Reposted by: Wim Thiery, Paul Lehmann
Result:
Solar now cheapest new power in many regions
Falling battery costs enable flexibility
Electrification gets more attractive

by Wim Thiery

by Wim Thiery

by Wim Thiery
www.nasw.org/article/toda...

Reposted by: Wim Thiery, Jonathan Bamber
New study by Codruț-Andrei Diaconu, introducing automated tool to map and quantify glacier area changes (+uncertainties)!
agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/...
Together with @jlbamber.bsky.social
Reposted by: Wim Thiery
🔗 www.brussels-school.be/research/pub...

by Wim Thiery
Reposted by: Wim Thiery

by Wim Thiery

by Wim Thiery

by Wim Thiery

by Wim Thiery
by Wim Thiery — Reposted by: Ed Hawkins
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

by Ed Hawkins — Reposted by: Wim Thiery
www.nature.com/articles/d41...

by Friederike Otto — Reposted by: Wim Thiery, Helmut Haberl, Friederike Otto


Reposted by: Wim Thiery
🔗 doi.org/10.1038/s415...

by Wim Thiery
by Wim Thiery
Reposted by: Wim Thiery

Reposted by: Wim Thiery

Reposted by: Wim Thiery, Sonia I. Seneviratne

by Wim Thiery
www.rtbf.be/article/a-qu...

by Wim Thiery
by Wim Thiery
by Wim Thiery
by Wim Thiery
by Wim Thiery
by Wim Thiery
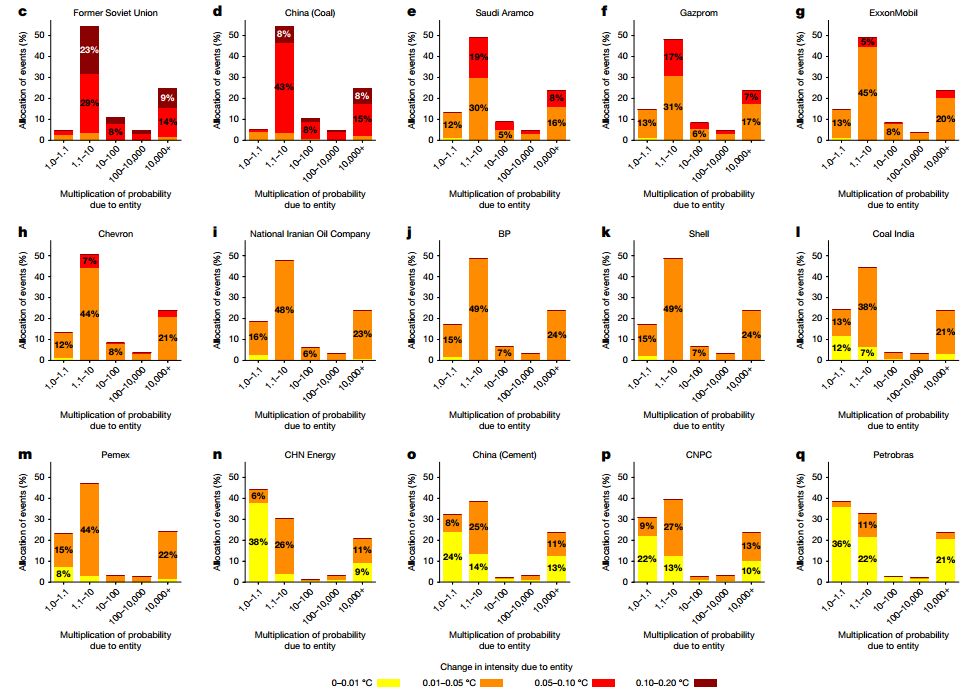
by Wim Thiery

by Wim Thiery



