@erzbergerlab.bsky.social
1.2K followers
2.3K following
33 posts
Studying ribosomes at UT Southwestern
Posts
Media
Videos
Starter Packs
Reposted
Reposted
Reposted
Reposted
Reposted
Molecular Cell
@cp-molcell.bsky.social
· Jul 22
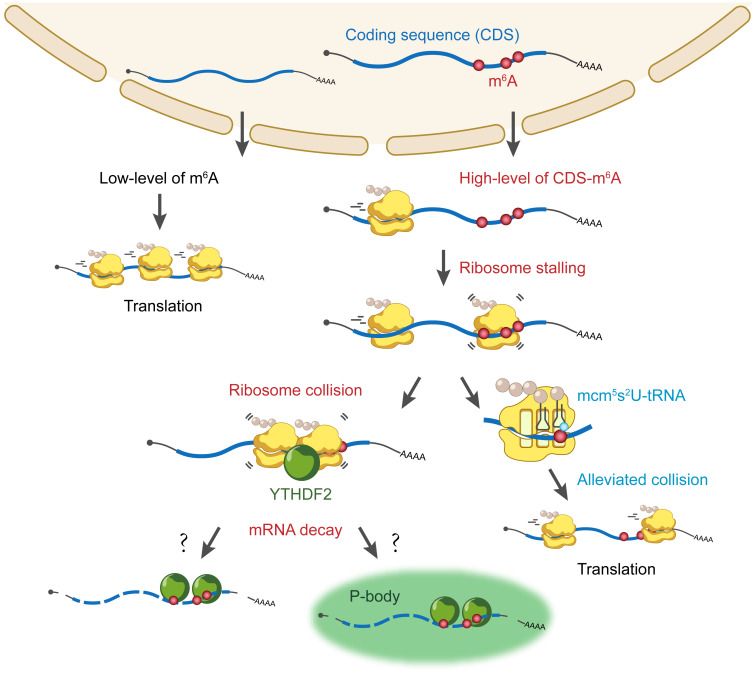
m6A-induced ribosome stalling and collision trigger mRNA decay
How m6A in different transcript regions regulates mRNA decay remains an intriguing question. Three studies from the labs of König, Jaffrey, and Steinmetz uncovered translation-dependent CDS-m6A decay: m6A in the coding sequence (CDS) induces ribosome stalling and collision to trigger mRNA decay, while tRNA modification alleviates the effects.
dlvr.it
Reposted
Reposted
Reposted
Science Magazine
@science.org
· Jun 20
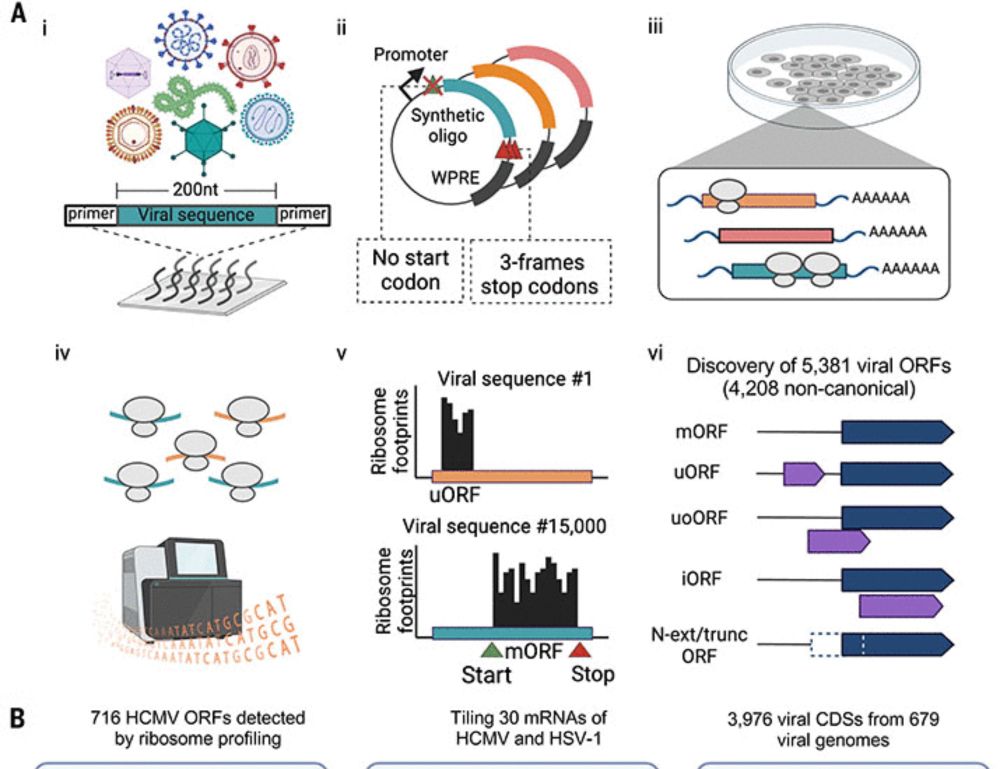
Pan-viral ORFs discovery using massively parallel ribosome profiling
Defining viral proteomes is crucial to understanding viral life cycles and immune recognition but the landscape of translated regions remains unknown for most viruses. We have developed massively para...
scim.ag
Reposted
Reposted
Reposted
Kermit Murray
@kkmurray.bsky.social
· May 25

The alternative initiation factor eIF2A regulates 40S subunit turnover in ribosome-associated quality control
The noncanonical translation initiation factor eIF2A plays critical roles in diverse cellular processes, including the integrated stress response, neurodegeneration and tumorigenesis. However, the precise molecular mechanism underlying eIF2A`s function remains poorly understood. Here, we exploit a TurboID-based proximity labeling combined with mass spectrometry to systematically map the interactome of eIF2A during homeostasis and stress. Combining polysome gradients with TurboID, we zoom into the interactions of eIF2A with the 40S small ribosomal subunit and map the eIF2A binding site close to the mRNA entry channel. We identify a network of interactors that link eIF2A to ribosome-associated quality control, including its strong interaction with G3BP1-USP10 complexes as well as RPS2 and RPS3. In the absence of eIF2A, RPS2 and RPS3 ubiquitination is diminished specifically upon ribosome stalling. 40S-specific footprinting in eIF2A knockout cells shows minimal changes in 5`UTR occupancy, consistent with a limited role for eIF2A in translation initiation. Using dynamic SILAC mass spectrometry, we characterize the novel function of eIF2A in ribosome-associated quality control and show that eIF2A antagonizes USP10-dependent rescue of 40S ribosomes, resulting in altered turnover of 40S subunits upon cellular stress. Collectively, our study identifies a previously unknown link between eIF2A and ribosome-associated quality control, implies that eIF2A promotes translation fidelity by tuning 40S ribosome rescue under stress and warrants further investigations into the role of ribosome-associated quality control in tumorigenesis.
dlvr.it
Reposted
Molecular Cell
@cp-molcell.bsky.social
· May 17
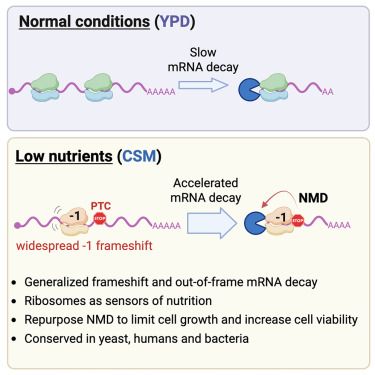
Ribosomes modulate transcriptome abundance via generalized frameshift and out-of-frame mRNA decay
Zhang et al. identify a regulatory mechanism for how cells adapt to nutrient scarcity through widespread −1 ribosomal frameshifts, culminating in accelerated mRNA decay. This process, dependent on codon optimality and conserved across species, establishes direct feedback coupling the translation of new proteins with the stability of the mRNA that encodes for them.
dlvr.it
Reposted
Reposted
Lori Passmore
@lapassmore.bsky.social
· May 2

A kinetic ruler controls mRNA poly(A) tail length
Poly(A) tails of newly synthesized mRNAs have uniform lengths, arising through cooperation between the cleavage and polyadenylation complex (CPAC) and poly(A) binding proteins (PABPs). In the budding ...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted
The Banfield Lab
@banfieldlab.bsky.social
· Apr 29
Ling-Dong Shi
@lingdong-shi.bsky.social
· Apr 29

Circular 23S rRNA within archaeal ribosomes
The ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) that form the core of ribosomes are believed to occur as linear molecules. Here, we investigated rRNAs from diverse and mostly uncultivated archaea and found evidence that, ...
www.biorxiv.org
Reposted
Reposted