Jakob Kasper
@jakobkas.bsky.social
200 followers
430 following
9 posts
PhD candidate @ippad_eu, @UvA_Amsterdam | Formerly MSc Psychology @Uniheidelberg | http://mastodon.world/@jakobkasper
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Jakob Kasper
@jakobkas.bsky.social
· May 7

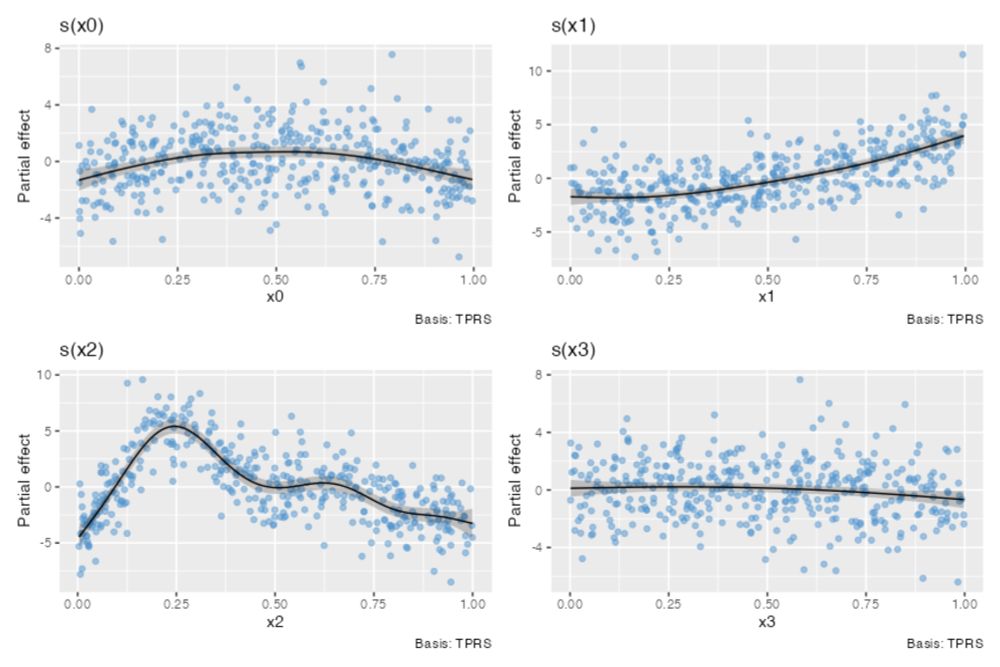
Establishing the construct and predictive validity of brief measures of affective polarization
Measuring affective polarization, defined as the liking for one's political ingroup and the dislike for political outgroups, poses methodological challenges in multiparty systems: evaluations of seve...
doi.org
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Joe Bak-Coleman
@jbakcoleman.bsky.social
· Jul 28
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Jakob Kasper
@jakobkas.bsky.social
· Sep 2
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper
Reposted by Jakob Kasper