Ben Pascoe
@benizao.bsky.social
350 followers
1.3K following
16 posts
Senior Research Fellow at the University of Oxford using genomics to investigate the global spread and evolution of bacterial pathogens.
Science | Sport | Music
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Ben Pascoe
@benizao.bsky.social
· Apr 17

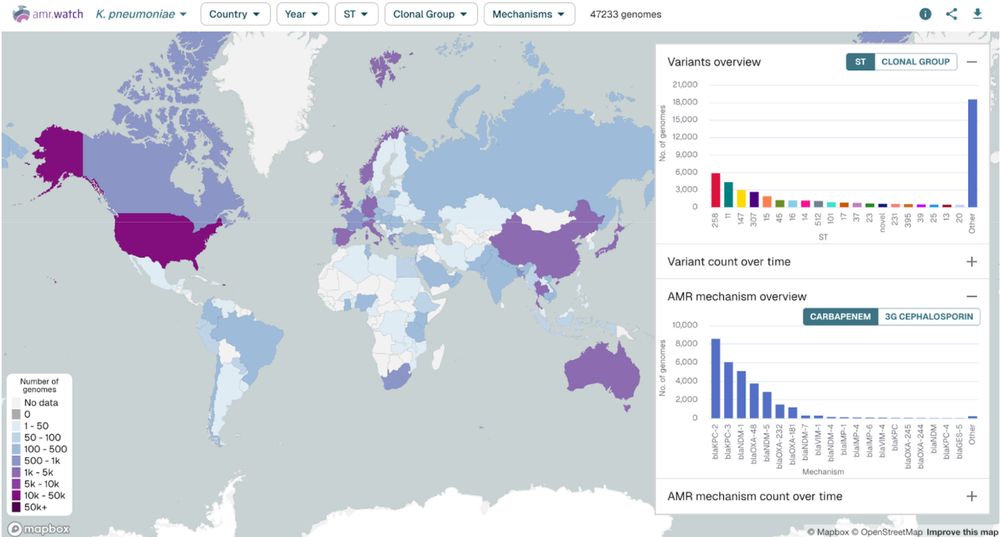
Methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus lineages contribute towards poor patient outcomes in orthopaedic device-related infections
Staphylococci are the most common cause of orthopaedic device-related infections (ODRIs), with Staphylococcus aureus responsible for a third or more of cases. This prospective clinical and laboratory ...
www.microbiologyresearch.org
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
CampyUK2025
@campyuk2025.bsky.social
· Mar 15
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
naturepoker
@binomicalabs.org
· Mar 15
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Evangelos Mourkas
@evanmou.bsky.social
· Mar 14

Genomic insights into extended-spectrum β-lactamase- and plasmid-borne AmpC-producing Escherichia coli transmission between humans and livestock in rural Cambodia
Introduction. The global spread of extended-spectrum cephalosporinase-producing Escherichia coli (producing extended-spectrum β-lactamase or plasmid-borne AmpC, hereafter ESC-Ec) is a major public hea...
doi.org
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Jay Hinton
@jayhinton.bsky.social
· Feb 23

Lysis of Escherichia coli by colicin Ib contributes to bacterial cross-feeding by releasing active β-galactosidase
Abstract. The diffusible toxin ColIb produced by Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium SL1344 is a potent inhibitor of Escherichia coli growth. To identi
academic.oup.com
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Marco Galardini
@mgalactus.bsky.social
· Feb 12

microGWAS: a computational pipeline to perform large-scale bacterial genome-wide association studies
Identifying genetic variants associated with bacterial phenotypes, such as virulence, host preference and antimicrobial resistance, has great potential for a better understanding of the mechanisms inv...
www.microbiologyresearch.org
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
CampyUK2025
@campyuk2025.bsky.social
· Feb 22

Home
Why now? Campylobacter infections are on the rise globally, with increasing levels of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) making treatment more challenging. As the world’s most common bacterial cause of gastroenteritis, Campylobacter poses a growing public health threat, yet effective interventions remain limited. There is an urgent need for research into novel and sustainable strategies to mitigate its impact—spanning genomics, surveillance, food safety, and public health interventions.
campyuk.web.ox.ac.uk
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Bill Hanage
@billhanage.bsky.social
· Feb 11
Felix M Key
@keyfm.bsky.social
· Feb 10

Bronze Age Yersinia pestis genome from sheep sheds light on hosts and evolution of a prehistoric plague lineage
Most human pathogens are of zoonotic origin. Many emerged during prehistory, coinciding with domestication providing more opportunities for spillover from original host species. However, we lack direc...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Ryan
@geekryan.bsky.social
· Feb 3

Brainwide silencing of prion protein by AAV-mediated delivery of an engineered compact epigenetic editor
Prion disease is caused by misfolding of the prion protein (PrP) into pathogenic self-propagating conformations, leading to rapid-onset dementia and death. However, elimination of endogenous PrP halts...
www.science.org
Reposted by Ben Pascoe
Ozan Gundogdu
@ozangundogdu11.bsky.social
· Jan 29

Impact of commercial gut health interventions on caecal metagenome and broiler performance - Microbiome
Background Maintaining gut health is a persistent and unresolved challenge in the poultry industry. Given the critical role of gut health in chicken performance and welfare, there is a pressing need t...
link.springer.com