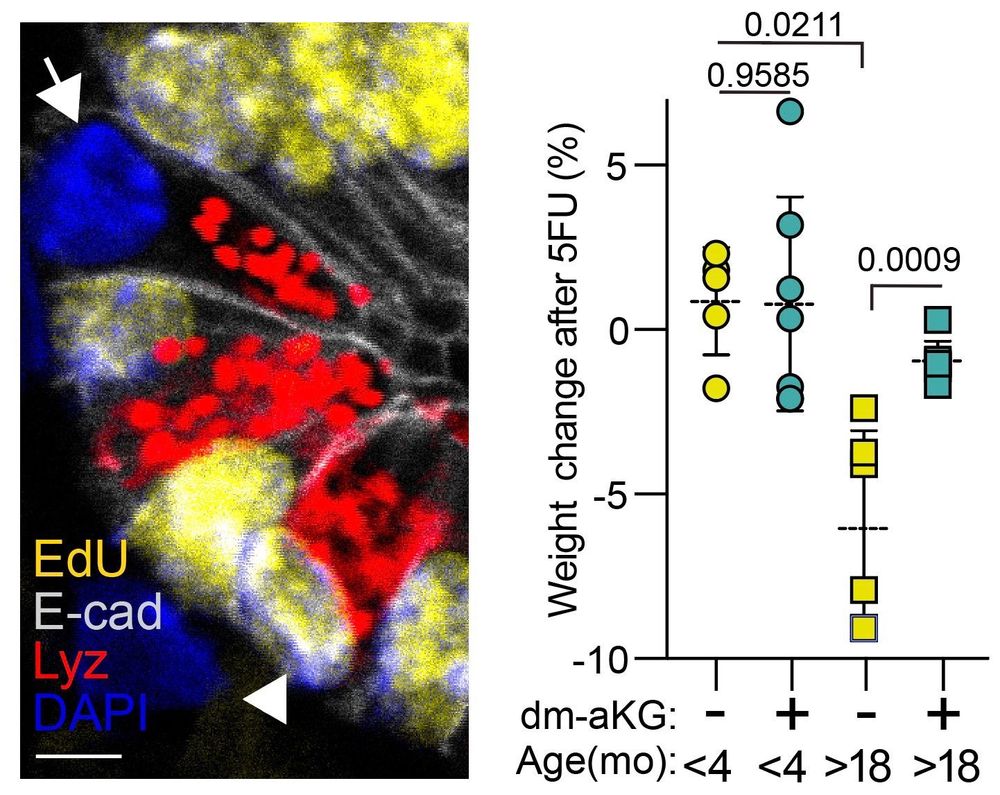
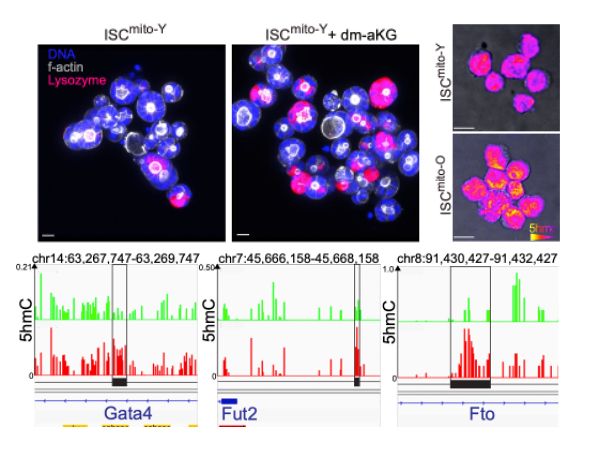
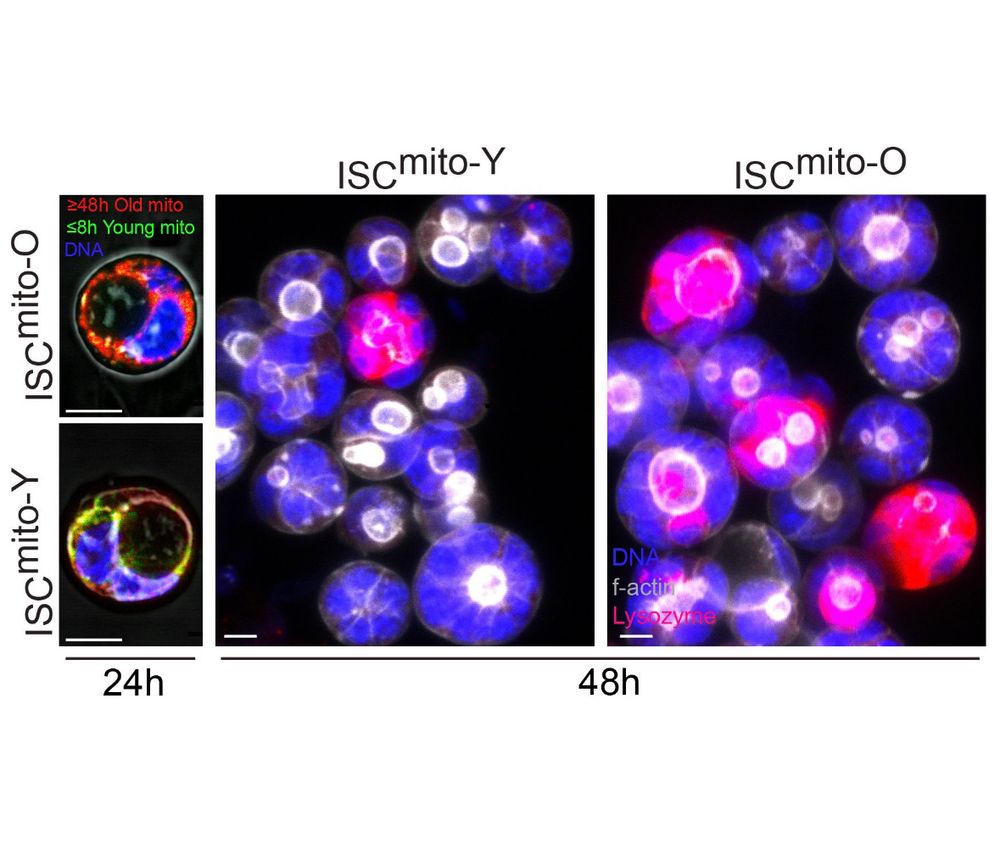
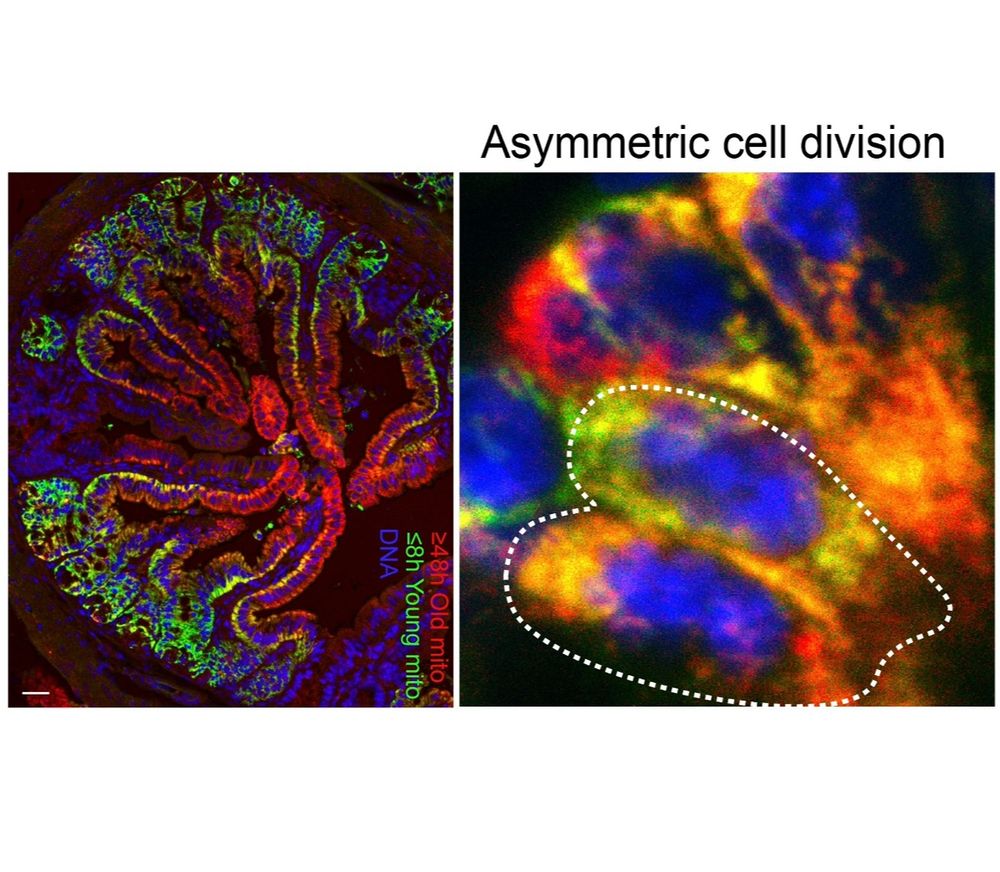
Old mitochondria regulate niche renewal via α-ketoglutarate metabolism in stem cells - Nature Metabolism
Andersson et al. show that intestinal stem cells enriched for old mitochondria are metabolically distinct and have enhanced ability to regenerate the epithelial niche.
www.nature.com
Reposted by KatajistoLab
Reposted by KatajistoLab
Reposted by KatajistoLab
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Jul 15
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Jul 15
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Jul 14
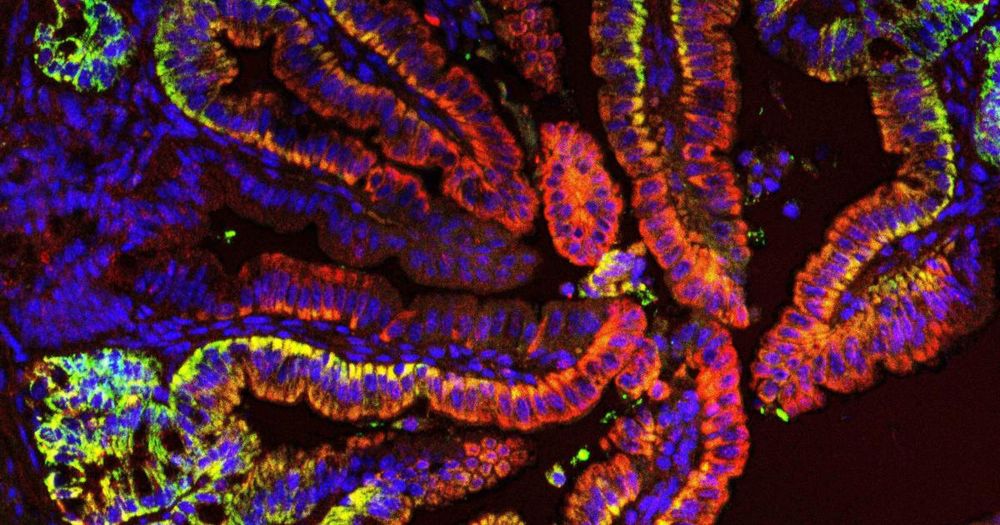
New Type of Intestinal Stem Cell Discovered, Offering Hope for Enhanced Regeneration and Chemotherapy Recovery | HiLIFE – Helsinki Institute of Life Science | University of Helsinki
A team of researchers from the University of Helsinki has discovered a previously unknown type of intestinal stem cell, which supports intestinal regeneration through its metabolically distinct mitoch...
www.helsinki.fi
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Jul 14
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Jul 14
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Jul 14

Old mitochondria regulate niche renewal via α-ketoglutarate metabolism in stem cells - Nature Metabolism
Andersson et al. show that intestinal stem cells enriched for old mitochondria are metabolically distinct and have enhanced ability to regenerate the epithelial niche.
www.nature.com
KatajistoLab
@katajistolab.bsky.social
· Apr 29