
Turns out many such chemicals, although labelled as 'fungicides' or similar, can inadvertently inhibit friendly gut bacteria.
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

‘Sewers to Seas: exploring pathogens and antimicrobial resistance on microplastics from hospital wastewater to marine environments’
FULL ARTICLE: www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
➡️ Check out @pml.ac.uk’s coverage: pml.ac.uk/news/micropl...

‘Sewers to Seas: exploring pathogens and antimicrobial resistance on microplastics from hospital wastewater to marine environments’
FULL ARTICLE: www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...
➡️ Check out @pml.ac.uk’s coverage: pml.ac.uk/news/micropl...
➡️ theconversation.com/plastic-bio-...
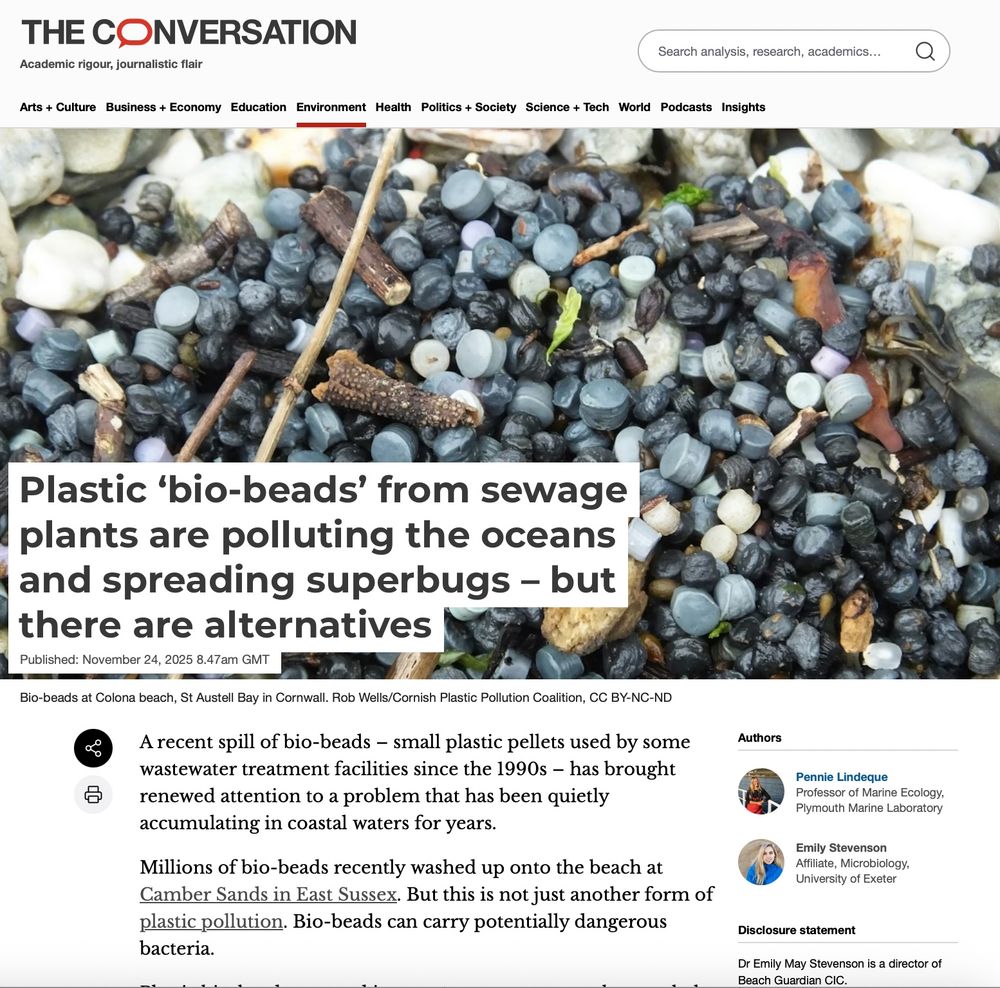
➡️ theconversation.com/plastic-bio-...
There are several opportunities to join the Wild Microbiome Lab in 2026! Scroll for more information, or visit the link below for full project descriptions and application information👇
xavharrison.github.io

There are several opportunities to join the Wild Microbiome Lab in 2026! Scroll for more information, or visit the link below for full project descriptions and application information👇
xavharrison.github.io
www.findaphd.com/phds/project...

www.findaphd.com/phds/project...
Geographics and bacterial networks differently shape the acquired and latent global sewage resistomes
doi.org/10.1038/s414...
Thrilled to share this massive global effort led by H.M. Martiny, @patrickmunk.bsky.social, F. Aarestrup & the Global Sewage Consortium

Geographics and bacterial networks differently shape the acquired and latent global sewage resistomes
doi.org/10.1038/s414...
Thrilled to share this massive global effort led by H.M. Martiny, @patrickmunk.bsky.social, F. Aarestrup & the Global Sewage Consortium
Have a look at our new website to see our confirmed plenary speakers, the mid-conference excursions, and more.
👉 evoxeco.uk 👈

Have a look at our new website to see our confirmed plenary speakers, the mid-conference excursions, and more.
👉 evoxeco.uk 👈
We just did that to study the history of #AMR spread @science.org
doi.org/10.1126/scie...
If you like time travel & biology, this 🧵is for you👇

We just did that to study the history of #AMR spread @science.org
doi.org/10.1126/scie...
If you like time travel & biology, this 🧵is for you👇
We're excited for users who might train new models, find phenotype/genotype mismatches, or any other use
EMBL-EBI’s new AMR portal brings together laboratory resistance data and bacterial genomes in one open platform.
#WAAW2025 #ActOnAMR
www.ebi.ac.uk/about/news/t...
🧬💻

We're excited for users who might train new models, find phenotype/genotype mismatches, or any other use
We're looking for someone keen on bioinformatics and microbiome evolution.
Important info below on eligibility & URSA competition funding👇
www.findaphd.com/phds/project...

We're looking for someone keen on bioinformatics and microbiome evolution.
Important info below on eligibility & URSA competition funding👇
www.findaphd.com/phds/project...
proGenomes4: providing 2 million accurately and consistently annotated high-quality prokaryotic genomes: academic.oup.com/nar/article/...

proGenomes4: providing 2 million accurately and consistently annotated high-quality prokaryotic genomes: academic.oup.com/nar/article/...

Apply for a 4y funded MRC DiMeN position with me and Jamie Wheeler @livuni-ives.bsky.social www.findaphd.com/phds/project...

Apply for a 4y funded MRC DiMeN position with me and Jamie Wheeler @livuni-ives.bsky.social www.findaphd.com/phds/project...
www.theguardian.com/society/2025...

www.theguardian.com/society/2025...
Why are alleles that increase disease susceptibility maintained in populations, when natural selection should eliminate them?
Why are alleles that increase disease susceptibility maintained in populations, when natural selection should eliminate them?
www.cell.com/trends/micro...
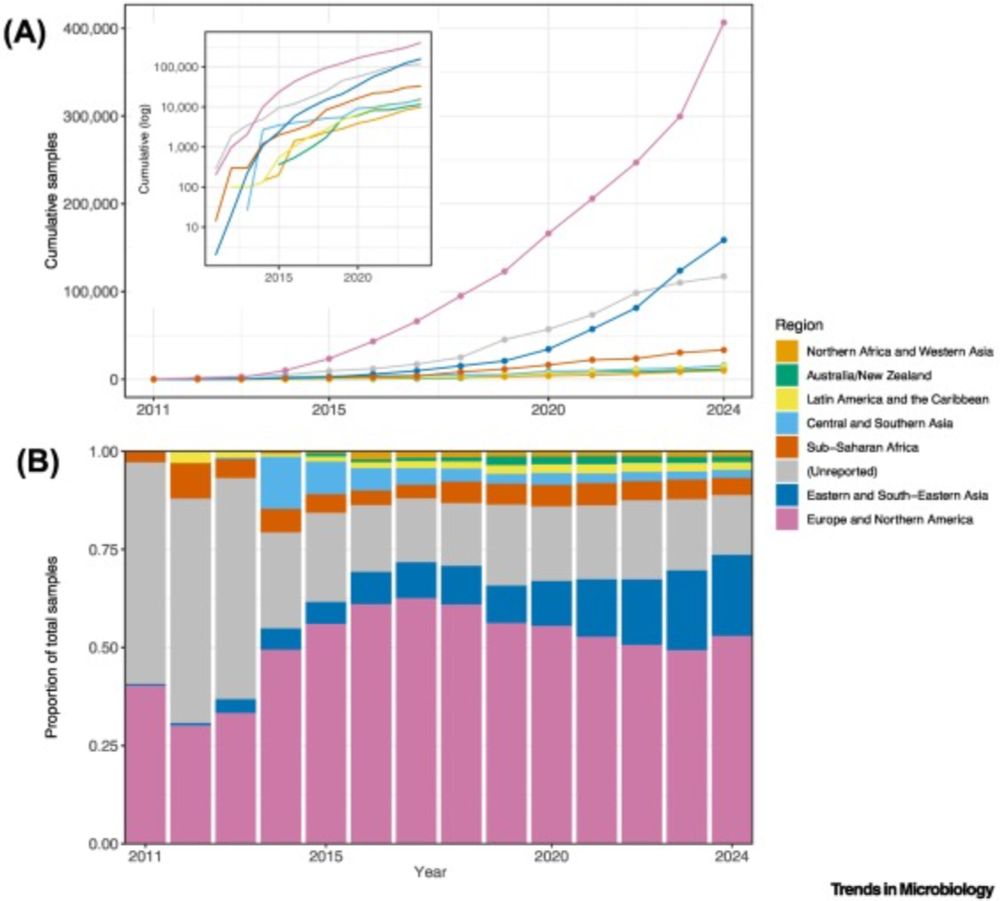
www.cell.com/trends/micro...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...


@quadraminstitute.bsky.social
@quadraminstitute.bsky.social
rdcu.be/eMmcT

@quadraminstitute.bsky.social
Do you like bacteria, genomics & puzzles?🦠🧬🧩
Do you wanna work in a cutting edge of science, with some awesome people @quadraminstitute.bsky.social?
Please apply or share by 2 Dec 🗓️
#PhDposition #academicsky
Find out more ⬇️
Do you like bacteria, genomics & puzzles?🦠🧬🧩
Do you wanna work in a cutting edge of science, with some awesome people @quadraminstitute.bsky.social?
Please apply or share by 2 Dec 🗓️
#PhDposition #academicsky
Find out more ⬇️
The fantastic Dr April Hayes explains how:
theconversation.com/growing-cocktail-of-medicines-in-worlds-waterways-could-be-fuelling-antibiotic-resistance-266945

The fantastic Dr April Hayes explains how:
theconversation.com/growing-cocktail-of-medicines-in-worlds-waterways-could-be-fuelling-antibiotic-resistance-266945
theconversation.com/growing-cock...

theconversation.com/growing-cock...

