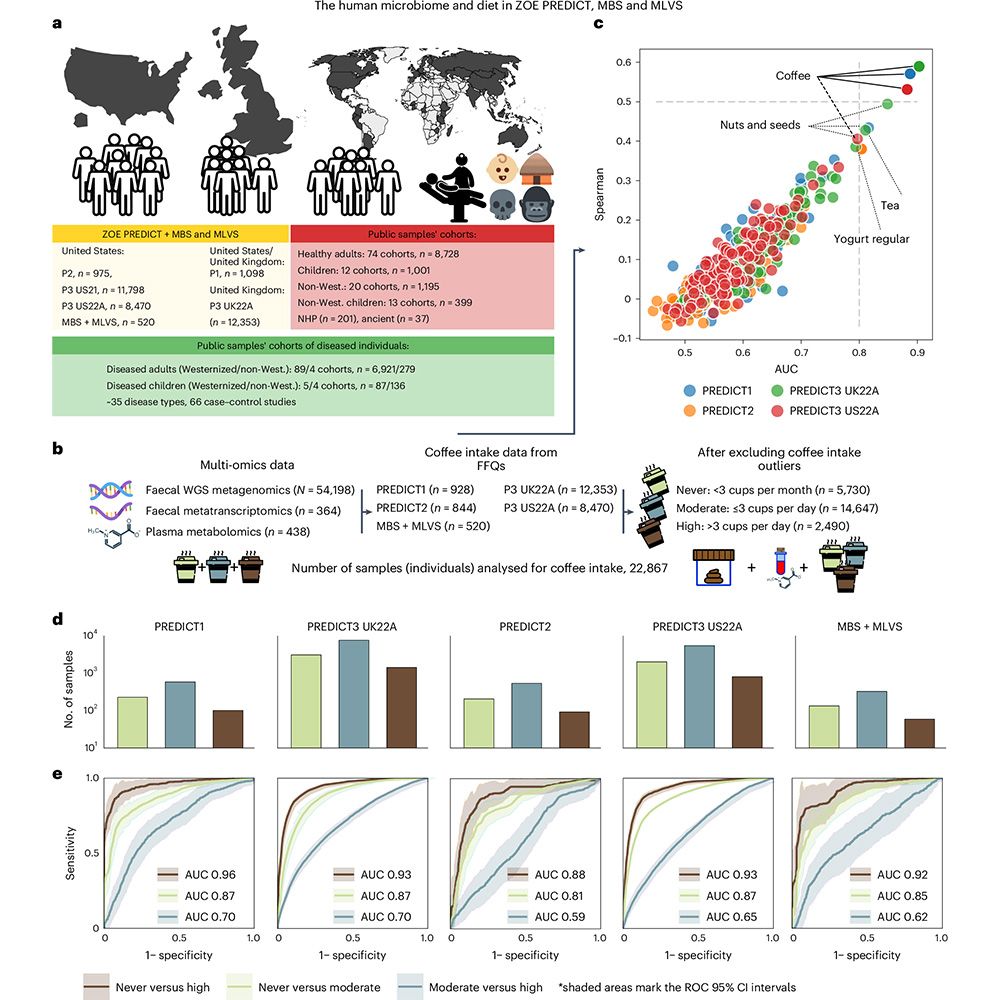
If you are a 𝗺𝗶𝗰𝗿𝗼𝗯𝗶𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝗶𝘀𝘁 who wants to help others while traveling,𝗗𝗼𝗰𝘁𝗼𝗿𝘀 𝗪𝗶𝘁𝗵𝗼𝘂𝘁 𝗕𝗼𝗿𝗱𝗲𝗿𝘀 needs you!
www.orthosurgeon.msf.org/en/job/micro...
#hiring @msf.ca #microsky #sciencesky #AMR
If you are a 𝗺𝗶𝗰𝗿𝗼𝗯𝗶𝗼𝗹𝗼𝗴𝗶𝘀𝘁 who wants to help others while traveling,𝗗𝗼𝗰𝘁𝗼𝗿𝘀 𝗪𝗶𝘁𝗵𝗼𝘂𝘁 𝗕𝗼𝗿𝗱𝗲𝗿𝘀 needs you!
www.orthosurgeon.msf.org/en/job/micro...
#hiring @msf.ca #microsky #sciencesky #AMR
#MicrobiomeSky

#MicrobiomeSky
alz-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...

alz-journals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/...
https://go.nature.com/3DSeS0d 🔒
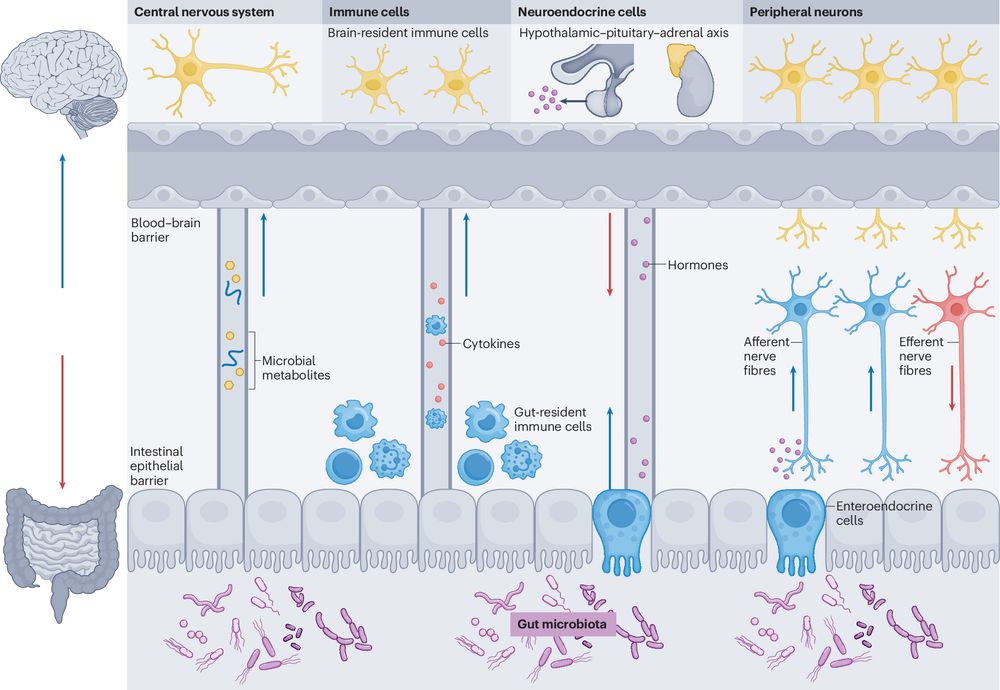
https://go.nature.com/3DSeS0d 🔒

#TalDiacomoHoy de 1912, un tal Alfred #Wegener presentaba en la Sociedad Geológica de Frankfurt una idea sobre el origen de los continentes y los océanos. ⚒️ 🧪
Aunque la teoría de la deriva continental no tuvo buena acogida inicial, fue muy importante para la #Geología.
Veámos la historia👇


#TalDiacomoHoy de 1912, un tal Alfred #Wegener presentaba en la Sociedad Geológica de Frankfurt una idea sobre el origen de los continentes y los océanos. ⚒️ 🧪
Aunque la teoría de la deriva continental no tuvo buena acogida inicial, fue muy importante para la #Geología.
Veámos la historia👇

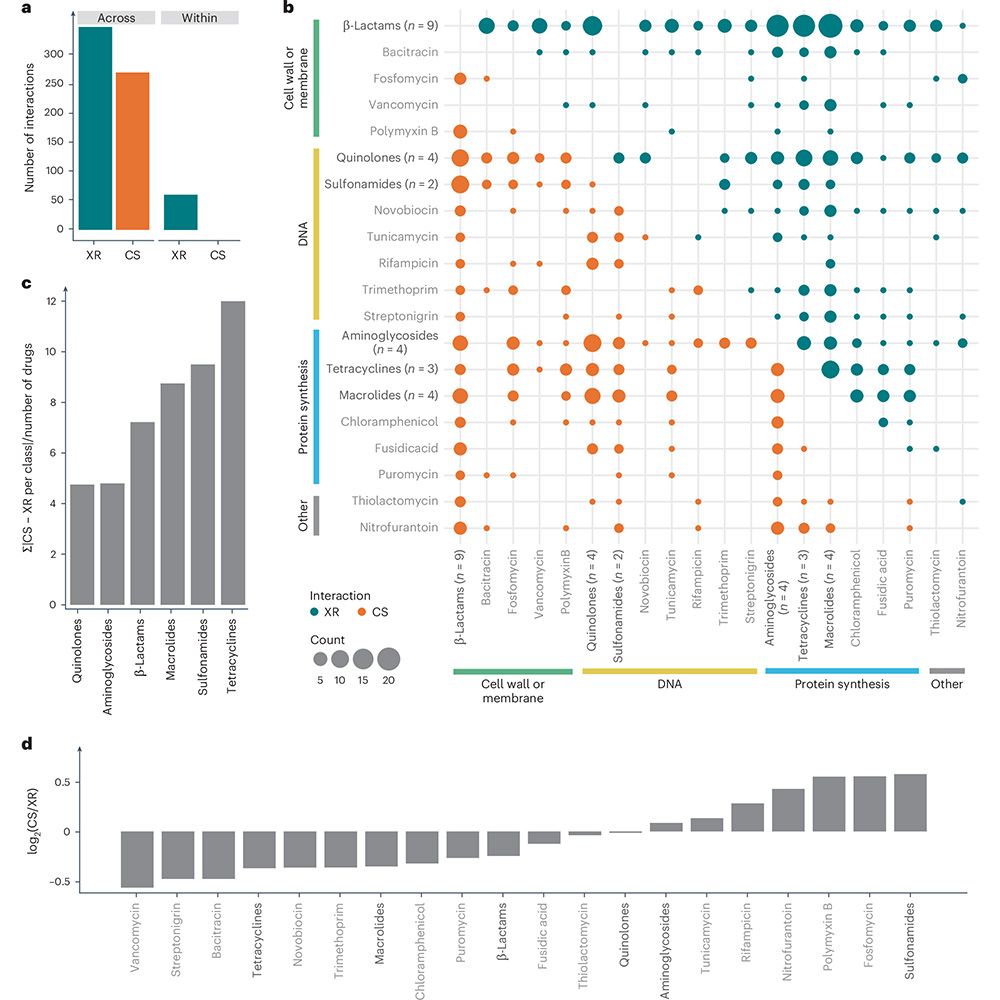
🔗 bit.ly/4f5bxrb

🔗 bit.ly/4f5bxrb