
Synergy between cis-regulatory elements can render cohesin dispensable for distal enhancer function
now revised and journal accepted at www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
🧵👇
Synergy between cis-regulatory elements can render cohesin dispensable for distal enhancer function
now revised and journal accepted at www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
🧵👇
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Key findings in a thread (1/6):

www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
Key findings in a thread (1/6):
Discover it in our new Nature paper! We show centromeres transition gradually via a mix of drift, selection, and sex, reaching new states that still work with the kinetochore.
👉 doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09779-1

Discover it in our new Nature paper! We show centromeres transition gradually via a mix of drift, selection, and sex, reaching new states that still work with the kinetochore.
👉 doi.org/10.1038/s41586-025-09779-1
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
tl;dr We identify protein vQTLs in multiple ancestries then use MVMR to show independent effects of mean & variance on disease, suggesting targeting protein variance could have therapeutic potential.



tl;dr We identify protein vQTLs in multiple ancestries then use MVMR to show independent effects of mean & variance on disease, suggesting targeting protein variance could have therapeutic potential.

Check it out, get in touch. We welcome any feedback, suggestions, wishes (& contributions).
It’s been a joy working with you @estellayixingdong.bsky.social!
Check it out, get in touch. We welcome any feedback, suggestions, wishes (& contributions).
It’s been a joy working with you @estellayixingdong.bsky.social!
Read about the 2024 competition in Molecular Biology and Evolution: doi.org/10.1093/molb...
And join the 2025 competition at ghist.bio!

Read about the 2024 competition in Molecular Biology and Evolution: doi.org/10.1093/molb...
And join the 2025 competition at ghist.bio!
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

tomtom-lite is a re-implementation of tomtom targeting the ML age of genomics. Fast annotations ("what is this motif?") and simple large-scale discovery of motifs.
Check it out!
academic.oup.com/bioinformati...
tomtom-lite is a re-implementation of tomtom targeting the ML age of genomics. Fast annotations ("what is this motif?") and simple large-scale discovery of motifs.
Check it out!
academic.oup.com/bioinformati...
(TLDR; low-affinity motifs matter as pioneers!)

(TLDR; low-affinity motifs matter as pioneers!)
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
1/n

www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
1/n
Apply by Dec 15th here: shorturl.at/4a4O6

Apply by Dec 15th here: shorturl.at/4a4O6
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

www.nature.com/articles/d41...

Submissions are open until February 5, 2026.
📥 Submit: https://www.iscb.org/uk2026/call-for-submissions/abstracts

Submissions are open until February 5, 2026.
📥 Submit: https://www.iscb.org/uk2026/call-for-submissions/abstracts
Highly recommended if you're sick of paying Adobe $. Maybe Canva can buy NPG too and get rid of the OA fees.

Highly recommended if you're sick of paying Adobe $. Maybe Canva can buy NPG too and get rid of the OA fees.

www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
If you want to know more, read the 🧵 below:
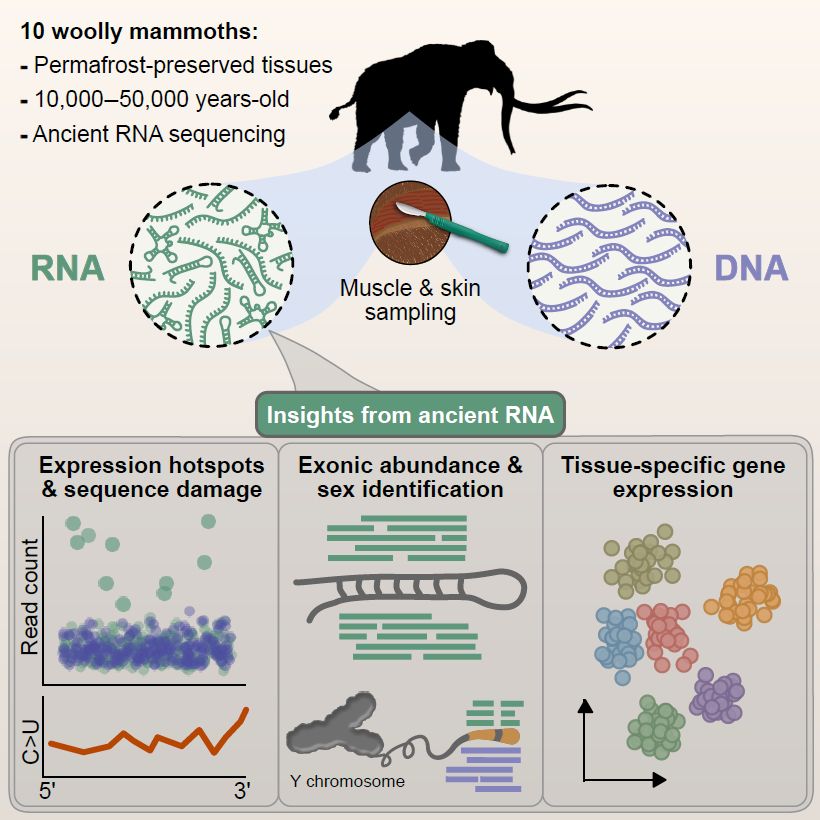
www.cell.com/cell/fulltex...
If you want to know more, read the 🧵 below:

Is it sponges (panels A & B) or comb jellies (C & D) that root the animal tree of life?
For over 15 years, #phylogenomic studies have been divided.
We provide new evidence suggesting that...
🔗: www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

Is it sponges (panels A & B) or comb jellies (C & D) that root the animal tree of life?
For over 15 years, #phylogenomic studies have been divided.
We provide new evidence suggesting that...
🔗: www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
By the great Sohini Ramachandran (@sramach.bsky.social) and your boy for The Boston Globe (@bostonglobe.com).
www.bostonglobe.com/2025/11/14/o...

By the great Sohini Ramachandran (@sramach.bsky.social) and your boy for The Boston Globe (@bostonglobe.com).
www.bostonglobe.com/2025/11/14/o...

