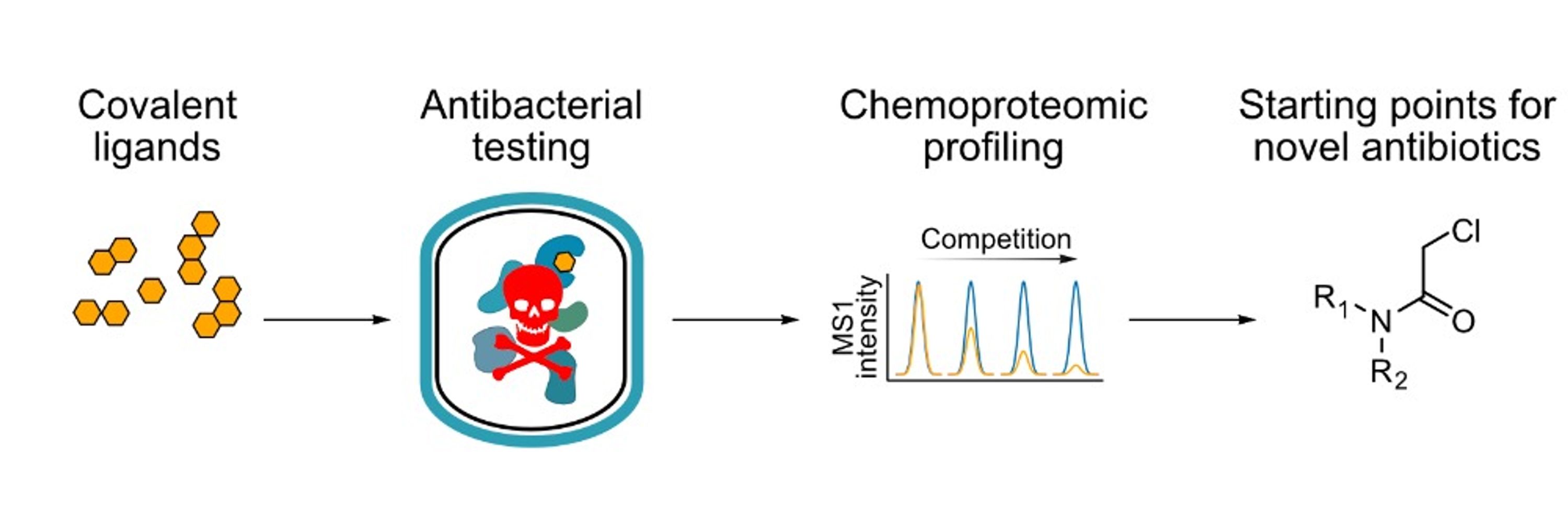
Jennifer Andexer, Helge Bode, Stephan Hammer, Akane Kawamura, Alexandria (Ali) Deliz Liang, Carina de Oliveira Mann, Stefan Raunser, Schraga Schwartz, Pierre Stallforth, Carine Tisné, Satpal Virdee, Wilfred van der Donk
#Chemistry #Meeting
CC: @gdch.de
Jennifer Andexer, Helge Bode, Stephan Hammer, Akane Kawamura, Alexandria (Ali) Deliz Liang, Carina de Oliveira Mann, Stefan Raunser, Schraga Schwartz, Pierre Stallforth, Carine Tisné, Satpal Virdee, Wilfred van der Donk
#Chemistry #Meeting
CC: @gdch.de
Great list @stephanhacker2.bsky.social and thanks for sharing.
Great list @stephanhacker2.bsky.social and thanks for sharing.
#Chemistry #ChemBio #Science #Antibiotics #Synthesis #TPD #Degrader #Proteomics #Kinases #RNA #Screening #CovalentInhibitors #DirectToBiology
#Chemistry #ChemBio #Science #Antibiotics #Synthesis #TPD #Degrader #Proteomics #Kinases #RNA #Screening #CovalentInhibitors #DirectToBiology
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...

www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
chemrxiv.org/engage/chemr...

chemrxiv.org/engage/chemr...
pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...

pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/...
aacrjournals.org/cancerdiscov...
aacrjournals.org/cancerdiscov...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.nature.com/articles/s41...

www.nature.com/articles/s41...
www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

www.sciencedirect.com/science/arti...

