Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
440 followers
780 following
34 posts
Virologist| Assistant Professor @ErasmusMC #RielScience | previous ESR in Marie Curie Network Antivirals @UtrechtUni |🇦🇹🇪🇺🇳🇱|
Opinions and Typos are my own!
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Pinned
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Aug 28

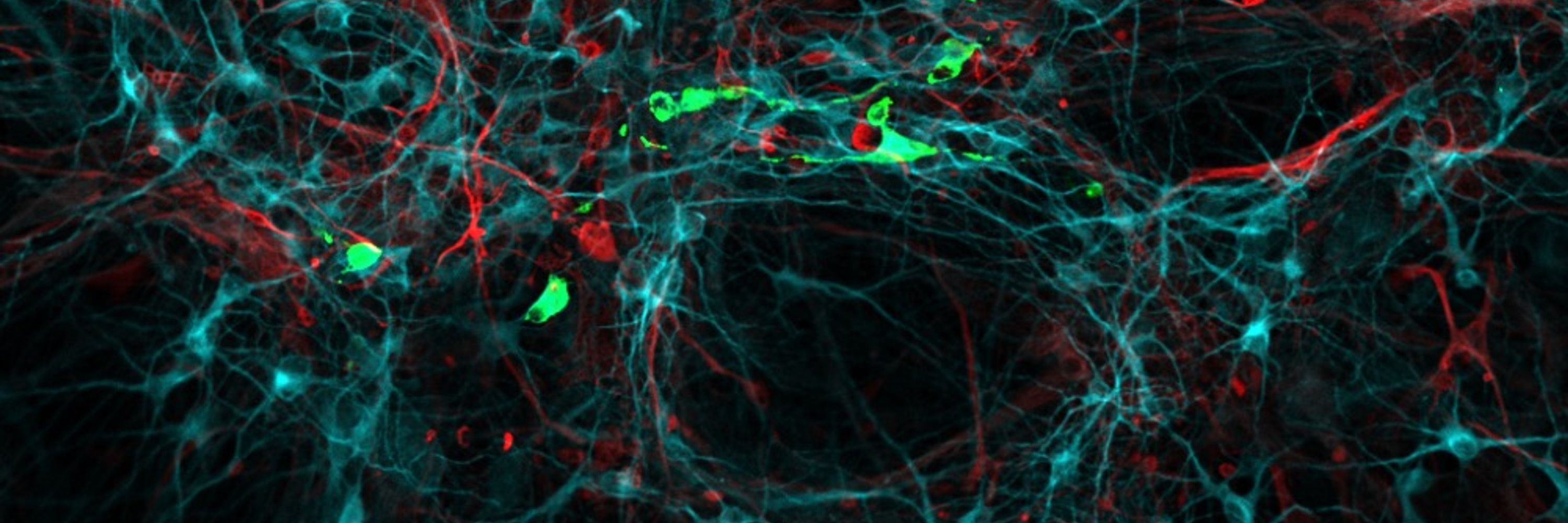
Non-polio enteroviruses compromise the electrophysiology of a human iPSC-derived neural network
The non-polio Enteroviruses enterovirus-D68 (EV-D68) and enterovirus-A71 (EV-A71) are highly prevalent and considered pathogens of increasing health concern. While most enterovirus infections are mild...
doi.org
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Aug 28

Non-polio enteroviruses compromise the electrophysiology of a human iPSC-derived neural network
The non-polio Enteroviruses enterovirus-D68 (EV-D68) and enterovirus-A71 (EV-A71) are highly prevalent and considered pathogens of increasing health concern. While most enterovirus infections are mild...
doi.org
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Aug 28
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Aug 28
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Aug 28
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Aug 28
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Aug 28

Non-polio enteroviruses compromise the electrophysiology of a human iPSC-derived neural network
The non-polio Enteroviruses enterovirus-D68 (EV-D68) and enterovirus-A71 (EV-A71) are highly prevalent and considered pathogens of increasing health concern. While most enterovirus infections are mild...
doi.org
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Meyer Lab
@themeyerlab.bsky.social
· Aug 28

Non-polio enteroviruses compromise the electrophysiology of a human iPSC-derived neural network
The non-polio Enteroviruses enterovirus-D68 (EV-D68) and enterovirus-A71 (EV-A71) are highly prevalent and considered pathogens of increasing health concern. While most enterovirus infections are mild...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Patrick Dolan
@ptdolan.bsky.social
· Jun 28

Strain-Specific Tropism and Transcriptional Responses of Enterovirus D68 Infection in Human Spinal Cord Organoids
The mechanisms by which Enterovirus D-68 (EV-D68) infection leads to acute flaccid myelitis (AFM), a severe neurological condition characterized by sudden muscle weakness and paralysis, remain poorly ...
www.biorxiv.org
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Jul 19

Hunting-training dogs and companion dogs in the Netherlands are frequently exposed to highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI H5) and human H1N1 virus, 2021–2023
Dogs are susceptible to the currently circulating highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5 and human H1N1pdm2009 (pandemic H1N1) viruses, yet littl…
www.sciencedirect.com
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Robert de Vries
@rpdevrieslab.bsky.social
· Jul 18
Epistasis in the receptor-binding domain of contemporary H3N2 viruses that reverted to bind sialylated di-LacNAc repeats
Liang et al. shows how contemporary H3N2 viruses reverted to bind sialylated di-LacNAc
at the molecular level. Using complex symmetrical and asymmetric N-glycans, major
epistatic interactions were rev...
www.cell.com
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Robert de Vries
@rpdevrieslab.bsky.social
· Jul 10
Reposted by Lisa Bauer
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Jul 10

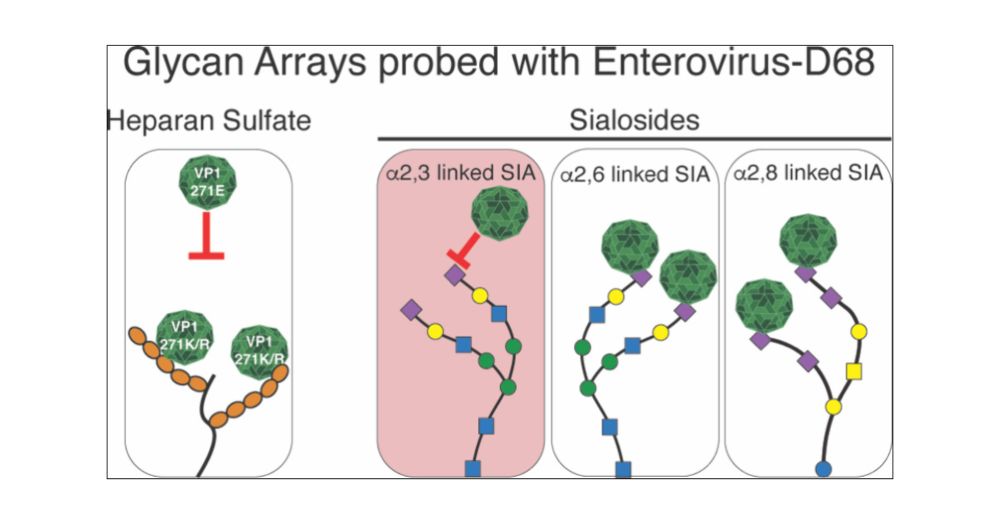
Sialic Acid-Containing Glycolipids Extend the Receptor Repertoire of Enterovirus-D68
Enterovirus D68 (EV-D68) emerged as a pathogen of increasing health concern globally, particularly due to its association with outbreaks of severe respiratory diseases and acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) in children. Knowledge regarding the tissue tropism and pathogenesis of EV-D68 within the respiratory tract and central nervous system remains limited, primarily due to an incomplete understanding of the host factors that facilitate the entry of EV-D68 into host cells. Several cellular receptors involved in EV-D68 infections have been identified, including ICAM-5, sialylated glycoproteins, and heparan sulfate (HS). Here, we investigate the receptor requirement of a panel of EV-D68 strains covering all clades, focusing on HS and sialosides utilizing glycan arrays. We found that all EV-D68 strains binding to HS harbor a cell culture adaptive substitution in the structural protein VP1 at position 271, which changes the amino acid into a positively charged one. Glycan array analyses revealed that EV-D68 strains prefer α2,6-linked sialic acids presented on N-glycans, α2,8-linked sialic acids on gangliosides, or both. Inhibition of glycolipid biosynthesis or multivalent glycolipid mimics confirmed that ganglioside structures serve as entry receptors for certain EV-D68 strains. Lastly, we examined whether EV-D68 strains that bind to HS or glycolipids require different uncoating mechanisms. Bafilomycin A1 minimally affected the cell entry of HS-binding EV-D68 strains B2/039 and B2/947, and the ganglioside preferring B1/2013 and other viruses were strongly inhibited. Together, we identified that EV-D68 strains can use disialoglycolipids as novel receptors and that different EV-D68 strains show a promiscuous sialic acid binding repertoire.
pubs.acs.org
Lisa Bauer
@lisabauervirus.bsky.social
· Jun 20