John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
1.6K followers
590 following
150 posts
Neuroimmunologist studying MS, autism, Alzheimer's disease, and brain injury at the University of Virginia. Father of two. Fan of Philly sports and US soccer.
www.lukenslab.com
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Sep 3

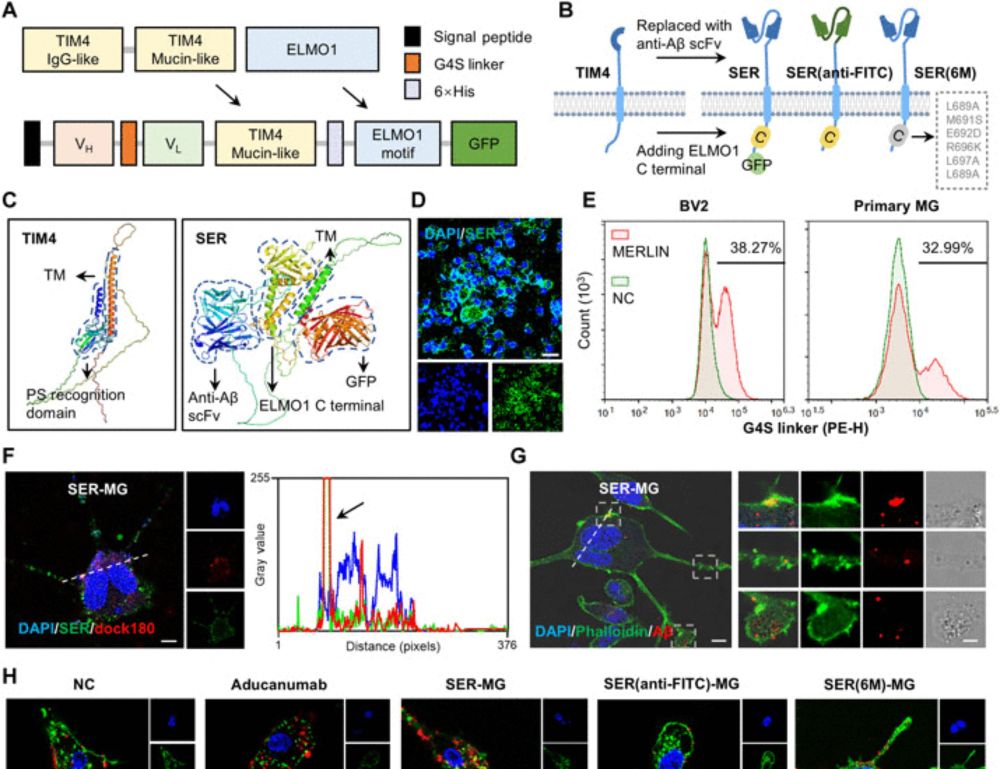
Innate immune sensing of Z-nucleic acids by ZBP1-RIPK1 axis drives neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease
Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation drives Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis,
yet the underlying mechanism is poorly understood. Song et al. demonstrate that toxic
amyloid-β induces oxidation and...
www.cell.com
Reposted by John Lukens
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 29
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 29
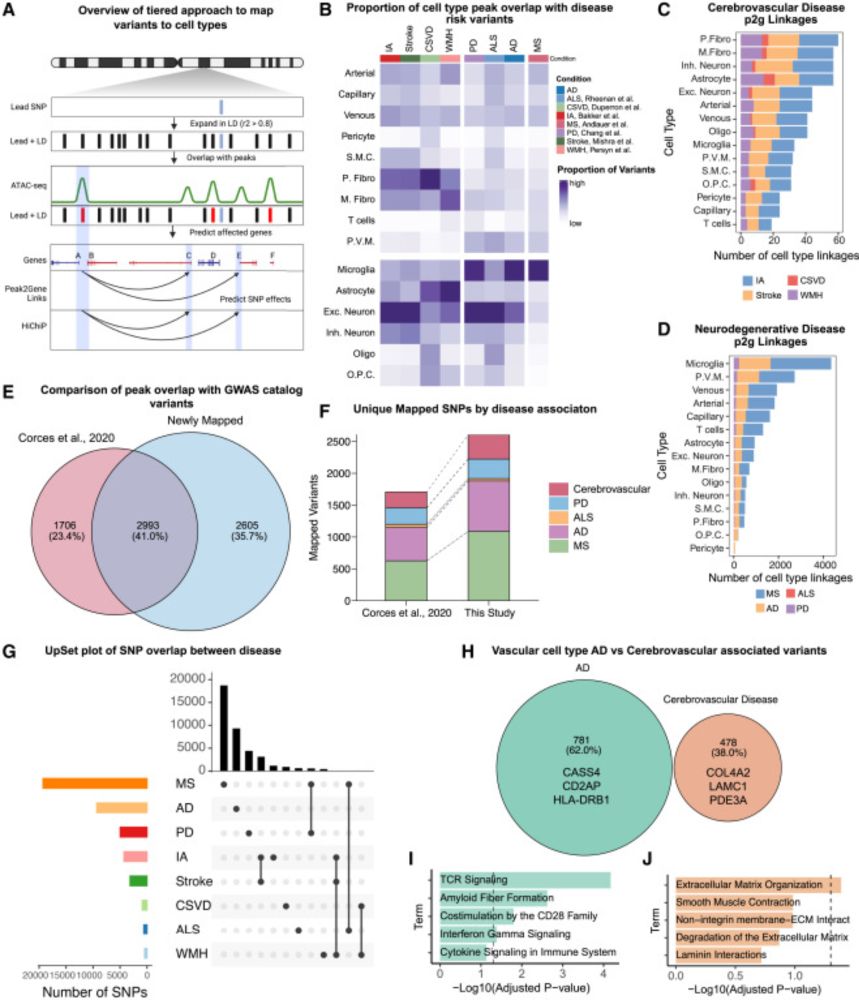
Human brain vascular multi-omics elucidates disease-risk associations
Reid et al. develop MultiVINE-seq to map thousands of non-coding disease variants
to genes in human brain vascular cells. Cerebrovascular disease variants compromise
vessel integrity, whereas Alzheime...
www.cell.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 28
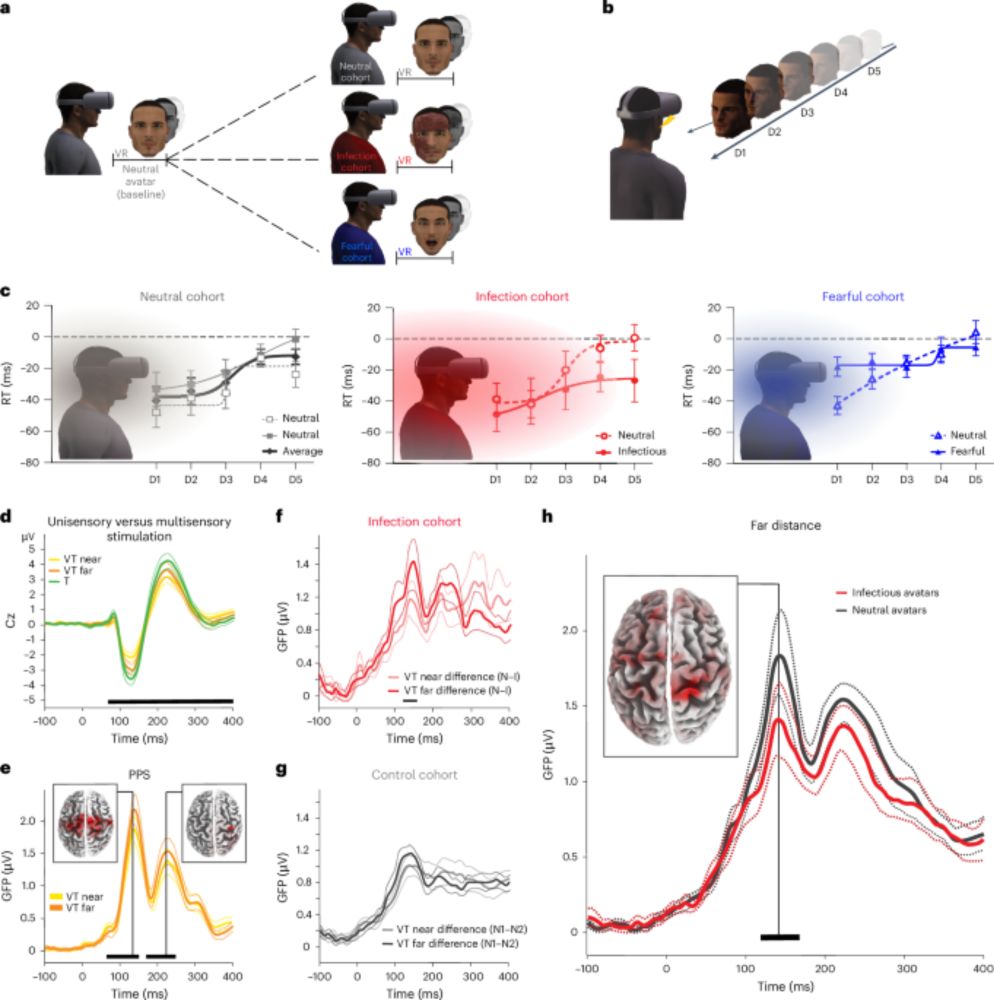
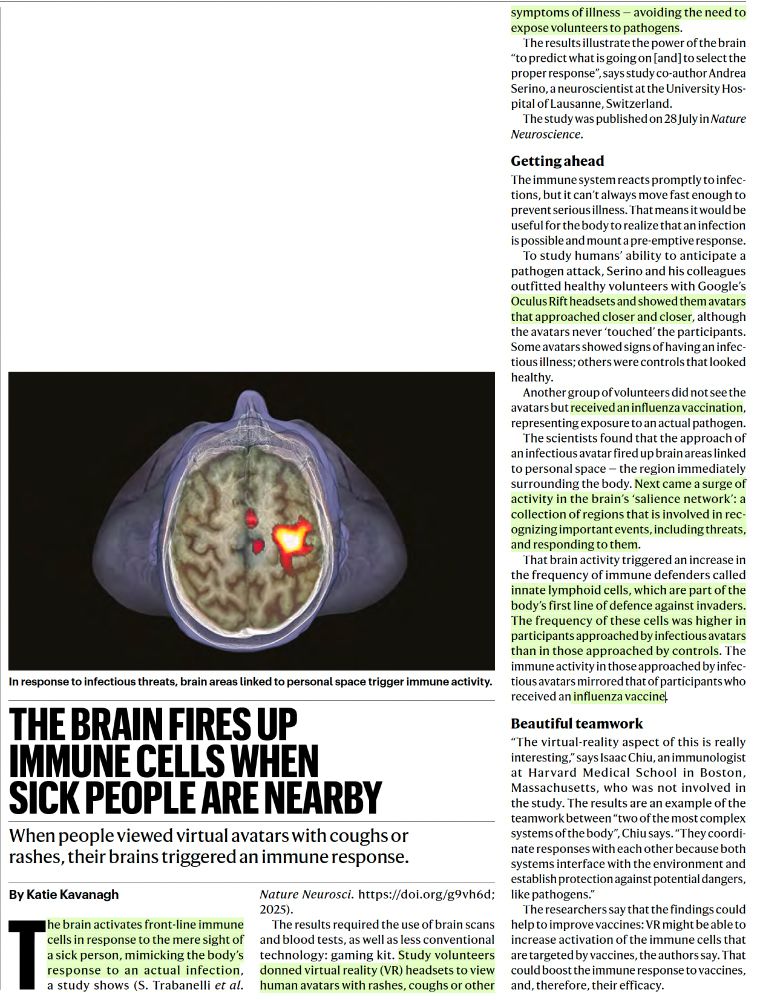
Neural anticipation of virtual infection triggers an immune response - Nature Neuroscience
Serino et al. show that seeing an infectious avatar approach the body in virtual reality triggers an immune response, indicating that the brain prepares the body to fight infections even for perceived...
www.nature.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 26
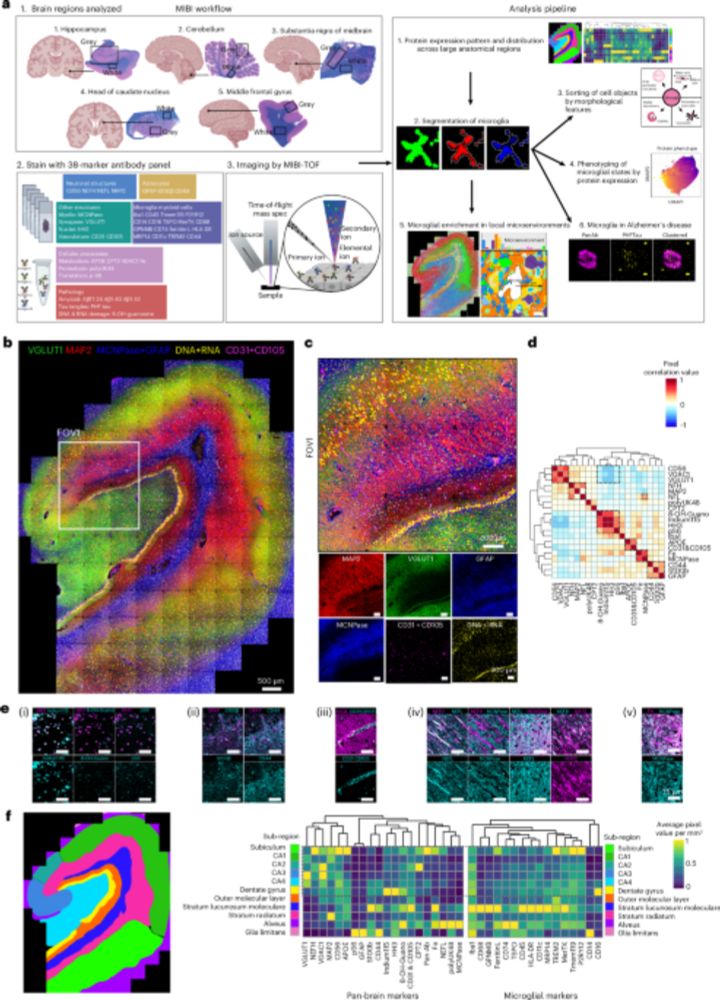
Spatial proteomics of Alzheimer’s disease-specific human microglial states - Nature Immunology
In this Resource paper, the authors use MIBI spatial proteomics to map microglial cell states in brains from cognitively normal humans and those with Alzheimer’s disease.
www.nature.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 25
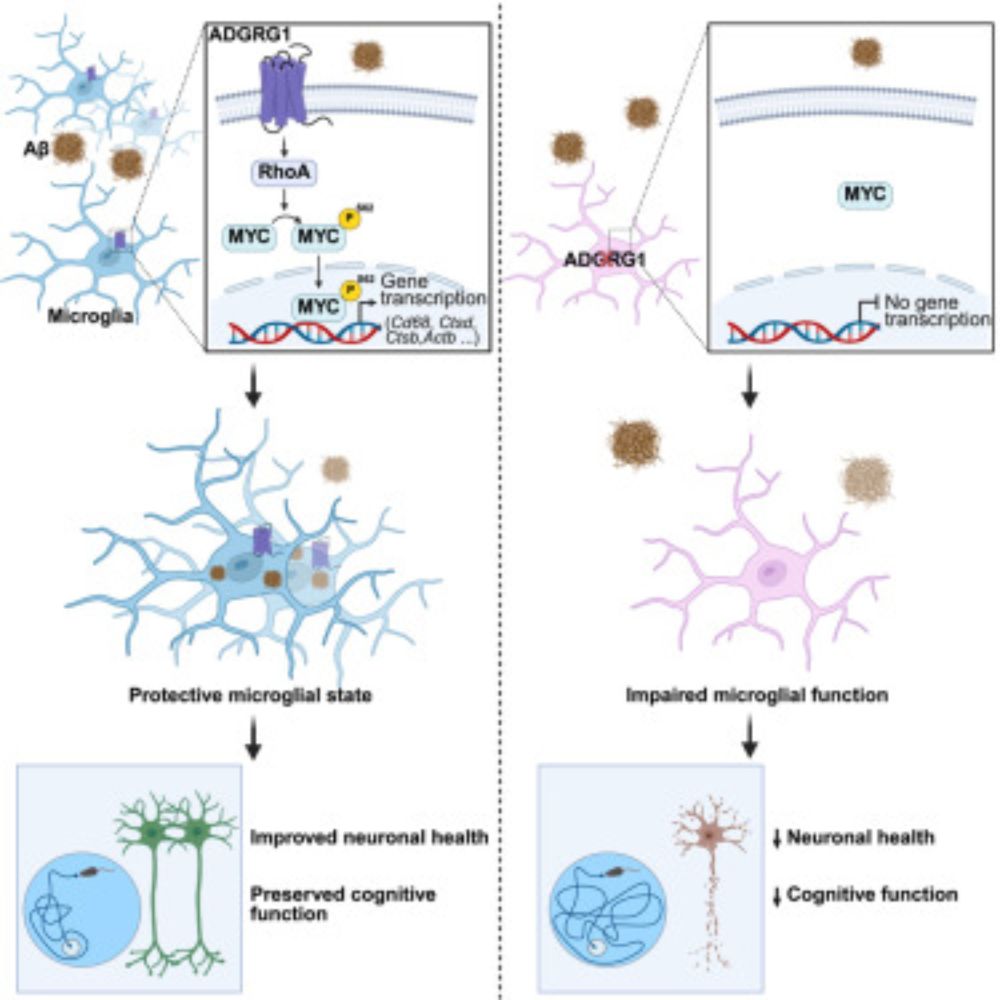
G-protein-coupled receptor ADGRG1 drives a protective microglial state in Alzheimer's disease through MYC activation
Microglial ADGRG1 drives a protective state in Alzheimer’s disease by activating the
transcription factor MYC, which upregulates genes associated with homeostasis, phagocytosis,
and lysosomal function...
www.cell.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 24
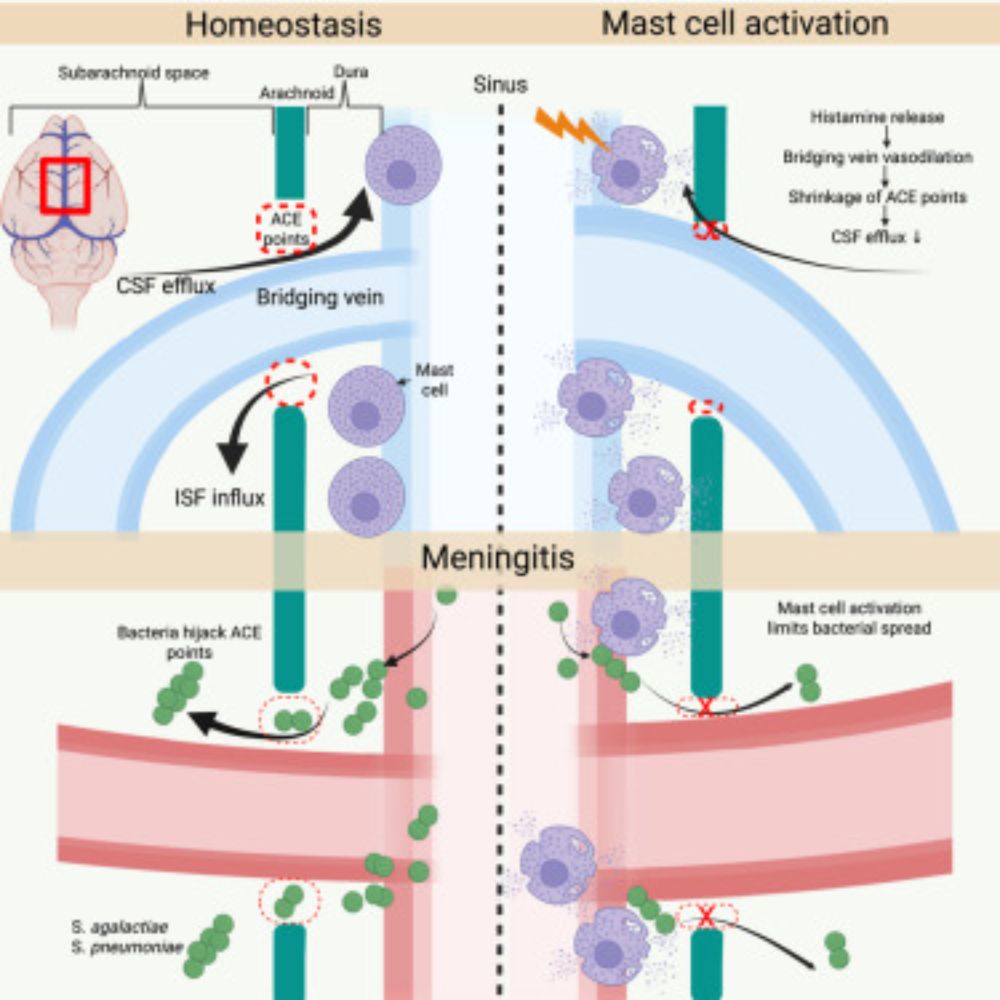
Mast cells regulate the brain-dura interface and CSF dynamics
Dural mast cells control cerebrospinal fluid dynamics at critical brain-dura interfaces,
specifically arachnoid cuff exit points. Their activation limits pathogen brain entry
via histamine-induced vas...
www.cell.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 18
Accelerating biomedical discoveries in brain health through transformative neuropathology of aging and neurodegeneration
Murray et al. introduce “transformative neuropathology” through dynamic, technology-integrated
approaches to accelerate tissue-based discoveries and offer actionable strategies
to strengthen brain ban...
www.cell.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 17
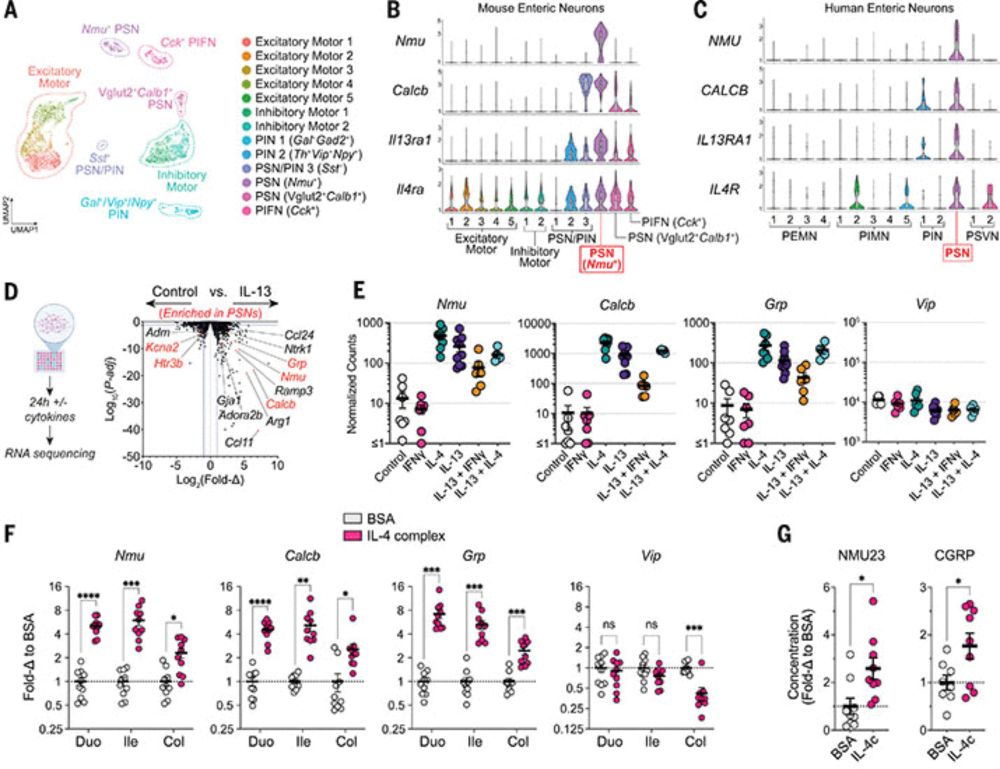
Type 2 cytokines act on enteric sensory neurons to regulate neuropeptide-driven host defense
Enteric nervous system (ENS)–derived neuropeptides modulate immune cell function, yet our understanding of how inflammatory cues directly influence enteric neuron responses during infection is conside...
www.science.org
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 15
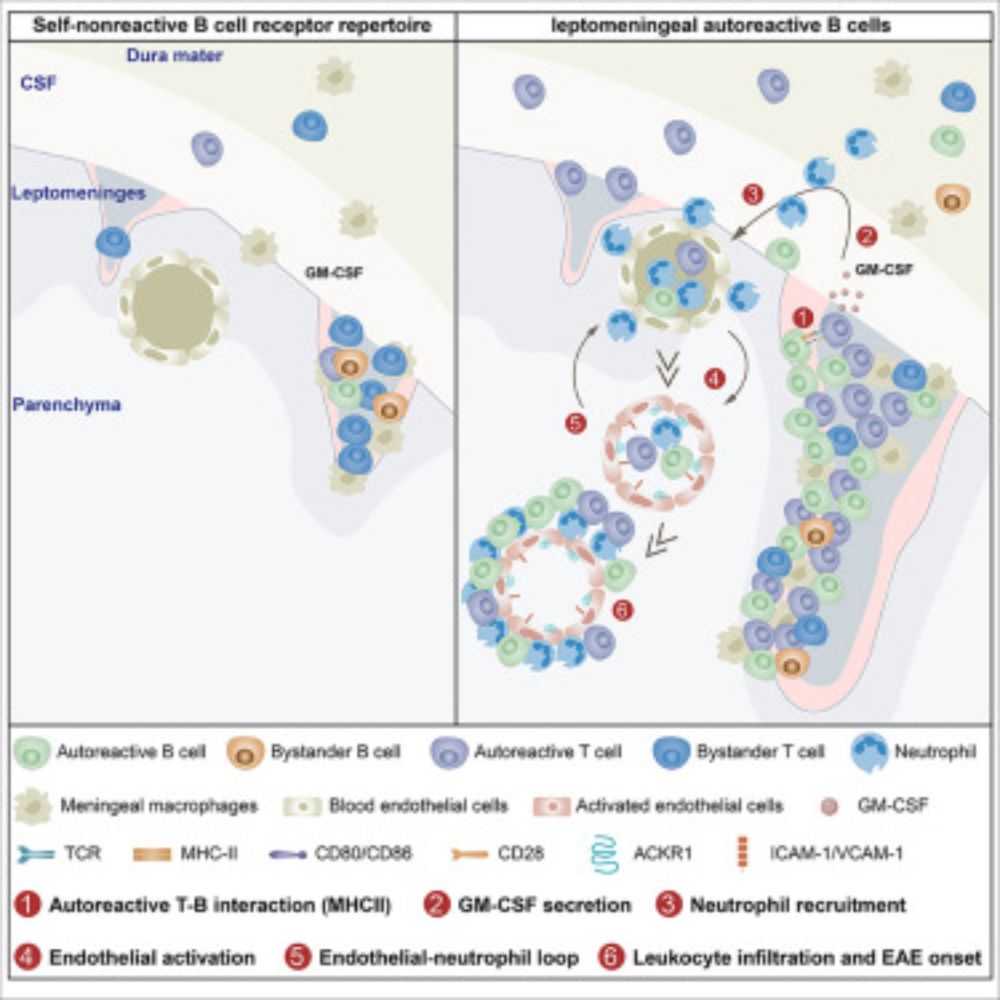
Cognate interaction-dependent pathogenicity of meningeal B cells drives neuroinflammation relapse
The brain meninges maintain self-tolerized B cells, but the pathological consequences
of breaking this tolerance are unknown. Wang et al. reveal that autoreactive leptomeningeal
B cells drive neuroinf...
www.cell.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 10
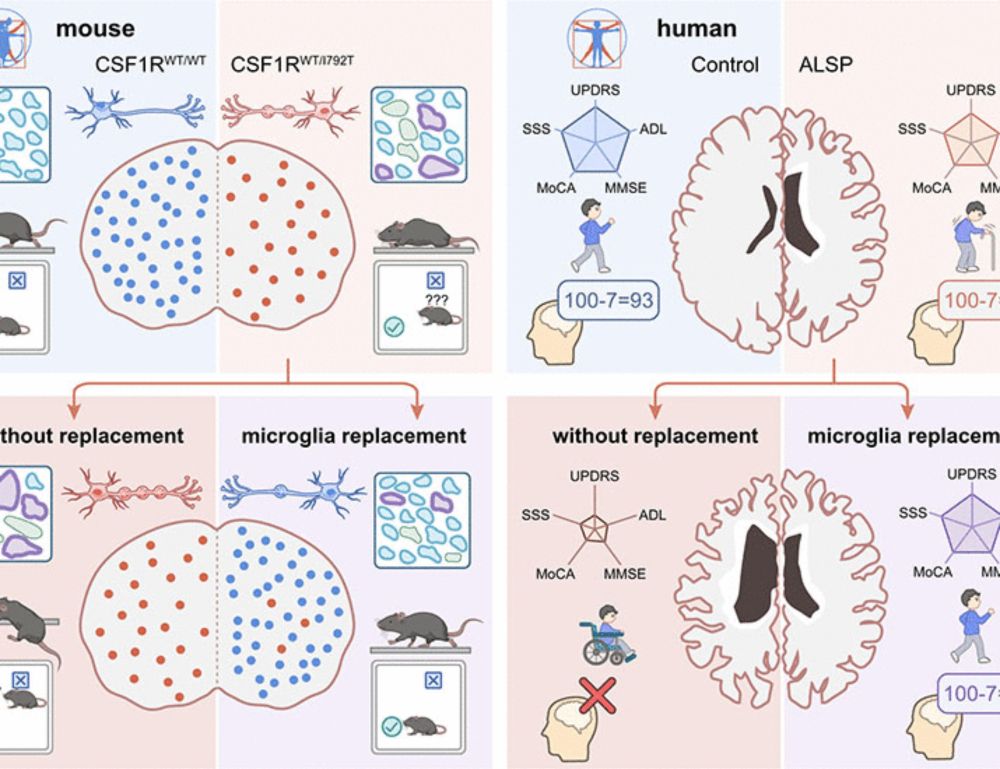
Microglia replacement halts the progression of microgliopathy in mice and humans
Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R) is primarily expressed in microglia. Its monoallelic mutation causes CSF1R-associated microgliopathy (CAMP), a major form of adult-onset leukoencephalopath...
www.science.org
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 7
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 2
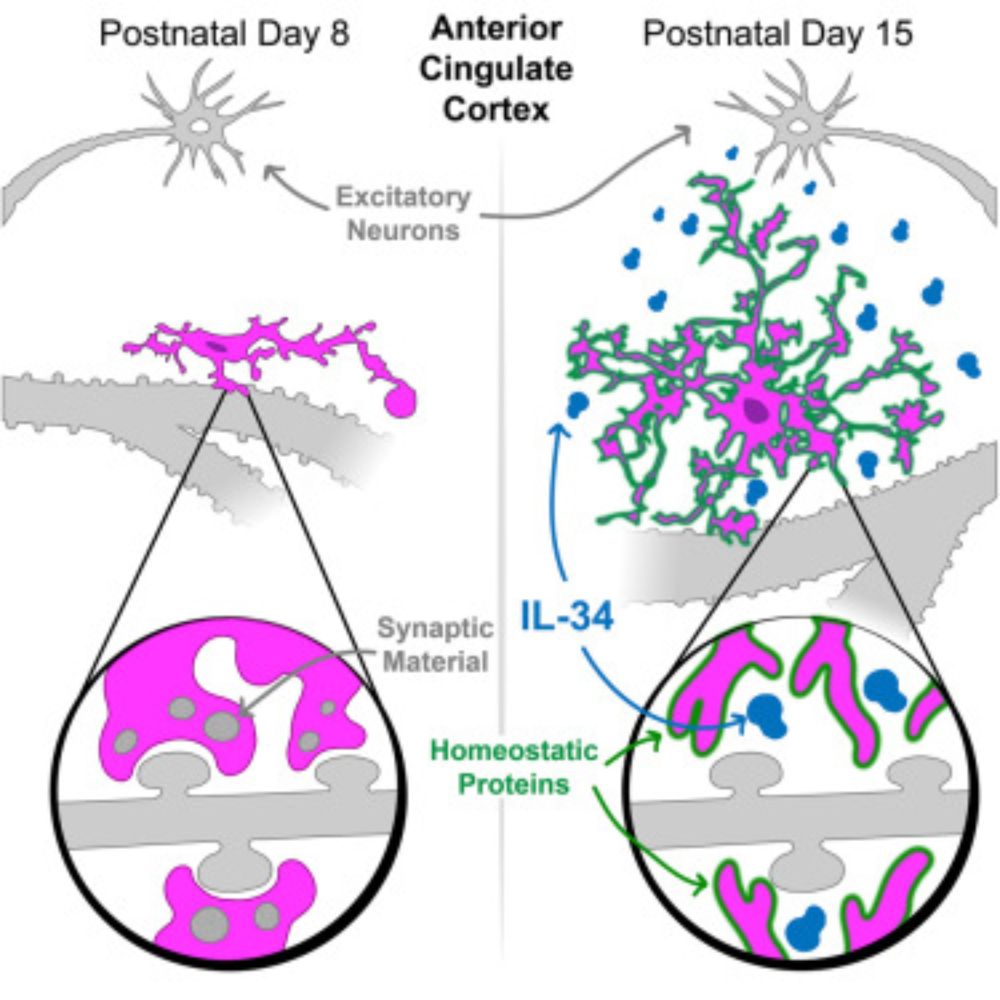
Excitatory-neuron-derived interleukin-34 supports cortical developmental microglia function
While neurons and microglia are known to talk to one another, the signals that regulate
their complex, important interactions are not comprehensively defined. Devlin et al.
find that the cytokine IL-3...
www.cell.com
John Lukens
@lukensjohnr.bsky.social
· Jul 2
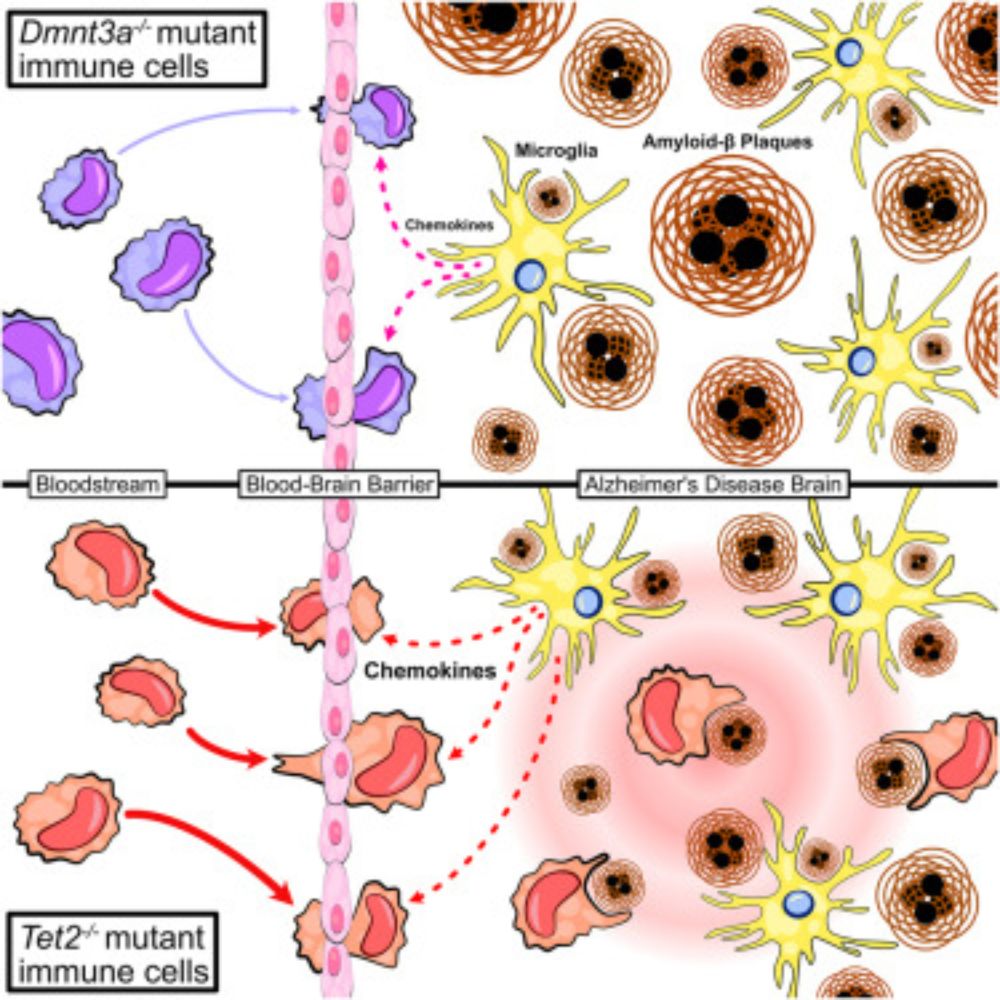
TET2-mutant myeloid cells mitigate Alzheimer’s disease progression via CNS infiltration and enhanced phagocytosis in mice
Matatall et al. uncover a mutation-specific association between clonal hematopoiesis
(CH) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) in mice and humans. TET2-mutant CH conferred lower
odds of AD in humans and reduc...
www.cell.com