Grant Kinsler
@grantkinsler.bsky.social
430 followers
780 following
39 posts
Postdoc at UPenn thinking about mutations, cells, and evolution.
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Grant Kinsler
@grantkinsler.bsky.social
· Aug 22
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Joao Ascensao
@joaoascensao.bsky.social
· Aug 21

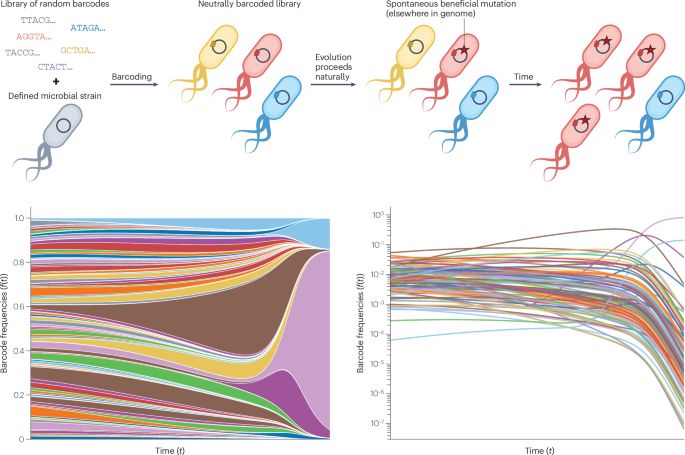
Frequency-dependent fitness effects are ubiquitous
In simple microbial populations, the fitness effects of most selected mutations are generally taken to be constant, independent of genotype frequency. This assumption underpins predictions about evolutionary dynamics, epistatic interactions, and the maintenance of genetic diversity in populations. Here, we systematically test this assumption using beneficial mutations from early generations of the Escherichia coli Long-Term Evolution Experiment (LTEE). Using flow cytometry-based competition assays, we find that frequency-dependent fitness effects are the norm rather than the exception, occurring in approximately 80\% of strain pairs tested. Most competitions exhibit negative frequency-dependence, where fitness advantages decline as mutant frequency increases. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the strength of frequency-dependence is predictable from invasion fitness measurements, with invasion fitness explaining approximately half of the biological variation in frequency-dependent slopes. Additionally, we observe violations of fitness transitivity in several strain combinations, indicating that competitive relationships cannot always be predicted from fitness relative to a single reference strain alone. Through high-resolution measurements of within-growth cycle dynamics, we show that simple resource competition explains a substantial portion of the frequency-dependence: when faster-growing genotypes dominate populations, they deplete shared resources more rapidly, reducing the time available for fitness differences to accumulate. Our results demonstrate that even in a simple model system designed to minimize ecological complexity, subtle ecological interactions between closely related genotypes create frequency-dependent selection that can fundamentally alter evolutionary dynamics. ### Competing Interest Statement The authors have declared no competing interest.
doi.org
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Roshni Patel
@roshnipatel.bsky.social
· Aug 6
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Tera Levin
@teralevin.bsky.social
· Aug 5

Hypermutable hotspot enables the rapid evolution of self/non-self recognition genes in Dictyostelium
Cells require highly polymorphic receptors to perform accurate self/non-self recognition. In the amoeba Dicytostelium discoideum, polymorphic TgrB1 & TgrC1 proteins are used to bind sister cells and e...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Dmitri Petrov
@petrovadmitri.bsky.social
· Jul 22
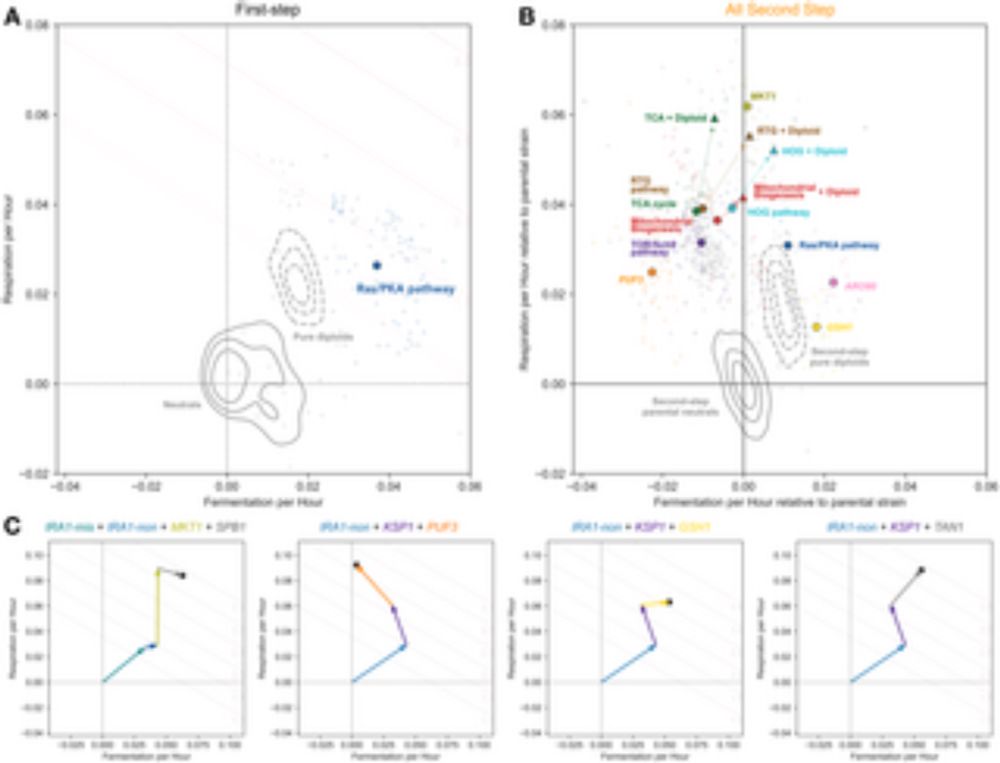
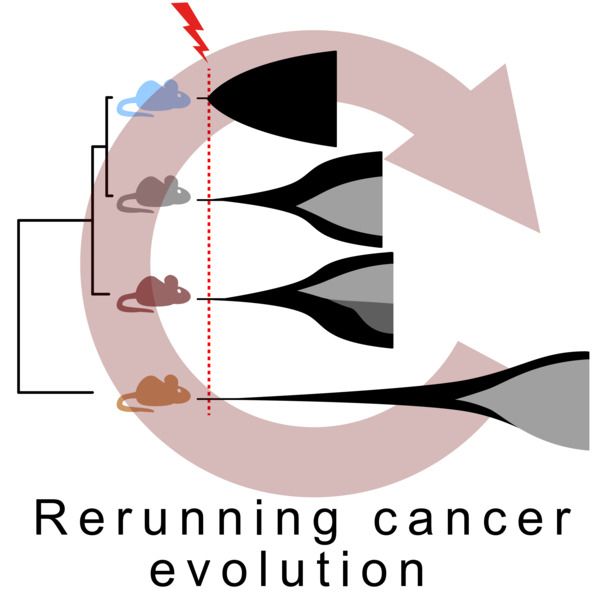
A high-resolution two-step evolution experiment in yeast reveals a shift from pleiotropic to modular adaptation
Evolution is expected to involve mutations that are small and modular in effect, but recent findings suggest that mutations early in an adaptive process can have strong and pleiotropic effects. This s...
journals.plos.org
Grant Kinsler
@grantkinsler.bsky.social
· Jul 21
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Joao Ascensao
@joaoascensao.bsky.social
· Jul 21
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Vinay Ayyappan
@vayyappan.bsky.social
· Jul 15

Gastruloid patterning reflects division of labor among biased stem cell clones
Embryonic development typically requires precise coordination among cells to achieve reproducible outcomes, leading to the assumption that cellular heterogeneity must be minimized or buffered against....
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Arjun Raj
@arjunraj.bsky.social
· Jul 15

Single-cell spatial mapping reveals reproducible cell type organization and spatially-dependent gene expression in gastruloids
Gastruloids are three-dimensional stem-cell-based models that recapitulate key aspects of mammalian gastrulation, including formation of an anterior-posterior (AP) axis. However, we do not have detail...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
John Murray
@jisaacmurray.bsky.social
· Jun 20
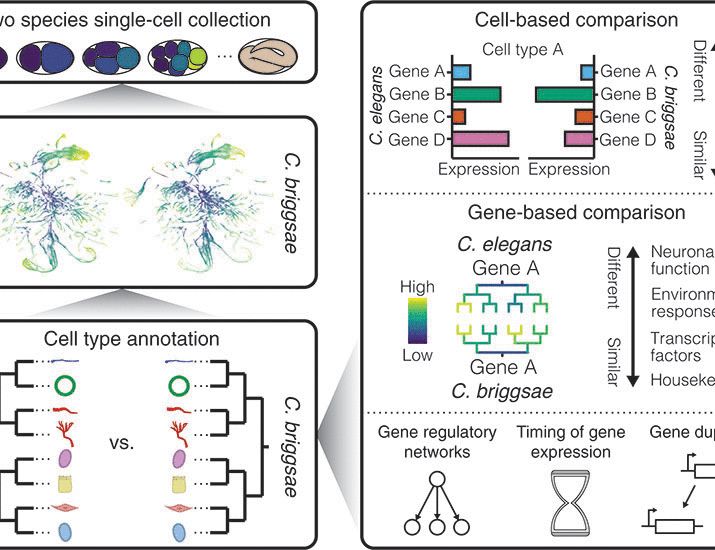
Lineage-resolved analysis of embryonic gene expression evolution in C. elegans and C. briggsae
The constraints that govern the evolution of gene expression patterns across development remain unclear. Single-cell RNA sequencing can detail these constraints by systematically profiling homologous ...
www.science.org
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Reposted by Grant Kinsler
Trevor Graham
@trevorgraham.bsky.social
· Jun 20
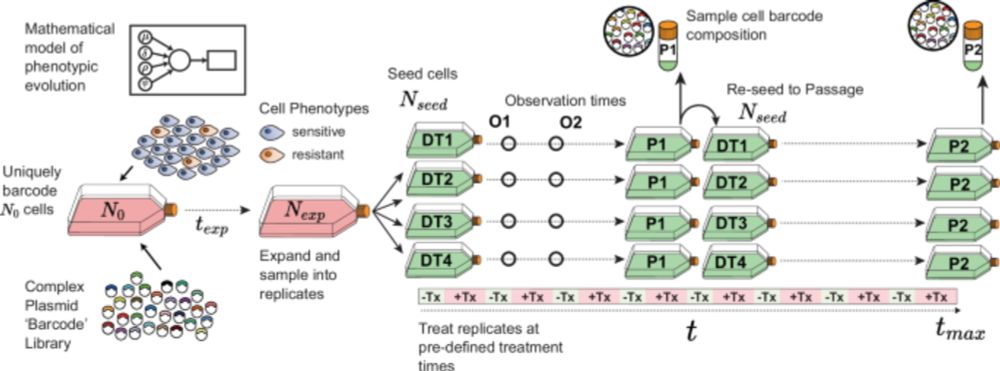
Quantitative measurement of phenotype dynamics during cancer drug resistance evolution using genetic barcoding - Nature Communications
Understanding the dynamics of how drug resistance originates in cancer remains crucial, but it is not possible to observe them directly. Here, the authors construct a mathematical framework to infer d...
www.nature.com